|
Arcturus Stream
In astronomy, the Arcturus moving group or Arcturus stream is a moving group or stellar stream, discovered by Olin J. Eggen (1971), comprising 53 stars moving at 275,000 miles per hour, which includes the nearby bright star Arcturus. It comprises many stars which share similar proper motion and so appear to be physically associated. This group of stars is not in the plane of the Milky Way galaxy, and has been proposed as a remnant of an ancient dwarf satellite galaxy, long since disrupted and assimilated into the Milky Way. It consists of old stars deficient in heavy elements. However, Bensby and colleagues, in analysing chemical composition of F and G dwarf stars in the solar neighbourhood, found there was no difference in chemical makeup of stars from the stream, suggesting an intragalactic rather than extragalactic origin. One possibility is that the stream appeared in a manner similar to the Hercules group, which is hypothesized to have formed due to Outer Lindblad Resonance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, Maya, and many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Astronomical Observatory
The Australian Astronomical Observatory (AAO), formerly the Anglo-Australian Observatory, was an optical and near-infrared astronomy observatory with its headquarters in North Ryde in suburban Sydney, Australia. Originally funded jointly by the United Kingdom and Australian governments, it was managed wholly by Australia's Department of Industry, Innovation, Science, Research and Tertiary Education. The AAO operated the 3.9-metre Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT) and 1.2-metre UK Schmidt Telescope (UKST) at Siding Spring Observatory, located near the town of Coonabarabran, Australia. In addition to operating the two telescopes, AAO staff carried out astronomical research, and designed and built astronomical instrumentation for the AAT, UKST, and other telescopes including the European Southern Observatory (ESO)'s Very Large Telescope in Chile, and the Japanese Subaru Telescope on Mauna Kea in Hawaii. UK involvement in the AAO ceased in June 2010, with the change of name and manage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
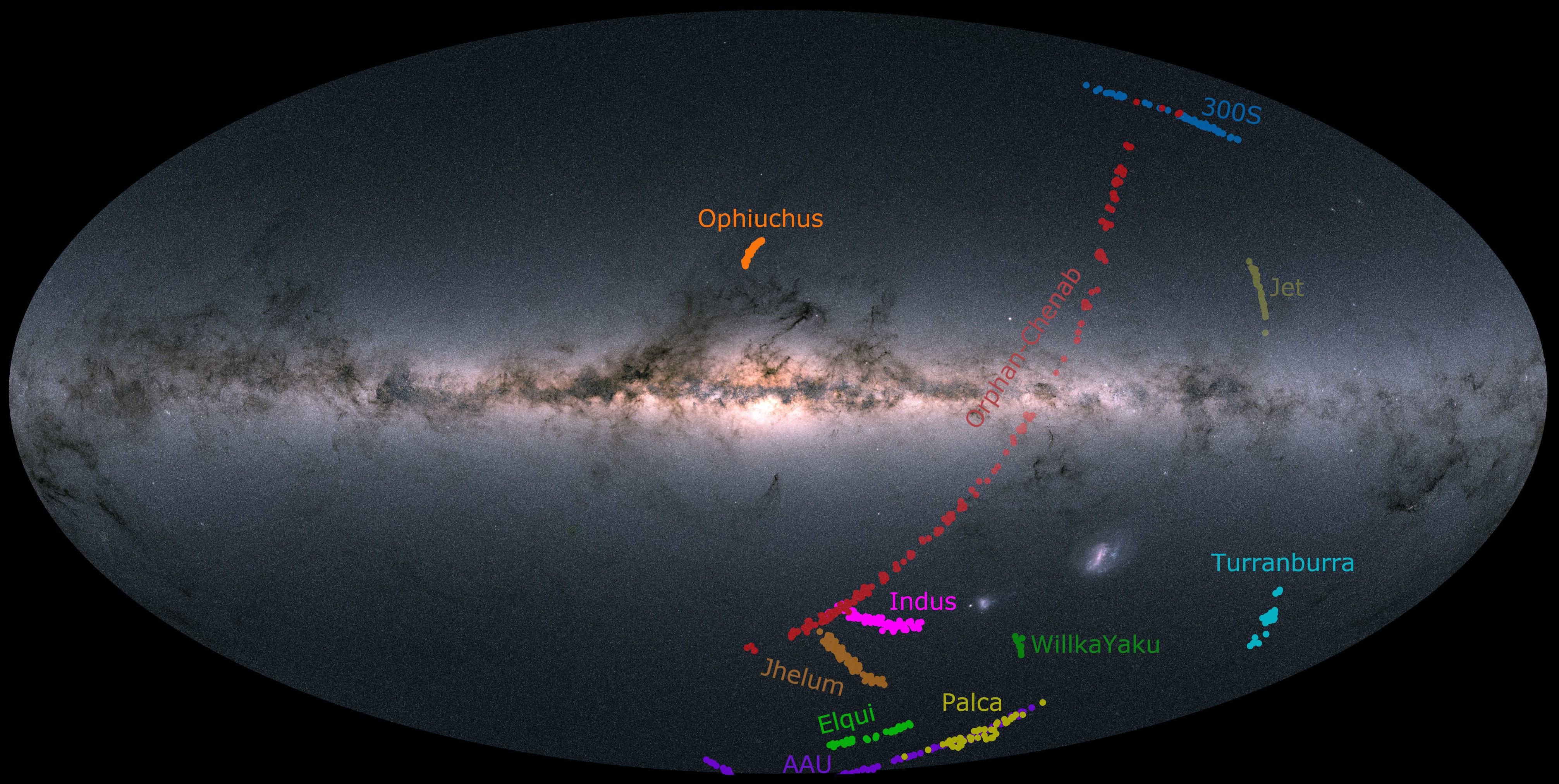
Stellar Streams
This is a list of stellar streams. A stellar stream is an association of stars orbiting a galaxy that was once a globular cluster or dwarf galaxy that has now been torn apart and stretched out along its orbit by tidal forces. An exception in the list about Milky Way streams given below is the Magellanic Stream, composed of gas (mostly hydrogen). Local Group streams Milky Way streams Andromeda Galaxy streams Streams beyond the Local Group See also * Lists of astronomical objects * List of nearby stellar associations and moving groups * Field of Streams * Stellar kinematics * Galaxy merger * Local Bubble * Satellite galaxies of the Milky Way The Milky Way has several smaller galaxies gravitationally bound to it, as part of the Milky Way subgroup, which is part of the local galaxy cluster, the Local Group. There are 59 small galaxies confirmed to be within of the Milky Way, but not a ... References Further reading * External links * * * * * {{Portal bar, Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcturus Moving Group
