|
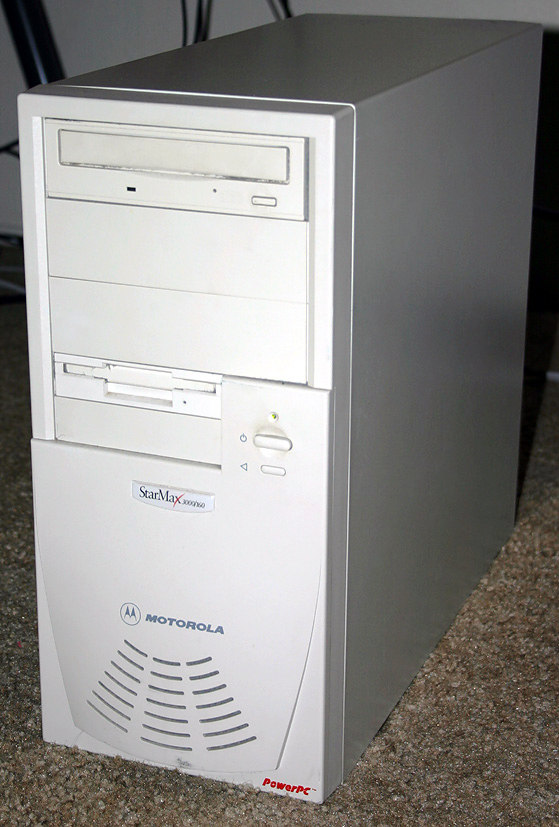
Apple Network Server
The Apple Network Server (ANS) was a line of PowerPC-based server computers designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer, Inc. from February 1996 to April 1997. It was codenamed "Shiner" and originally consisted of two models, the Network Server 500/132 ("Shiner LE", i.e., "low-end") and the Network Server 700/150 ("Shiner HE", i.e., "high-end"), which got a companion model, the Network Server 700/200 (also "Shiner HE") with a faster CPU in November 1996. The machines were not a part of the Apple Macintosh line of computers; they were designed to run IBM's AIX operating system and their ROM specifically prevented booting the classic Mac OS. This makes them the last non-Macintosh desktop computers made by Apple to date. The 500/132, 700/150, and 97 sold in the U.S. market for $11,000, $15,000 and $19,000, respectively. Apple Network Servers are not to be confused with the Apple Workgroup Servers and the Macintosh Servers, which were Macintosh workstations that shipped with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, United States. Apple is the largest technology company by revenue (totaling in 2021) and, as of June 2022, is the world's biggest company by market capitalization, the fourth-largest personal computer vendor by unit sales and second-largest mobile phone manufacturer. It is one of the Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet, Amazon, Meta, and Microsoft. Apple was founded as Apple Computer Company on April 1, 1976, by Steve Wozniak, Steve Jobs and Ronald Wayne to develop and sell Wozniak's Apple I personal computer. It was incorporated by Jobs and Wozniak as Apple Computer, Inc. in 1977 and the company's next computer, the Apple II, became a best seller and one of the first mass-produced microcomputers. Apple went public in 1980 to instant financial success. The company developed computers featuring innovative graphical user interfaces, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenDoc
OpenDoc is a defunct multi-platform software componentry framework standard created by Apple in the 1990s for compound documents, intended as an alternative to Microsoft's proprietary Object Linking and Embedding (OLE). It is one of Apple's earliest experiments with open standards and collaborative development methods with other companies. OpenDoc development was transferred to the non-profit Component Integration Laboratories, Inc. (CI Labs), owned by a growing team of major corporate backers and effectively starting an industry consortium. In 1992, the AIM alliance launched between Apple, IBM, and Motorolawith OpenDoc as a foundation. With the return of Steve Jobs to Apple, OpenDoc was discontinued in March 1997. Overview The core idea of OpenDoc is to create small, reusable components, responsible for a specific task, such as text editing, bitmap editing, or browsing an FTP server. OpenDoc is a framework in which these components can run together, and a compound document for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parity RAM
RAM parity checking is the storing of a redundant parity bit representing the parity (odd or even) of a small amount of computer data (typically one byte) stored in random-access memory, and the subsequent comparison of the stored and the computed parity to detect whether a data error has occurred. The parity bit was originally stored in additional individual memory chips; with the introduction of plug-in DIMM, SIMM, etc. modules, they became available in non-parity and parity (with an extra bit per byte, storing 9 bits for every 8 bits of actual data) versions. History Early computers sometimes required the use of parity RAM, and parity-checking could not be disabled. A parity error typically caused the machine to halt, with loss of unsaved data; this is usually a better option than saving corrupt data. ''Logic parity RAM'', also known as fake parity RAM, is non-parity RAM that can be used in computers that require parity RAM. Logic parity RAM recalculates an always-valid parity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIMM
A DIMM () (Dual In-line Memory Module), commonly called a RAM stick, comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory integrated circuits. These memory modules are mounted on a printed circuit board and designed for use in personal computers, workstations, printers, and servers. They are the predominant method for adding memory into a computer system. The vast majority of DIMMs are standardized through JEDEC standards, although there are proprietary DIMMs. DIMMs come in a variety of speeds and sizes, but generally are one of two lengths - PC which are and laptop (SO-DIMM) which are about half the size at . History DIMMs (Dual In-line Memory Module) were a 1990s upgrade for SIMMs (Single In-line Memory Modules) as Intel P5-based Pentium processors began to gain market share. The Pentium had a 64-bit bus width, which would require SIMMs installed in matched pairs in order to populate the data bus. The processor would then access the two SIMMs in parallel. DIMMs were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
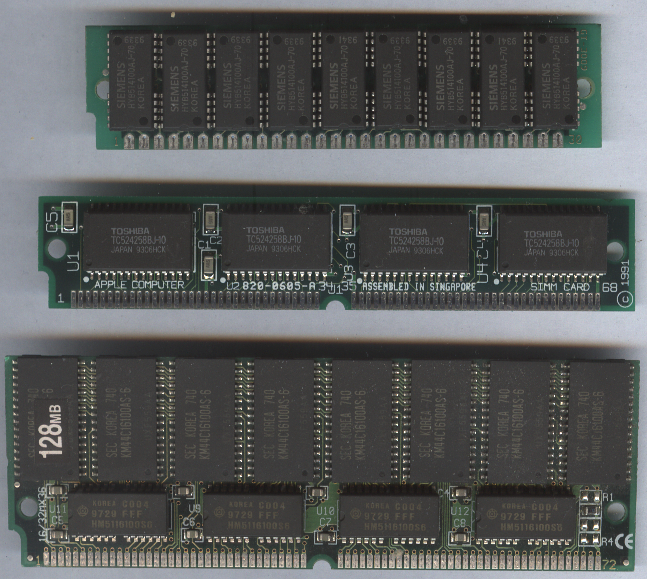
SIMM
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module containing random-access memory used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It differs from a dual in-line memory module (DIMM), the most predominant form of memory module since the late 1990s, in that the contacts on a SIMM are redundant on both sides of the module. SIMMs were standardised under the JEDEC JESD-21C standard. Most early PC motherboards (8088-based PCs, XTs, and early ATs) used socketed DIP chips for DRAM. As computer memory capacities grew, memory modules were used to save motherboard space and ease memory expansion. Instead of plugging in eight or nine single DIP chips, only one additional memory module was needed to increase the memory of the computer. History SIMMs were invented in 1982 by James J. Parker at Zenith Microcircuits and the first Zenith Microcircuits customer was Wang Laboratories. Wang Laboratories tried to patent it and were granted a patent in April 1987. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L2 Cache
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations. Most CPUs have a hierarchy of multiple cache levels (L1, L2, often L3, and rarely even L4), with different instruction-specific and data-specific caches at level 1. The cache memory is typically implemented with static random-access memory (SRAM), in modern CPUs by far the largest part of them by chip area, but SRAM is not always used for all levels (of I- or D-cache), or even any level, sometimes some latter or all levels are implemented with eDRAM. Other types of caches exist (that are not counted towards the "cache size" of the most important caches mentioned above), such as the translation lookaside buffer (TLB) which is part of the memory management unit (MMU) whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L1 Cache
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations. Most CPUs have a hierarchy of multiple cache levels (L1, L2, often L3, and rarely even L4), with different instruction-specific and data-specific caches at level 1. The cache memory is typically implemented with static random-access memory (SRAM), in modern CPUs by far the largest part of them by chip area, but SRAM is not always used for all levels (of I- or D-cache), or even any level, sometimes some latter or all levels are implemented with eDRAM. Other types of caches exist (that are not counted towards the "cache size" of the most important caches mentioned above), such as the translation lookaside buffer (TLB) which is part of the memory management unit (MMU) whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerPC 600
The PowerPC 600 family was the first family of PowerPC processors built. They were designed at the Somerset facility in Austin, Texas, jointly funded and staffed by engineers from IBM and Motorola as a part of the AIM alliance. Somerset was opened in 1992 and its goal was to make the first PowerPC processor and then keep designing general purpose PowerPC processors for personal computers. The first incarnation became the PowerPC 601 in 1993, and the second generation soon followed with the PowerPC 603, PowerPC 604 and the 64-bit PowerPC 620. Nuclear family PowerPC 601 The PowerPC 601 was the first generation of microprocessors to support the basic 32-bit PowerPC instruction set. The design effort started in earnest in mid-1991 and the first prototype chips were available in October 1992. The first 601 processors were introduced in an IBM RS/6000 workstation in October 1993 (alongside its more powerful multichip cousin IBM POWER2 line of processors) and the first Apple Power M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macintosh Clones
A Macintosh clone, also known as a Clonintosh (a portmanteau of " Clone" and "Macintosh"), is a computer running the Mac OS operating system that was not produced by Apple Inc. The earliest Mac clones were based on emulators and reverse-engineered Macintosh ROMs. During Apple's short lived Mac OS 7 licensing program, authorized Mac clone makers were able to either purchase 100% compatible motherboards or build their own hardware using licensed Mac reference designs. Since Apple's switch to the Intel platform, many non-Apple Wintel/ PC computers are technologically so similar to Mac computers that they are able to boot the Mac operating system using a varying combination of community-developed patches and hacks. Such a Wintel/PC computer running macOS is more commonly referred to as a Hackintosh. Background The Apple II and IBM PC computer lines were "cloned" by other manufacturers who had reverse-engineered the minimal amount of firmware in the computers' ROM chips and subsequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Firmware
Open Firmware is a standard defining the interfaces of a computer firmware system, formerly endorsed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). It originated at Sun Microsystems, where it was known as OpenBoot, and has been used by vendors including Sun, Apple, IBM and ARM. Open Firmware allows the system to load platform-independent drivers directly from a PCI device, improving compatibility. Open Firmware may be accessed through its command line interface, which uses the Forth programming language. Open Firmware is described by IEEE standard ''IEEE 1275-1994'', which was not reaffirmed by the Open Firmware Working Group (OFWG) since 1998 and has therefore been officially withdrawn by IEEE. Several commercial implementations of Open Firmware have been released to the Open Source community in 2006, including Sun OpenBoot, Firmworks OpenFirmware and Codegen SmartFirmware. The source code is available from the OpenBIOS project. Sun's implementation is av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RS/6000
The RISC System/6000 (RS/6000) is a family of Reduced instruction set computer, RISC-based Unix Server (computing), servers, workstations and supercomputers made by IBM in the 1990s. The RS/6000 family replaced the IBM RT PC computer platform in February 1990 and was the first computer line to see the use of IBM's IBM Power microprocessors, POWER and PowerPC based microprocessors. In October 2000, the RS/6000 brand was retired for POWER-based servers and replaced by the pSeries, eServer pSeries. Workstations continued under the RS/6000 brand until 2002, when new POWER-based workstations were released under the IntelliStation POWER brand. History The first RS/6000 models used the Micro Channel architecture, Micro Channel bus, later models used Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI. Some later models conformed to the PReP and Common Hardware Reference Platform, CHRP standard platforms, which were co-developed with Apple Inc., Apple and Motorola, with Open Firmware. The plan was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |