|
Arctic Geoengineering
Temperatures in the Arctic region have tended to increase more rapidly than the global average. Projections of sea ice loss that are adjusted to take account of recent rapid Arctic shrinkage suggest that the Arctic will likely be free of summer sea ice sometime between 2059 and 2078. Various climate engineering schemes have been suggested to reduce the chance of significant and irreversible effects such as Arctic methane release. Several climate engineering proposals have been made which are specific to the Arctic. They are usually hydrological in nature, and principally center upon measures to prevent Arctic ice loss. In addition, other solar radiation management climate engineering techniques, such as stratospheric sulfate aerosols have been proposed. These would cool the Arctic by adjusting the albedo of the atmosphere. Background The Arctic region plays an important role in the regulation of the Earth's climate. Conditions in the Arctic may suggest the existence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2007 Arctic Sea Ice
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube. As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has greatly symbolic associations in religion, mythology, superstition and philosophy. The seven Classical planets resulted in seven being the number of days in a week. It is often considered lucky in Western culture and is often seen as highly symbolic. Unlike Western culture, in Vietnamese culture, the number seven is sometimes considered unlucky. It is the first natural number whose pronunciation contains more than one syllable. Evolution of the Arabic digit In the beginning, Indians wrote 7 more or less in one stroke as a curve that looks like an uppercase vertically inverted. The western Ghubar Arabs' main contribution was to make the longer line diagonal rather than straight, though they showed some tendencies to making the digit more rectilinear. The eastern Arabs developed the digit fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
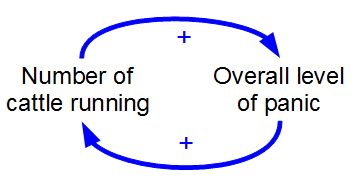
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, ''A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A''.Keesing, R.M. (1981). Cultural anthropology: A contemporary perspective (2nd ed.) p.149. Sydney: Holt, Rinehard & Winston, Inc. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics. Mathematically, positive feedback is defined as a positive loop gain around a closed loop of cause and effect. That is, positive feedback is Phase (waves), in phase with the input, in the sense that it adds to make the input larger. Positive feedback tends to cause Control theory#Stability, system i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Of The Arctic
Environment most often refers to: __NOTOC__ * Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally * Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or a group of organisms Other physical and cultural environments *Ecology, the branch of ethology that deals with the relations of organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings *Environment (systems), the surroundings of a physical system that may interact with the system by exchanging mass, energy, or other properties *Built environment, constructed surroundings that provide the setting for human activity, ranging from the large-scale civic surroundings to the personal places *Social environment, the culture that an individual lives in, and the people and institutions with whom they interact *Market environment, business term Arts, entertainment and publishing * ''Environment'' (magazine), a peer-reviewed, popular enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Research
Arctic studies may include: *Arctic ecology *Geology *Meteorology *Pedology *Oceanography See also * List of Arctic research programs * List of research stations in the Arctic A number of governments maintain permanent research stations in the Arctic. Also known as Arctic bases, polar stations or ice stations, these bases are widely distributed across the northern polar region of Earth. Historically few research st ... References Earth sciences Arctic research {{arctic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Engineering
Planetary engineering is the development and application of technology for the purpose of influencing the environment of a planet. Planetary engineering encompasses a variety of methods such as terraforming, seeding, and geoengineering. Widely discussed in the scientific community, terraforming refers to the alteration of other planets to create a habitable environment for terrestrial life. Seeding refers to the introduction of life from Earth to habitable planets. Geoengineering refers to the engineering of a planet's climate, and has already been applied on Earth. Each of these methods are composed of varying approaches and possess differing levels of feasibility and ethical concern. Terraforming Terraforming is the process of modifying the atmosphere, temperature, surface topography or ecology of a planet, moon, or other body in order to replicate the environment of Earth. Technologies A common object of discussion on potential terraforming is the planet Mars. To terr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoengineering
Climate engineering (also called geoengineering) is a term used for both carbon dioxide removal (CDR) and solar radiation management (SRM), also called solar geoengineering, when applied at a planetary scale.IPCC (2022Chapter 1: Introduction and FramingiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA However, they have very different geophysical characteristics which is why the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) no longer uses this overarching term.IPCC, 2021Annex VII: Glossary atthews, J.B.R., V. Möller, R. van Diemen, J.S. Fuglestvedt, V. Masson-Delmotte, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, A. Reisinger (eds.) IClimate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[Masson-Delmot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yukon River
The Yukon River (Gwichʼin language, Gwich'in: ''Ųųg Han'' or ''Yuk Han'', Central Alaskan Yup'ik language, Yup'ik: ''Kuigpak'', Inupiaq language, Inupiaq: ''Kuukpak'', Deg Xinag language, Deg Xinag: ''Yeqin'', Hän language, Hän: ''Tth'echù'' or ''Chuu k'onn'', Southern Tutchone: Chu Nìikwän, russian: Юкон, Yukon) is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. From its source in British Columbia, Canada, it flows through Canada's territory of Yukon (itself named after the river). The lower half of the river continues westwards through the U.S. state of Alaska. The river is long and empties into the Bering Sea at the Yukon–Kuskokwim Delta. The average flow is . The total drainage area is , of which lies in Canada. The total area is more than 25% larger than Texas or Alberta. The longest river in Alaska and Yukon, it was one of the principal means of transportation during the 1896–1903 Klondike Gold Rush. A portion of the river in Yukon—"The Thirty Mile" se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratospheric Sulfate Aerosols (geoengineering)
Stratospheric aerosol injection is a proposed method of solar geoengineering (or solar radiation modification) to reduce global warming. This would introduce aerosols into the stratosphere to create a cooling effect via global dimming and increased albedo, which occurs naturally from volcanic eruptions. It appears that stratospheric aerosol injection, at a moderate intensity, could counter most changes to temperature and precipitation, take effect rapidly, have low direct implementation costs, and be reversible in its direct climatic effects. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change concludes that it "is the most-researched olar geoengineeringmethod, with ''high agreement'' that it could limit warming to below 1.5°C." However, like other solar geoengineering approaches, stratospheric aerosol injection would do so imperfectly and other effects are possible, particularly if used in a suboptimal manner. Various forms of sulfur have been shown to cool the planet after large vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowell Wood
Lowell Lincoln Wood Jr. (born 1941) is an American astrophysicist who has been involved with the Strategic Defense Initiative and with geoengineering studies. He has been affiliated with Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and the Hoover Institution, and chaired the EMP Commission. Wood is a prolific inventor listed on 1,761 U.S. patents as of August 21, 2018. Wood passed Thomas Edison on June 30, 2015, becoming the all-time most prolific inventor from the United States based on number of issued U.S. utility patents. Wood earned a PhD in geophysics from the University of California at Los Angeles in 1965 for thesis titled ''Hyperthermal Processes in the Solar Atmosphere''. He currently works for Intellectual Ventures. Political work Wood meets and consults with global think tanks on global warming. He has suggested anti-global warming measures, including space mirrors, carbon sequestration in the ocean, employing stratospheric sulfate aerosols, and super-efficient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Caldeira
Kenneth Caldeira (born 1960) is an American atmospheric scientist. His areas of research include ocean acidification, climate effects of trees, intentional climate modification, interactions in the global carbon cycle/climate system, and sustainable energy. As of 2021, Caldeira is Senior Scientist in the energy research company Breakthrough Energy, Senior Staff Scientist (emeritus) in the Carnegie Institution for Science's Department of Global Ecology, and Professor (by courtesy) in the Stanford University Department of Earth System Sciences. Early life and education In the 1980s, Caldeira worked as a software developer. He received his Ph.D in Atmospheric Sciences in 1991 from the New York University Department of Applied Science. From 1991 to 1993, Caldeira worked at Penn State University as a post-doctoral researcher. He then worked as an Environmental Scientist and Physicist at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory until 2005. Climate change research In 2005, Calde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Insulator
Thermal insulation is the reduction of heat transfer (i.e., the transfer of thermal energy between objects of differing temperature) between objects in thermal contact or in range of radiative influence. Thermal insulation can be achieved with specially engineered methods or processes, as well as with suitable object shapes and materials. Heat flow is an inevitable consequence of contact between objects of different temperature. Thermal insulation provides a region of insulation in which thermal conduction is reduced, creating a thermal break or thermal barrier, or thermal radiation is reflected rather than absorbed by the lower-temperature body. The insulating capability of a material is measured as the inverse of thermal conductivity (k). Low thermal conductivity is equivalent to high insulating capability ( resistance value). In thermal engineering, other important properties of insulating materials are product density (ρ) and specific heat capacity (c). Definition T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |