|
Araucaria Project
The Araucaria Project is an international science collaboration focused on improving the calibration of the extragalactic distance scale based on observations of major distance indicators in several nearby galaxies. Project The Araucaria Project is a collaboration between astronomers from institutions in Europe, Chile and the US. Its principal aim is to provide an improved calibration of the local extragalactic distance scale. In the process of setting up the extragalactic distance scale, the greatest difficulty leading to the currently largest contribution on the systematic uncertainty of the Hubble constant lies in the determination of accurate absolute distances to nearby galaxies. The principal reason for this persisting difficulty is in the unknown dependencies of stellar standard candles, used to measure the distances of nearby galaxies, on the environmental properties of their host galaxies (metallicity, age of the stellar populations etc.). The Araucaria Project is an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extragalactic Distance Scale
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A ''direct'' distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are "close enough" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity. The ladder analogy arises because no single technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IC 1613
IC 1613 (object 1613 in the Index Catalogues (IC), also known as Caldwell 51) is an irregular dwarf galaxy, visible in the constellation Cetus near the star 26 Ceti. It was discovered in 1906 by Max Wolf, and is approaching Earth at 234 km/s. IC 1613 is a member of the Local Group. It has played an important role in the calibration of the Cepheid variable period-luminosity relation for estimating distances. Other than the Magellanic Clouds, it is one of the few Local Group dwarf irregular galaxy where RR Lyrae-type variables have been observed; this factor, along with an unusually low abundance of interstellar dust both within IC 1613 and along the line of sight enable especially accurate distance estimates. In 1999, Cole et al. used the Hubble Space Telescope to find that the dominant population of this galaxy has an age of ~7 Gyr. Using its Hess diagram, they found that its evolutionary history may be similar to that of the Pegasus Dwarf Irregular Galaxy. Both gal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sculptor Group
The Sculptor Group is a loose group of galaxies visible near the south galactic pole. The group is one of the closest groups of galaxies to the Local Group; the distance to the center of the group from the Milky Way is approximately . The Sculptor Galaxy (NGC 253) and a few other galaxies form a gravitationally-bound core in the center of this group. A few other galaxies at the periphery may be associated with the group but may not be gravitationally bound. Because most of the galaxies in this group are actually weakly gravitationally bound, the group may also be described as a filament. It is considered to be at an early stage of evolution in which galaxies are still falling into the group along filamentary structures. Members The table below lists galaxies that have been identified as associated with the Sculptor Galaxy (and hence associated with the group) by I. D. Karachentsev and collaborators. The object names used in the above table differ from the names used by Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 7793
