|
Arch Of Cabanes
The Arch of Cabanes is a Roman triumphal arch built in the 2nd century AD. It is located approximately from Cabanes ( Castellón, Valencia), on the via Augusta, situated in the middle of the plain to which it lends its name. History The construction of the arch is attributed to the 2nd century on the basis of the discovery of ceramic material and coinage from this period at the base of the monument. It was probably erected as part of a private funerary monument, perhaps in connection with a rural villa of the area. It is mentioned in documents from 1243 (''Carta Puebla'') and in 1873 the provincial commission of monuments redirected the street which passed under the arch, in order to safeguard the monument. The arch was declared a historic artistic monument among the national artistic treasures of Spain in 1931. In 2004, the commune of Cabanes approved the "Special Plan for the Protection of the Roman Road and Arch at Cabanes" [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Castellón
Castellón (officially in ca-valencia, Castelló) is a province in the northern part of the Valencian Community. It is bordered by the provinces of Valencia to the south, Teruel to the west, Tarragona to the north, and by the Mediterranean Sea to the east. The western side of the province is in the mountainous Sistema Ibérico area. Geography Castellón's capital is Castellón de la Plana (). The province had a population of 579,962 at the start of 2019, 30% of whom were residing in the capital, 60% in its metropolitan area, and 85% along the coastline. As of the 2011 Census, the population had grown to 594,423 people, but has since declined.Instituto Nacional de Estadistica, Madrid, 2019. The province, and in particular its idle large airport, has become a symbol of the wasteful spending prior to the 2008-14 Spanish financial crisis. It is a bilingual territory whose inhabitants speak both Spanish and the local co-official language Valencian. Other major cities of the provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
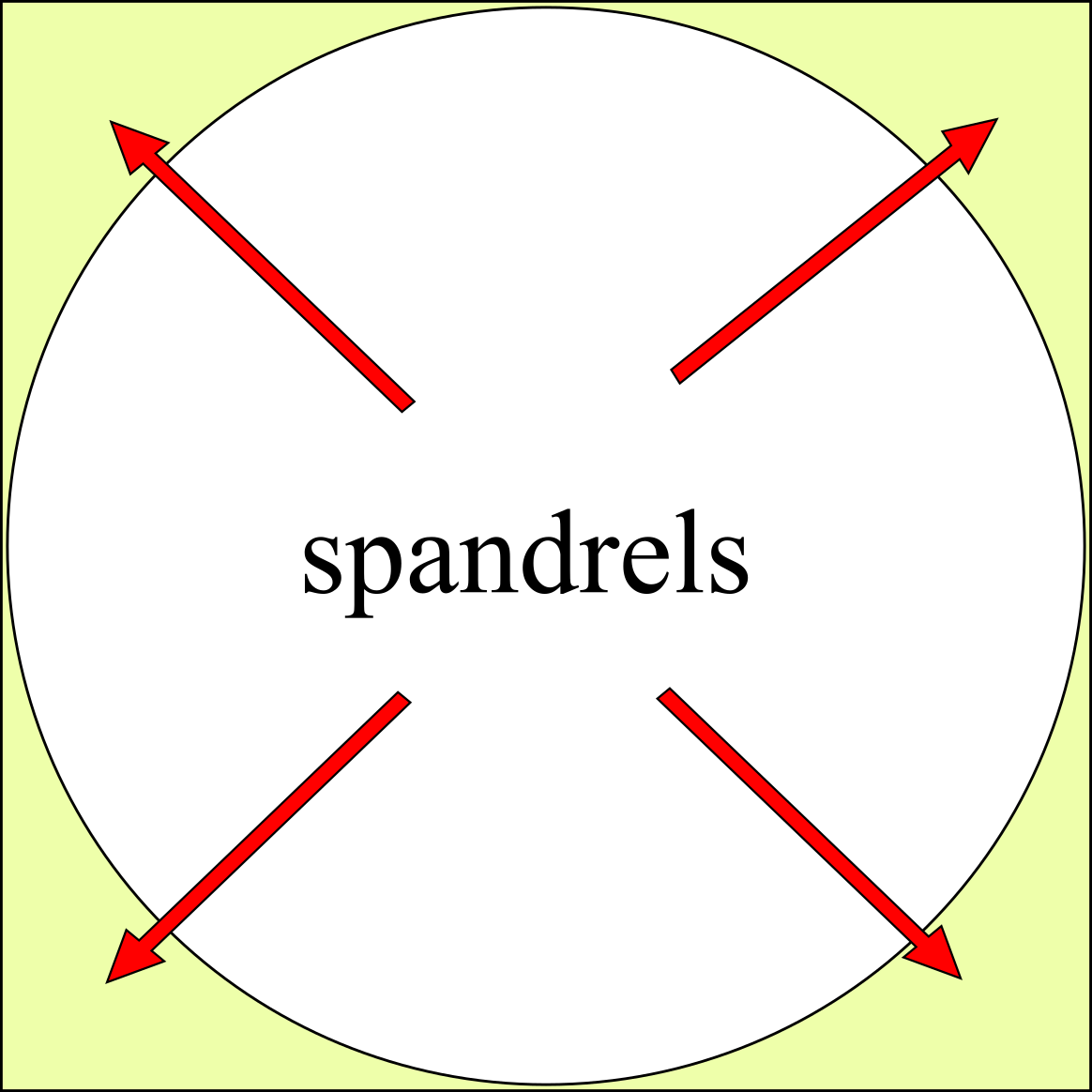
Spandrel
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more than one floor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Roman Triumphal Arches
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Roman Triumphal Arches ...
This is a list of Roman triumphal arches. Triumphal arches were constructed across the Roman Empire and are an archetypal example of Roman architecture. Most surviving Roman arches date from the Imperial period (1st century BC onwards). They were preceded by honorific arches set up under the Roman Republic. Existing arches Destroyed arches Note: MUR stands for the 12th century Mirabilia Urbis Romae See also *List of post-Roman triumphal arches *Victory column *Rostral column *Roman architecture *Roman engineering *Roman technology Sources * {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Roman Triumphal Arches Triumphal arches A triumphal arch is a free-standing monumental structure in the shape of an archway with one or more arched passageways, often designed to span a road. In its simplest form a triumphal arch consists of two massive piers connected by an arch, crow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortar (masonry)
Mortar is a workable paste which hardens to bind building blocks such as stones, bricks, and concrete masonry units, to fill and seal the irregular gaps between them, spread the weight of them evenly, and sometimes to add decorative colors or patterns to masonry walls. In its broadest sense, mortar includes pitch, asphalt, and soft mud or clay, as those used between mud bricks, as well as cement mortar. The word "mortar" comes from Old French ''mortier'', "builder's mortar, plaster; bowl for mixing." (13c.). Cement mortar becomes hard when it cures, resulting in a rigid aggregate structure; however, the mortar functions as a weaker component than the building blocks and serves as the sacrificial element in the masonry, because mortar is easier and less expensive to repair than the building blocks. Bricklayers typically make mortars using a mixture of sand, a binder, and water. The most common binder since the early 20th century is Portland cement, but the ancient binder lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia (architecture)
Fascia () is an architectural term for a vertical frieze or band under a roof edge, or which forms the outer surface of a cornice, visible to an observer. Typically consisting of a wooden board, unplasticized PVC (uPVC), or non-corrosive sheet metal, many of the non-domestic fascias made of stone form an ornately carved or pieced together cornice, in which case the term fascia is rarely used. The word fascia derives from Latin ''fascia'' meaning "band, bandage, ribbon, swathe". The term is also used, although less commonly, for other such band-like surfaces like a wide, flat trim strip around a doorway, different and separate from the wall surface. The horizontal "fascia board" which caps the end of rafters outside a building may be used to hold the rain gutter. The finished surface below the fascia and rafters is called the soffit or eave. In classical architecture, the fascia is the plain, wide band (or bands) that make up the architrave section of the entablature, directl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave (the supporting member immediately above; equivalent to the lintel in post and lintel construction), the frieze (an unmolded strip that may or may not be ornamented), and the cornice (the projecting member below the pediment). The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification. Overview The structure of an entablature varies with the orders of architecture. In each order, the proportions of the subdivisions (architrave, frieze, cornice) are defined by the proportions of the column. In Roman and Renaissance interpretations, it is usually approximately a quarter of the height of the column. Varian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabanes, Castellón
Cabanes (), also known as Cabanes de l'Arc, is a village and Municipalities of Spain, municipality located in the Comarques of the Valencian Community, comarca of Plana Alta, in the province of Castellón, Valencian Community, Spain. Cabanes is located near the old Ancient Rome, Roman road Via Augusta, along which the Arch of Cabanes, a triumphal arch from the 2nd century AD, can be seen. In the municipality stands the old settlement of Albalat dels Ànecs, where several fortified buildings still remain. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Cabanes, Castellon Municipalities in the Province of Castellón Plana Alta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Roma Cabanes
ARC may refer to: Business * Aircraft Radio Corporation, a major avionics manufacturer from the 1920s to the '50s * Airlines Reporting Corporation, an airline-owned company that provides ticket distribution, reporting, and settlement services * Airport Regions Conference, a European organization of major airports * Amalgamated Roadstone Corporation, a British stone quarrying company * American Record Company (1904–1908, re-activated 1979), one of two United States record labels by this name * American Record Corporation (1929–1938), a United States record label also known as American Record Company * ARC (American Recording Company) (1978-present), a vanity label for Earth, Wind & Fire * ARC Document Solutions, a company based in California, formerly American Reprographics Company * Amey Roadstone Construction, a former British construction company * Aqaba Railway Corporation, a freight railway in Jordan * ARC/Architectural Resources Cambridge, Inc., Cambridge, Massachusetts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |