|
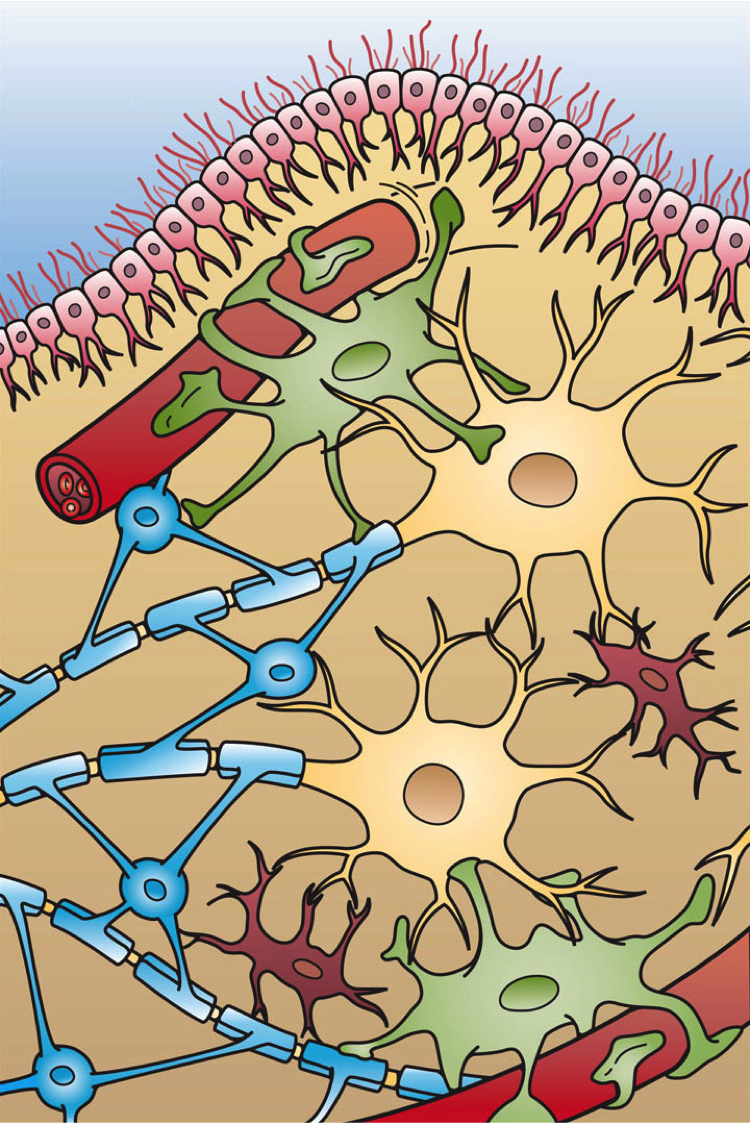
Aquaporin 4
Aquaporin-4, also known as AQP-4, is a water channel protein encoded by the ''AQP4'' gene in humans. AQP-4 belongs to the aquaporin family of integral membrane proteins that conduct water through the cell membrane. A limited number of aquaporins are found within the central nervous system (CNS): AQP1, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, and 11, but more exclusive representation of AQP1, 4, and 9 are found in the brain and spinal cord. AQP4 shows the largest presence in the cerebellum and spinal cord grey matter. In the CNS, AQP4 is the most prevalent aquaporin channel, specifically located at the perimicrovessel astrocyte foot processes, glia limitans, and ependyma. In addition, this channel is commonly found facilitating water movement near cerebrospinal fluid and vasculature. Aquaporin-4 was first identified in 1986. It was the first evidence of the existence of water transport channels. The method that was used to discover the existence of the transport channels was through knockout experiments. Wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulation Of Gene Expression
Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (protein or RNA). Sophisticated programs of gene expression are widely observed in biology, for example to trigger developmental pathways, respond to environmental stimuli, or adapt to new food sources. Virtually any step of gene expression can be modulated, from Transcriptional regulation, transcriptional initiation, to RNA processing, and to the post-translational modification of a protein. Often, one gene regulator controls another, and so on, in a gene regulatory network. Gene regulation is essential for viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes as it increases the versatility and adaptability of an organism by allowing the cell to express protein when needed. Although as early as 1951, Barbara McClintock showed interaction between two genetic loci, Activator (''Ac'') and Dissociator (''Ds''), in the color f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that results in the progressive loss of motor neurons that control voluntary muscles. ALS is the most common type of motor neuron diseases. Early symptoms of ALS include stiff muscles, muscle twitches, and gradual increasing weakness and muscle wasting. ''Limb-onset ALS'' begins with weakness in the arms or legs, while ''bulbar-onset ALS'' begins with difficulty speaking or swallowing. Half of the people with ALS develop at least mild difficulties with thinking and behavior, and about 15% develop frontotemporal dementia. Most people experience pain. The affected muscles are responsible for chewing food, speaking, and walking. Motor neuron loss continues until the ability to eat, speak, move, and finally the ability to breathe is lost. ALS eventually causes paralysis and early death, usually from respiratory failure. Most cases of ALS (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased intracranial pressure, pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary incontinence, personality changes, or mental impairment. In babies, it may be seen as a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and Parinaud's syndrome, downward pointing of the eyes. Hydrocephalus can occur due to birth defects or be acquired later in life. Associated birth defects include neural tube defects and those that result in aqueductal stenosis. Other causes include meningitis, brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, intraventricular hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. The four types of hydrocephalus are communicating, noncommunicating, ''ex vacuo'', and normal pressure hydrocephalus, normal pressure. Diagnosis is typically made by physical examination and medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular System
The ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricular system is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate. All of the ventricular system and the central canal of the spinal cord are lined with ependyma, a specialised form of epithelium connected by tight junctions that make up the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Structure The system comprises four ventricles: * lateral ventricles right and left (one for each hemisphere) * third ventricle * fourth ventricle There are several foramina, openings acting as channels, that connect the ventricles. The interventricular foramina (also called the foramina of Monro) connect the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle through which the cerebrospinal fluid can flow. Ventric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azathioprine
Azathioprine (AZA), sold under the brand name Imuran, among others, is an immunosuppressive medication. It is used in rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and systemic lupus erythematosus, and in kidney transplants to prevent rejection. It is listed by the International Agency for Research on Cancer as a group 1 carcinogen (carcinogenic to humans). It is taken by mouth or injected into a vein. Common side effects include bone-marrow suppression and vomiting. Bone-marrow suppression is especially common in people with a genetic deficiency of the enzyme thiopurine S-methyltransferase. Other serious risk factors include an increased risk of certain cancers. Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby. Azathioprine is in the purine analogue and antimetabolite family of medications. It works via 6-thioguanine to disrupt the making of RNA and DNA by cells. Azathioprine was first made in 1957. It is on the World Hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reaction to treatment of other conditions. In general, deliberately induced immunosuppression is performed to prevent the body from rejecting an organ transplant. Additionally, it is used for treating graft-versus-host disease after a bone marrow transplant, or for the treatment of auto-immune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome, or Crohn's disease. This is typically done using medications, but may involve surgery (splenectomy), plasmapheresis, or radiation. A person who is undergoing immunosuppression, or whose immune system is weak for some other reasons (such as chemotherapy or HIV), is said to be ''immunocompromised''. Deliberately induced Administration of immunosuppressive medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin G (Ig G) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG antibody has two paratopes. Function Antibodies are major components of humoral immunity. IgG is the main type of antibody found in blood and extracellular fluid, allowing it to control infection of body tissues. By binding many kinds of pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi, IgG protects the body from infection. It does this through several mechanisms: * IgG-mediated binding of pathogens causes their immobilization and binding together via agglutination; IgG coating of pathogen surfaces (known as opsonization) allows their recognition and ingestion by phagocytic immune cells leading to the elimination of the pathogen itself; * IgG activates all the classical pathway of the complement system, a cascade of immune protein pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuromyelitis Optica
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD), including neuromyelitis optica (NMO), are autoimmune diseases characterized by acute inflammation of the optic nerve (optic neuritis, ON) and the spinal cord (myelitis). Episodes of ON and myelitis can be simultaneous or successive. A relapsing disease course is common, especially in untreated patients. In more than 80% of cases, NMO is caused by immunoglobulin G Autoantibody, autoantibodies to aquaporin 4 (anti-AQP4 diseases, anti-AQP4), the most abundant Aquaporin, water channel protein in the central nervous system. A subset of anti-AQP4-negative cases is associated with antibodies against myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (Anti-MOG associated encephalomyelitis, anti-MOG). Rarely, NMO may occur in the context of other autoimmune diseases (e.g. Connective tissue disease, connective tissue disorders, paraneoplastic syndromes) or infectious diseases. In some cases, the etiology remains unknown (Idiopathic disease, idiopathic NMO). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory (''see Hebbian theory''). Plastic change often results from the alteration of the number of neurotransmitter receptors located on a synapse. There are several underlying mechanisms that cooperate to achieve synaptic plasticity, including changes in the quantity of neurotransmitters released into a synapse and changes in how effectively cells respond to those neurotransmitters. Synaptic plasticity in both excitatory and inhibitory synapses has been found to be dependent upon postsynaptic calcium release. Historical discoveries In 1973, Terje Lømo and Tim Bliss first described the now widely studied phenomenon of long-term pote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ Of Corti
The organ of Corti, or spiral organ, is the receptor organ for hearing and is located in the mammalian cochlea. This highly varied strip of epithelial cells allows for transduction of auditory signals into nerve impulses' action potential. Transduction occurs through vibrations of structures in the inner ear causing displacement of cochlear fluid and movement of hair cells at the organ of Corti to produce electrochemical signals.The Ear Pujol, R., Irving, S., 2013 Italian anatomist (1822–1876) discovered the organ of Corti in 1851. The structure evolved from the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |