|
April 2005 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on April 24, 2005, the first of two lunar eclipses in 2005. At maximum eclipse, 86.5% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a slight shadow gradient across its disc; this subtle effect may have been visible to careful observers. No part of the Moon was in complete shadow. The eclipse lasted 4 hours and 6 minutes overall, and was visible from east Asia, Australia, and the Americas. Visibility Member This is the 23rd member of Lunar Saros 141. The previous event was the April 1987 lunar eclipse. The next event is the May 2023 lunar eclipse. Related eclipses Eclipse season This is the second eclipse this season. First eclipse this season: 8 April 2005 Hybrid Solar Eclipse Eclipses of 2005 * A hybrid solar eclipse on April 8. * A penumbral lunar eclipse on April 24. * An annular solar eclipse on October 3. * A partial lunar eclipse on October 17. Lunar eclipse 2002-2005 It is the last of four lunar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penumbral Eclipse Minneapolis 24 April 2005
The umbra, penumbra and antumbra are three distinct parts of a shadow, created by any light source after impinging on an opaque object. Assuming no diffraction, for a collimated beam (such as a point source) of light, only the umbra is cast. These names are most often used for the shadows cast by celestial bodies, though they are sometimes used to describe levels, such as in sunspots. Umbra The umbra (Latin for "shadow") is the innermost and darkest part of a shadow, where the light source is completely blocked by the occluding body. An observer within the umbra experiences a total eclipse. The umbra of a round body occluding a round light source forms a right circular cone. When viewed from the cone's apex, the two bodies appear the same size. The distance from the Moon to the apex of its umbra is roughly equal to that between the Moon and Earth: . Since Earth's diameter is 3.7 times the Moon's, its umbra extends correspondingly farther: roughly . Penumbra The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of October 3, 2005
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on October 3, 2005, with a magnitude of 0.958. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an Annulus (mathematics), annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 4.8 days after apogee (September 28, 2005), the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. It was visible from a narrow corridor through the Iberian peninsula and Africa and Brazil. A Solar eclipse, partial eclipse was seen from the much broader path of the Moon The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of April 17, 1996
A partial solar eclipse occurred on April 17, 1996. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ..., thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. Images Related eclipses Eclipses of 1996 * A total lunar eclipse on April 4. * A partial solar eclipse on April 17. * A total lunar eclipse on September 27. * A partial solar eclipse on October 12. Solar eclipses 1993–1996 Metonic series References External links NASA graphics 1996 4 17 1996 in science 1996 4 17 April 1996 events {{Solar-eclipse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
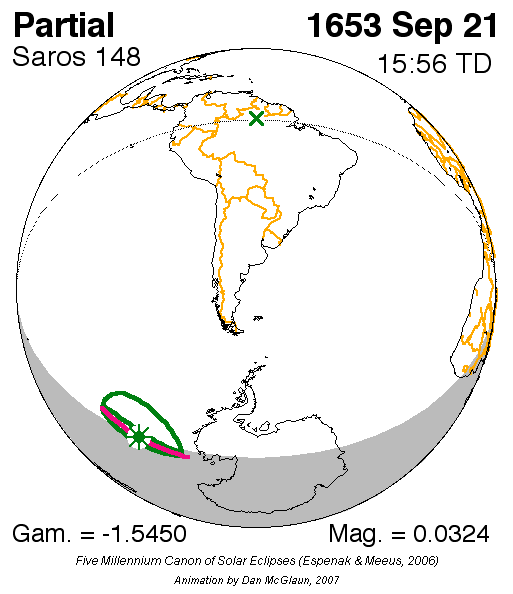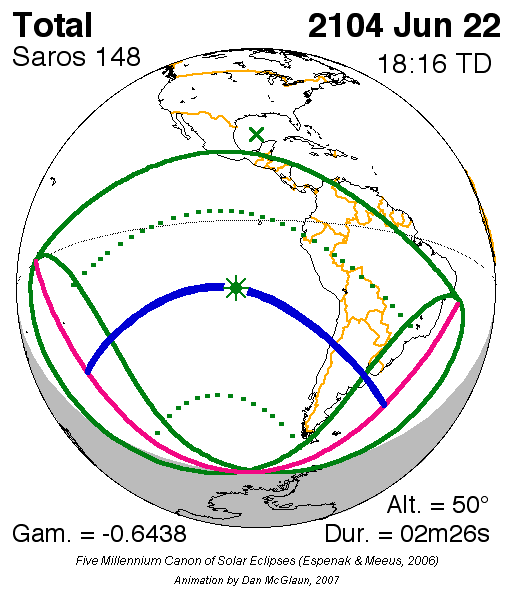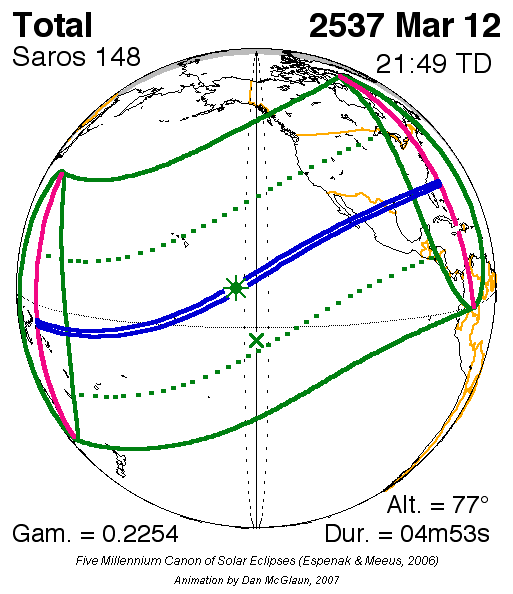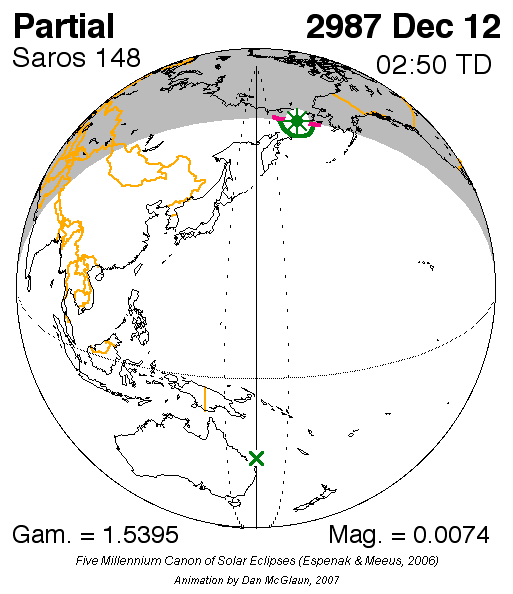
Solar Saros 148
Saros cycle series 148 for solar eclipses occurs at the Moon's descending node, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 75 events. All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon's descending node. This solar saros is linked to Lunar Saros 141 Saros cycle series 141 for lunar eclipses occurs at the moon's descending node, repeats every 18 years 11 and 1/3 days. It contains 72 events. This lunar saros is linked to Solar Saros 148. List See also * List of lunar eclipses There are .... Umbral eclipses Umbral eclipses (annular, total and hybrid) can be further classified as either: 1) Central (two limits), 2) Central (one limit) or 3) Non-Central (one limit). The statistical distribution of these classes in Saros series 148 appears in the following table. Events References * http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEsaros/SEsaros148.html External linksSaros cycle 148 - Information and visualization {{Solar eclipses Solar saros series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saros (astronomy)
