|
Aram (Biblical Region)
Aram ( arc, ܐܪܡ, Ārām; he, אֲרָם, Arām) was a historical region mentioned in early cuneiforms and in the Bible. The area of Aram did not develop into a bigger empire, it consisted of a number of small states in present-day Syria and northern Palestine. Some of these states are mentioned in the Old Testament, Damascus being the most outstanding one, which came to encompass most of Syria. Furthermore, Aram-Damascus is commonly referred to as simply Aram in the Old Testament. After the final conquest by the rising Neo-Assyrian Empire in the second half of the 8th century and also during the later consecutive rules of the Neo-Babylonian Empire (612–539 BCE) and the Achaemenid Empire (539–332 BCE), the region of Aram lost most of its sovereignty. During the Seleucid period (312-64 BCE), the term ''Syria'' was introduced as Hellenistic designation for this region, but the native name (Aram) persisted in use among Arameans, up to the Arab conquest in the 7th century CE. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdoms Of The Levant Map 830
Kingdom commonly refers to: * A monarchy ruled by a king or queen * Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy Kingdom may also refer to: Arts and media Television * Kingdom (British TV series), ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama starring Stephen Fry * Kingdom (American TV series), ''Kingdom'' (American TV series), a 2014 US television drama starring Frank Grillo * Kingdom (South Korean TV series), ''Kingdom'' (South Korean TV series), a 2019 South Korean television series *''Kingdom: Legendary War'', a 2021 South Korean television series Music * Kingdom (group), a South Korean boy group * Kingdom (Koda Kumi album), ''Kingdom'' (Koda Kumi album), 2008 * Kingdom (Bilal Hassani album), ''Kingdom'' (Bilal Hassani album), 2019 * Kingdom (Covenant Worship album), ''Kingdom'' (Covenant Worship album), 2014 * Kingdoms (LIYW album), ''Kingdoms'' (Life in Your Way album), 2011 * Kingdoms (Broadway album), ''Kingdoms'' (Broadway album), 2009 * King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
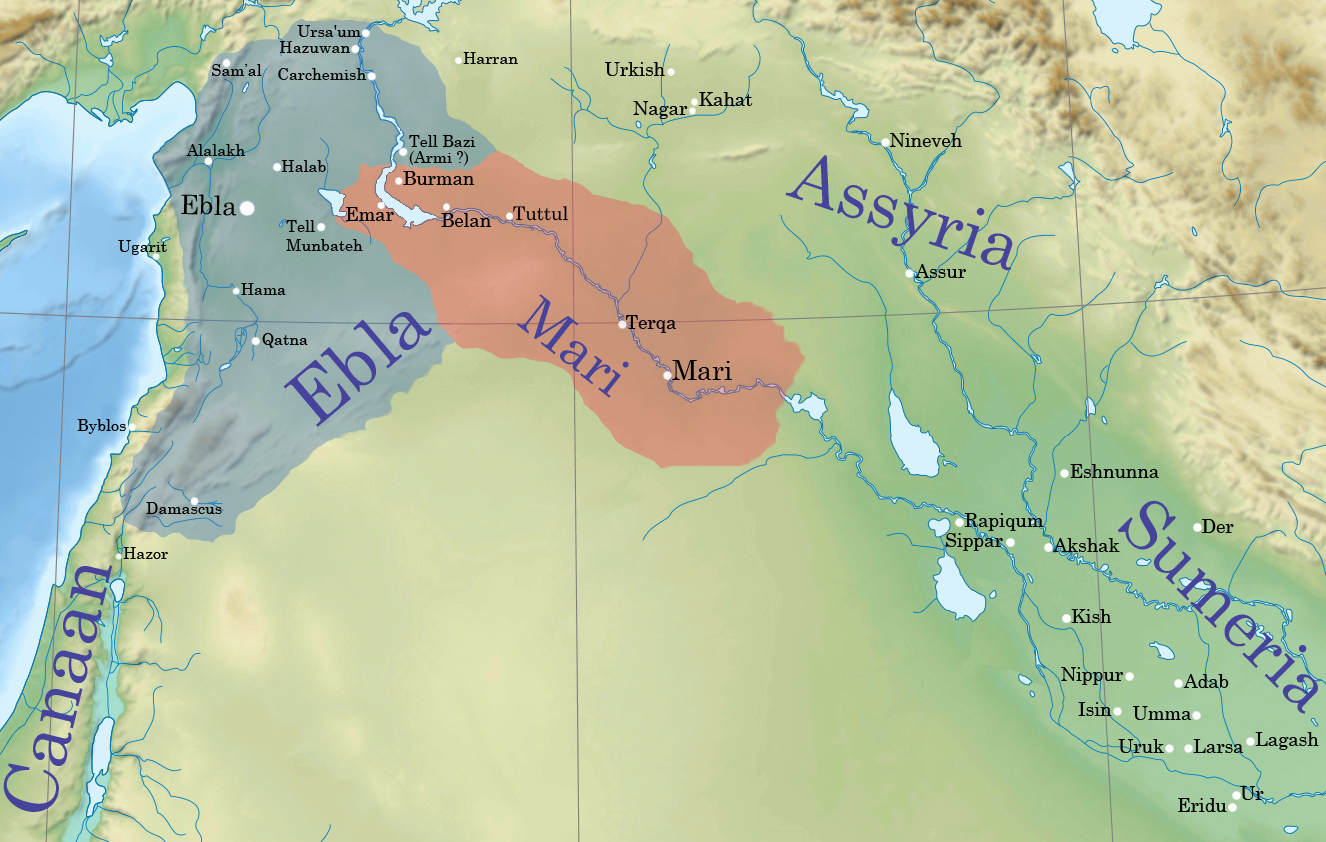
Mari, Syria
Mari (Cuneiform: , ''ma-riki'', modern Tell Hariri; ar, تل حريري) was an ancient Semitic city-state in modern-day Syria. Its remains form a tell 11 kilometers north-west of Abu Kamal on the Euphrates River western bank, some 120 kilometers southeast of Deir ez-Zor. It flourished as a trade center and hegemonic state between 2900 BC and 1759 BC. The city was purposely built in the middle of the Euphrates trade routes between Sumer in the south and the Eblaite kingdom and the Levant in the west. Mari was first abandoned in the middle of the 26th century BC but was rebuilt and became the capital of a hegemonic East Semitic state before 2500 BC. This second Mari engaged in a long war with its rival Ebla and is known for its strong affinity with Sumerian culture. It was destroyed in the 23rd century BC by the Akkadians, who allowed the city to be rebuilt and appointed a military governor (''Shakkanakku''). The governors became independent with the disint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simurrum
The Simurrum Kingdom ( akk, 𒋛𒈬𒌨𒊑𒅎: ''Si-mu-ur-ri-im'') was an important city state of the Mesopotamian area from around 2000 BCE to 1500 BCE, during the period of the Akkadian Empire down to Ur III. The Simurrum Kingdom disappears from records after the Old Babylonian period. It was neighbour and sometimes ally with the Lullubi kingdom. It has been proposed that the city was on the Sirwan River (in Iran) which becomes the Diyala river in Iraq. Kingdom The Simurrum Kingdom seems to have been part of a belt of Hurrian city states in the northeastern portion of Mesopotamian area. They were often in conflict with the rulers of Ur III. Several Kings (𒈗, pronounced ''Šàr'', "''Shar''", in Akkadian) of Simurrum are known, such as Iddin-Sin and his son Zabazuna. Various inscriptions suggest that they were contemporary with king Ishbi-Erra (1953—c.1920 BCE). Another king, mentioned in The Great Revolt against Narām-Sîn, was mPu-ut-ti-ma-da-al. Conflicts Several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitive
In grammar, the genitive case (abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can also serve purposes indicating other relationships. For example, some verbs may feature arguments in the genitive case; and the genitive case may also have adverbial uses (see adverbial genitive). Genitive construction includes the genitive case, but is a broader category. Placing a modifying noun in the genitive case is one way of indicating that it is related to a head noun, in a genitive construction. However, there are other ways to indicate a genitive construction. For example, many Afroasiatic languages place the head noun (rather than the modifying noun) in the construct state. Possessive grammatical constructions, including the possessive case, may be regarded as a subset of genitive construction. For example, the genitive construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensí
Ensi (cuneiform: , "lord of the plowland"; Emesal dialect: ''umunsik''; akk, iššakkum, script=Latn, italic=yes) was a Sumerian title designating the ruler or prince of a city-state. Originally it may have designated an independent ruler, but in later periods the title presupposed subordinance to a lugal. For the Early Dynastic Period (about 2800–2350 BC), the meaning of the titles en, ensi and lugal cannot be differentiated clearly: see lugal, ensi and en for details. Ensi may have originally been a designation of the ruler restricted to Lagash and Umma. The ''ensi'' was considered a representative of the city-state's patron deity. In later periods, an ensi was normally seen as subordinate to a lugal. Nevertheless, even the powerful rulers of the Second Dynasty of Lagash (c. 2100 BC) such as Gudea were satisfied with the title ensi. During the Third Dynasty of Ur (about 2100–2000 BC) ensi referred to the provincial governors of the kingdom. These exercised great pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naram-Sin Of Akkad
Naram-Sin, also transcribed Narām-Sîn or Naram-Suen ( akk, : '' DNa-ra-am D Sîn'', meaning "Beloved of the Moon God Sîn", the "𒀭" being a silent honorific for "Divine"), was a ruler of the Akkadian Empire, who reigned c. 2254–2218 BC (middle chronology), and was the third successor and grandson of King Sargon of Akkad. Under Naram-Sin the empire reached its maximum strength. He was the first Mesopotamian king known to have claimed divinity for himself, taking the title "God of Akkad", and the first to claim the title "King of the Four Quarters, King of the Universe". As part of that he became city god of Akkade in the same way Enlil was city god of Nippur. Biography Naram-Sin was born as a son of Manishtushu. He was thus a nephew of King Rimush and grandson of Sargon and Tashlultum. Naram-Sin's aunt was the High Priestess En-hedu-ana. To be fully correct, rather than Naram-Sin or Naram-Suen "in Old Akkadian, the name in question should rather be reconstructed as Nar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebla Tablets
The Ebla tablets are a collection of as many as 1,800 complete clay tablets, 4,700 fragments, and many thousands of minor chips found in the palace archives of the ancient city of Ebla, Syria. The tablets were discovered by Italian archaeologist Paolo Matthiae and his team in 1974–75 during their excavations at the ancient city at Tell Mardikh. The tablets, which were found ''in situ'' on collapsed shelves, retained many of their contemporary clay tags to help reference them. They all date to the period between c. 2500 BC and the destruction of the city c. 2250 BC.Dumper; Stanley, 2007, p.141. Today, the tablets are held in museums in the Syrian cities of Aleppo, Damascus, and Idlib. Discovery and archaeological context The tablets were discovered just where they had fallen when their wooden shelves burned in the final conflagration of "Palace G". The archive was kept in orderly fashion in two small rooms off a large audience hall (with a raised dais at one end); one repository ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idlib
ar, إدلبي, Idlibi , coordinates = , elevation_m = 500 , area_code = 23 , geocode = C3871 , blank_name = Climate , blank_info = Csa , parts_type = Control , parts_style = para , p1 = Syrian Salvation Government , website eIdleb Idlib ( ar, إِدْلِب, ʾIdlib, also spelt Idleb or Edlib) is a city in northwestern Syria, and is the capital of the Idlib Governorate. It has an elevation of nearly above sea level, and is southwest of Aleppo. The city was taken over by Syrian revolution at the beginning of the Syrian Civil War in 2011, and by 2017 was the seat of the Syrian Salvation Government. Demographics In the 2004 census by the Central Bureau of Statistics, Idlib had a population of 98,791 and in 2010 the population was around 165,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eblaite Language
Eblaite (, also known as Eblan ISO 639-3), or Palaeo-Syrian, is an extinct East Semitic language used during the 3rd millennium BC by the populations of Northern Syria. It was named after the ancient city of Ebla, in modern western Syria. Variants of the language were also spoken in Mari and Nagar. According to Cyrus H. Gordon, although scribes might have spoken it sometimes, Eblaite was probably not spoken much, being rather a written lingua franca with East and West Semitic features. The language was discovered through cuneiform tablets found in Ebla. Discovery The 1964 discovery at the Tell Mardikh site in Northern Syria of an ancient city from the second half of the third millennium BC completely altered archaeological knowledge of the time, as it indicated the existence of a contemporary urban culture during the Early Dynastic Period of Mesopotamia, within a geographic zone where, at the time, previous excavations had revealed nothing on the same scale. In agreemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla was a continuation of the first, ruled by a new royal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Semitic
The East Semitic languages are one of three divisions of the Semitic languages. The East Semitic group is attested by three distinct languages, Akkadian, Eblaite and possibly Kishite, all of which have been long extinct. They were influenced by the non-Semitic Sumerian language and adopted cuneiform writing. East Semitic languages stand apart from other Semitic languages, which are traditionally called West Semitic, in a number of respects. Historically, it is believed that the linguistic situation came about as speakers of East Semitic languages wandered further east, settling in Mesopotamia during the 3rd millennium BC, as attested by Akkadian texts from this period. By the early 2nd millennium BC, East Semitic languages, in particular Akkadian, had come to dominate the region. Phonology Modern understanding of the phonology of East Semitic languages can be derived only from careful study of written texts and comparison with the reconstructed Proto-Semitic. Most striking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)
_Syria.jpg)