In astronomy, the Arcturus moving group or Arcturus stream is a moving group or stellar stream, discovered by Olin J. Eggen (1971), comprising 53 stars moving at 275,000 miles per hour, which includes the nearby bright star Arcturus. It comprises many stars which share similar proper motion and so appear to be physically associated. This group of stars is not in the plane of the Milky Way galaxy, and has been proposed as a remnant of an ancient dwarf satellite galaxy, long since disrupted and assimilated into the Milky Way. It consists of old stars deficient in heavy elements. However, Bensby and colleagues, in analysing chemical composition of F and G dwarf stars in the solar neighbourhood, found there was no difference in chemical makeup of stars from the stream, suggesting an intragalactic rather than extragalactic origin. One possibility is that the stream appeared in a manner similar to the Hercules group, which is hypothesized to have formed due to Outer Lindblad Resonance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Stellar Streams
This is a list of stellar streams. A stellar stream is an association of stars orbiting a galaxy that was once a globular cluster or dwarf galaxy that has now been torn apart and stretched out along its orbit by tidal forces. An exception in the list about Milky Way streams given below is the Magellanic Stream, composed of gas (mostly hydrogen). Local Group streams Milky Way streams Andromeda Galaxy streams Streams beyond the Local Group See also * Lists of astronomical objects * List of nearby stellar associations and moving groups * Field of Streams * Stellar kinematics * Galaxy merger * Local Bubble * Satellite galaxies of the Milky Way The Milky Way has several smaller galaxies gravitationally bound to it, as part of the Milky Way subgroup, which is part of the local galaxy cluster, the Local Group. There are 59 small galaxies confirmed to be within of the Milky Way, but not a ... References Further reading * External links * * * * * {{Portal bar, Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Vulpeculae
Alpha Vulpeculae (α Vulpeculae, abbreviated Alpha Vul, α Vul), officially named Anser , is the brightest star in the constellation of Vulpecula. It is approximately 291 light-years from Earth. It forms a wide optical binary with 8 Vulpeculae. Alpha Vulpeculae is a red giant of spectral class M1 and has an apparent magnitude of +4.4. It has been analyzed as a member of the Arcturus stream, a group of stars with high proper motion and metal-poor properties thought to be the remnants of a small galaxy consumed by the Milky Way. Nomenclature ''α Vulpeculae'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Vulpeculae'') is the system's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional name ''Anser'', derived from when the constellation had the name ''Vulpecula cum Ansere'' 'the little fox with the goose'. In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Anser'' for this star on 30 June 2017 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
27 Cancri
27 Cancri is a single star in the zodiac constellation of Cancer, located around 990 light-years away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued star with a typical apparent visual magnitude of around +5.56. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −8.3 km/s. It is a member of the Arcturus stream, a group of stars with high proper motion and metal-poor properties thought to be the remnants of a small galaxy consumed by the Milky Way. This is an aging red giant with a stellar classification of M3 IIIa, currently on the asymptotic giant branch. It is classified as a semiregular variable star of type SRb and its brightness varies from magnitude +5.41 to +5.75 with a period of 40 days. The star is radiating around 2,455 times the Sun's luminosity The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux (power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the lumin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kappa Gruis
κ Gruis, Romanization of Greek, Latinised as Kappa Gruis, is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Grus (constellation), Grus. With an apparent magnitude of 5.37, it is visible to the naked eye as a dim, orange-hued point. The distance to this system, as determined from an annual parallax shift of 8.87 milliarcsecond, mas as seen from the Earth, is roughly 368 light years. It is drifting further away with a heliocentric radial velocity of +18 km/s. It is a member of the Arcturus moving group. This is an stellar evolution, evolved K-type star, K-type giant star on the asymptotic giant branch with a stellar classification of K5 III. With the supply of hydrogen at its stellar core, core exhausted, it has expanded and now spans 29.6 times the radius of the Sun. It is radiating 200 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature of 3,990 K. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Kappa Gruis K-type giants Grus (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around or lower. The appearance of the red giant is from yellow-white to reddish-orange, including the spectral types K and M, sometimes G, but also class S stars and most carbon stars. Red giants vary in the way by which they generate energy: * most common red giants are stars on the red-giant branch (RGB) that are still fusing hydrogen into helium in a shell surrounding an inert helium core * red-clump stars in the cool half of the horizontal branch, fusing helium into carbon in their cores via the triple-alpha process * asymptotic-giant-branch (AGB) stars with a helium burning shell outside a degenerate carbon–oxygen core, and a hydrogen-burning shell just beyond that. Many of the well-known bright stars are red giants because they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAVE (survey)
RAVE (RAdial Velocity Experiment) is a multi-fiber spectroscopic astronomical survey of stars in the Milky Way using the 1.2-metre UK Schmidt Telescope of the Australian Astronomical Observatory (AAO). The RAVE collaboration consists of researchers from over 20 institutions around the world and is coordinated by the Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam (AIP). As a southern hemisphere survey covering 20,000 square degrees of the sky, RAVE's primary aim is to derive the radial velocity of stars from the observed spectra. Additional information is also derived such as effective temperature, surface gravity, metallicity, photometric parallax and elemental abundance data for the stars. On April 5, 2013 RAVE concluded its phase of data taking. In an almost ten year observing campaign, a total of 574,630 spectra have been obtained on 483,330 individual stars by a small team of AAO observers, with other observers making occasional visits from RAVE participating institutions. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moving Group
In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the Observational astronomy, observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space. Stellar kinematics encompasses the measurement of stellar Velocity, velocities in the Milky Way and its Satellite galaxies of the Milky Way, satellites as well as the internal kinematics of more distant Galaxy, galaxies. Measurement of the kinematics of stars in different subcomponents of the Milky Way including the thin disk, the thick disk, the Bulge (astronomy), bulge, and the stellar halo provides important information about the formation and evolutionary history of our Galaxy. Kinematic measurements can also identify exotic phenomena such as hypervelocity stars escaping from the Milky Way, which are interpreted as the result of gravitational encounters of binary stars with the Sagittarius A*, supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center. Stellar kinematics is related to but distinct from the subject of stellar dynamics, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)