The saros () is a period of exactly 223 synodic months, approximately 6585.3211 days, or 18 years, 10, 11, or 12 days (depending on the number of leap years), and 8 hours, that can be used to predict eclipses of the Sun and Moon. One saros period after an eclipse, the Sun, Earth, and Moon return to approximately the same relative geometry, a near straight line, and a nearly identical eclipse will occur, in what is referred to as an eclipse cycle. A sar is one half of a saros. A series of eclipses that are separated by one saros is called a ''saros series''. It corresponds to: *6,585.321347 solar days *18.029 years *223 synodic months *241.999 draconic months *18.999 eclipse years (38 eclipse seasons) *238.992 anomalistic months The 19 eclipse years means that if there is a solar eclipse (or lunar eclipse), then after one saros a new moon will take place at the same node of the orbit of the Moon, and under these circumstances another eclipse can occur. History The earliest disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metonic Cycle
The Metonic cycle or enneadecaeteris (from grc, ἐννεακαιδεκαετηρίς, from ἐννεακαίδεκα, "nineteen") is a period of almost exactly 19 years after which the lunar phases recur at the same time of the year. The recurrence is not perfect, and by precise observation the Metonic cycle defined as 235 lunar month, synodic months is just 2 hours, 4 minutes and 58 seconds longer than 19 tropical year, tropical years. Meton of Athens, in the 5th century BC, judged the cycle to be a whole number of days, 6,940. Using these whole numbers facilitates the construction of a lunisolar calendar. A tropical year is longer than 12 lunar months and shorter than 13 of them. The arithmetic identity 12×12 + 7×13 = 235 shows that a combination of 12 "short" years (12 months) and 7 "long" years (13 months) will be almost exactly equal to 19 solar years. Application in traditional calendars In the Babylonian calendar, Babylonian and Hebrew calendar, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
June 2095 Lunar Eclipse
June is the sixth month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars and is the second of four months to have a length of 30 days, and the third of five months to have a length of less than 31 days. June contains the summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere, the day with the most daylight hours, and the winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere, the day with the fewest daylight hours (excluding polar regions in both cases). June in the Northern Hemisphere is the seasonal equivalent to December in the Southern Hemisphere and vice versa. In the Northern Hemisphere, the beginning of the traditional astronomical summer is 21 June (meteorological summer begins on 1 June). In the Southern Hemisphere, meteorological winter begins on 1 June. At the start of June, the sun rises in the constellation of Taurus; at the end of June, the sun rises in the constellation of Gemini. However, due to the precession of the equinoxes, June begins with the sun in the astrological sign of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
June 2077 Lunar Eclipse
June is the sixth month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars and is the second of four months to have a length of 30 days, and the third of five months to have a length of less than 31 days. June contains the summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere, the day with the most daylight hours, and the winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere, the day with the fewest daylight hours (excluding polar regions in both cases). June in the Northern Hemisphere is the seasonal equivalent to December in the Southern Hemisphere and vice versa. In the Northern Hemisphere, the beginning of the traditional astronomical summer is 21 June (meteorological summer begins on 1 June). In the Southern Hemisphere, meteorological winter begins on 1 June. At the start of June, the sun rises in the constellation of Taurus; at the end of June, the sun rises in the constellation of Gemini. However, due to the precession of the equinoxes, June begins with the sun in the astrological sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