NGC 7793 is a flocculent spiral galaxy in the southern constellation of Sculptor. It was discovered in 1826 by Scottish astronomer James Dunlop. The galaxy is located at a distance of million light years and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of . NGC 7793 is one of the five brightest galaxies within the Sculptor Group. The morphological class of NGC 7793 is SA(s)d, indicating it is unbarred spiral galaxy (SA) with no inner ring structure (s) and the arms are loosely wound and disorganized (d). It is flocculent in appearance with a very small bulge and a star cluster at the nucleus. The galactic disk is inclined at an angle of 53.7° to the line of sight from the Earth. The visible profile is elliptical in form with an angular size of and a major axis aligned along a position angle of 99.3°. There are two nearby dwarf galaxy companions. On March 25, 2008, a type II-P supernova designated SN 2008bk was discovered in NGC 7793. At apparent magnitude 12.5, it be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 300
NGC 300 (also known as Caldwell 70) is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Sculptor. It is one of the closest galaxies to the Local Group, and probably lies between the latter and the Sculptor Group. It is the brightest of the five main spirals in the direction of the Sculptor Group. It is inclined at an angle of 42° when viewed from Earth and shares many characteristics of the Triangulum Galaxy. It is 94,000 light-years in diameter, somewhat smaller than the Milky Way, and has an estimated mass of (2.9 ± 0.2) × 1010 . Nearby galaxies and group information NGC 300 and the irregular galaxy NGC 55 have traditionally been identified as members of the Sculptor Group, a nearby group of galaxies in the constellation of the same name. However, recent distance measurements indicate that these two galaxies actually lie in the foreground. It is likely that NGC 300 and NGC 55 form a gravitationally bound pair. Distance estimates In 1986, Allan Sandage estima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 247
NGC 247 (also known as Caldwell 62 and commonly known as the Claw Galaxy) is an intermediate spiral galaxy (although it is sometimes classified as a dwarf spiral galaxy) about 11.1 Mly away in the constellation Cetus. This distance was confirmed in late February 2011. Previous measurements showed that the galaxy was about 12.2 Mly away, but this was proved to be wrong. NGC 247 is a member of the Sculptor Group, and is 70 000 light years in diameter. NGC 247 has an unusually large void on one side of its spiral disk. This void contains some older, redder stars but no younger, bluer stars. Nearby galaxies and galaxy group information NGC 247 is one of several galaxies that is gravitationally bound to the Sculptor Galaxy (NGC 253). These galaxies form a small core in the center of the Sculptor Group, which is one of the nearest groups of galaxies to the Milky Way The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 55
NGC 55, is a Magellanic type barred spiral galaxy located about 6.5 million light-years away in the constellation Sculptor. Along with its neighbor NGC 300, it is one of the closest galaxies to the Local Group, probably lying between the Milky Way and the Sculptor Group. It has an estimated mass of (2.0 ± 0.4) × 1010 . Nearby galaxies and group information NGC 55 and the spiral galaxy NGC 300 have traditionally been identified as members of the Sculptor Group, a nearby group of galaxies in the constellation of the same name. However, recent distance measurements indicate that the two galaxies actually lie in the foreground. It is likely that NGC 55 and NGC 300 form a gravitationally bound pair. Visual appearance The ''Webb Society Deep-Sky