May 2059 Lunar Eclipse
May is the fifth month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars and is the third of seven months to have a length of 31 days. May is a month of spring in the Northern Hemisphere, and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere. Therefore, May in the Southern Hemisphere is the seasonal equivalent of November in the Northern Hemisphere and vice versa. Late May typically marks the start of the summer vacation season in the United States ( Memorial Day) and Canada ( Victoria Day) that ends on Labor Day, the first Monday of September. May (in Latin, ''Maius'') was named for the Greek goddess Maia, who was identified with the Roman era goddess of fertility, Bona Dea, whose festival was held in May. Conversely, the Roman poet Ovid provides a second etymology, in which he says that the month of May is named for the ''maiores,'' Latin for "elders," and that the following month (June) is named for the ''iuniores,'' or "young people" (''Fasti VI.88''). Eta Aquariids meteor sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
May 2041 Lunar Eclipse
A partial lunar eclipse will take place on May 16, 2041. Visibility Member This is the 25th member of Lunar Saros 141. The previous event was the May 2023 lunar eclipse A penumbral lunar eclipse will take place on Friday, May 5, 2023, the first of two lunar eclipses in 2023. The moon's apparent diameter will be only 0.1% smaller than average because it occurs 5.5 days before perigee (Perigee on May 11, 2023). .... Related lunar eclipses Lunar year series (354 days) Saros series Metonic series This eclipse is the fourth and final of four Metonic cycle lunar eclipses on the same date, May 15–16, each separated by 19 years. See also * List of lunar eclipses and List of 21st-century lunar eclipses Notes External links * 2041-05 2041-05 2041 in science {{lunar-eclipse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
April 1969 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday, April 2, 1969, the first of three penumbral lunar eclipses in 1969, the second being on Wednesday, August 27, and the last being on Thursday, September 25. Visibility It was completely visible over Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. Member This is the 21st member of Lunar Saros 141. The previous event was the March 1951 lunar eclipse. The next event is the April 1987 lunar eclipse. Related lunar eclipses Lunar year series Saros series Lunar Saros 141, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 72 lunar eclipse events including 26 total lunar eclipses. First Penumbral Lunar Eclipse: 1608 Aug 25 First Partial Lunar Eclipse: 2041 May 16 First Total Lunar Eclipse: 2167 Aug 01 First Central Lunar Eclipse: 2221 Sep 02 Greatest Eclipse of the Lunar Saros 141: 2293 Oct 16 Last Central Lunar Eclipse: 2546 Mar 18 Last Total Lunar Eclipse: 2618 May 01 Last Partial Lunar Eclipse: 2744 Jul 16 Last Penumbral Lun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March 1951 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Friday, March 23, 1951. This subtle penumbral eclipse may have been visible to a skilled observer at maximum eclipse. 64% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth (none of it was in total shadow), which caused a gentle shadow gradient across its disc at maximum; the eclipse as a whole lasted 3 hours and 34 minutes. Visibility Member This is the 20th member of Lunar Saros 141. The previous event was the March 1933 lunar eclipse. The next event is the April 1969 lunar eclipse. Related lunar eclipses Lunar year series Saros series Lunar Saros 141, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 72 lunar eclipse events including 26 total lunar eclipses. First Penumbral Lunar Eclipse: 1608 Aug 25 First Partial Lunar Eclipse: 2041 May 16 First Total Lunar Eclipse: 2167 Aug 01 First Central Lunar Eclipse: 2221 Sep 02 Greatest Eclipse of the Lunar Saros 141: 2293 Oct 16 Last Central Lunar Eclipse: 2546 Mar 18 Last T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)