Observer's Handbook'' writes the following about NGC 55: "Nearly edge-on and appears asymmetrical with some signs of dust near the bulge, which is diffuse, broad and somewhat elongated with the south edge sharp; southeast of the bulge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of . It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about and are moving toward one another with a velocity of . The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies. The two largest members, the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies: * The Andromeda Galaxy's satellite system consists of Messier 32 (M32), Messier 110 (M110), NGC 147, NGC 185, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
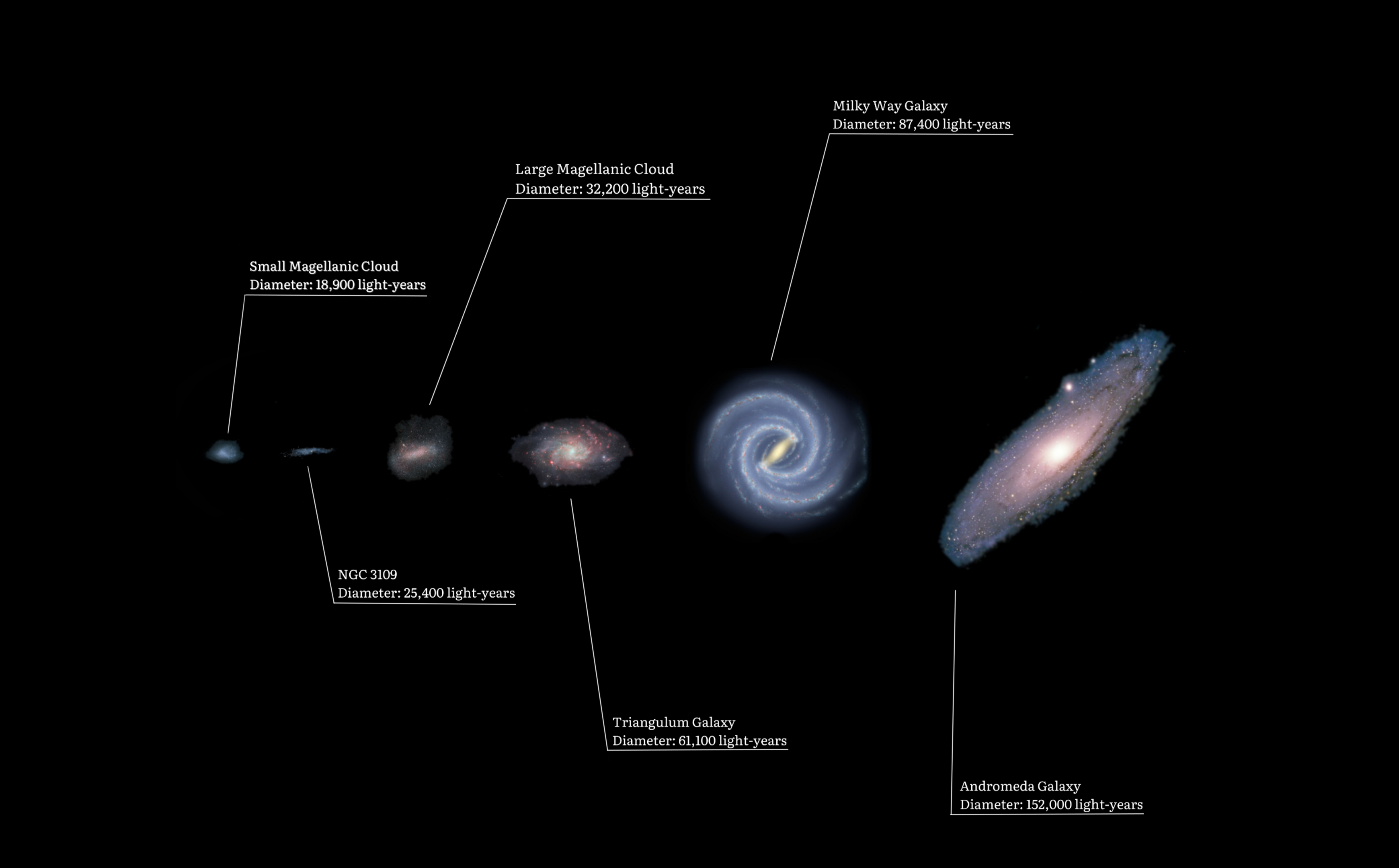
NGC 3109
NGC 3109 is a small barred Magellanic type spiral or irregular galaxy around 4.34 Mly away in the direction of the constellation of Hydra. NGC 3109 is believed to be tidally interacting with the dwarf elliptical galaxy Antlia Dwarf. It was discovered by John Herschel on March 24, 1835 while he was in what is now South Africa.''Irregular Galaxy NGC 3109'' Size and morphology NGC 3109 is classified as a Magellanic type irregular galaxy, but it may in fact be a small |
NGC 6822
NGC 6822 (also known as Barnard's Galaxy, IC 4895, or Caldwell 57) is a barred irregular galaxy approximately 1.6 million light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius. Part of the Local Group of galaxies, it was discovered by E. E. Barnard in 1884 (hence its name), with a six-inch refractor telescope. It is the closest non-satellite galaxy to the Milky Way, but lies just outside its virial radius. It is similar in structure and composition to the Small Magellanic Cloud. It is about 7,000 light-years in diameter. Observational history NGC 6822 was discovered by E. E. Barnard in 1884 using a six-inch refractor telescope. Edwin Hubble, in the paper ''N.G.C. 6822, A Remote Stellar System'', identified 15 variable stars (11 of which were Cepheids) of this galaxy. He also surveyed the galaxy's stars distribution down to magnitude 19.4. He provided spectral characteristics, luminosities and dimensions for the five brightest "diffuse nebulae" (giant H II regions) that includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a hundred million stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology as elliptical, spiral, or irregular. Many are thought to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than the Sun. As of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Supergiant
A blue supergiant (BSG) is a hot, luminous star, often referred to as an OB supergiant. They have luminosity class I and spectral class B9 or earlier. Blue supergiants are found towards the top left of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, above and to the right of the main sequence. They are larger than the Sun but smaller than a red supergiant, with surface temperatures of 10,000–50,000 K and luminosities from about 10,000 to a million times that of the Sun. Formation Supergiants are evolved high-mass stars, larger and more luminous than main-sequence stars. O class and early B class stars with initial masses around evolve away from the main sequence in just a few million years as their hydrogen is consumed and heavy elements start to appear near the surface of the star. These stars usually become blue supergiants, although it is possible that some of them evolve directly to Wolf–Rayet stars. Expansion into the supergiant stage occurs when hydrogen in the core of the sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |