|
Apparent Oxygen Utilisation
In freshwater or marine systems apparent oxygen utilization (AOU) is the difference between oxygen gas solubility (i.e. the concentration at saturation) and the measured oxygen concentration in water with the same physical and chemical properties. AOU= _2 \ solubility _2 \ observed General influences Differences in O2 solubility and measured concentration (AOU) typically occur when biological activity, ocean circulation, or ocean mixing act to change the ambient concentration of oxygen. For example, primary production liberates oxygen and increases its concentration, while respiration consumes it and decreases its concentration. Consequently, the AOU of a water sample represents the sum of the biological activity that the sample has experienced since it was last in equilibrium with the atmosphere. In shallow water systems (e.g. lakes), the full water column is generally in close contact with the atmosphere, and oxygen concentrations are typically close to saturation, and AOU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WOA09 1000m AOU AYool
WOA may refer to: __NOTOC__ Computing * Web-oriented architecture, a computer systems architectural style * Windows on ARM (other), a series of operating systems for ARM architecture computers * WebObjects application, the file system suffix of an application written using the WebObjects framework from NeXT, later Apple Wars * War of Attrition, a conflict between Israel and Egypt * War of aggression Music * Wacken Open Air, the largest exclusively metal music festival in the world * War of Ages, metalcore band from Pennsylvania * W.O.A Records of India and Dubai Sports * World Olympians Association * Welsh Orienteering Association Other uses * World Ocean Atlas * World of Art, a series of books on art * the ICAO airline designator for World Airways World Airways, Inc. was a United States airline headquartered in Peachtree City, Georgia in Greater Atlanta. The company operated mostly non-scheduled services but did fly scheduled passenger services as well, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
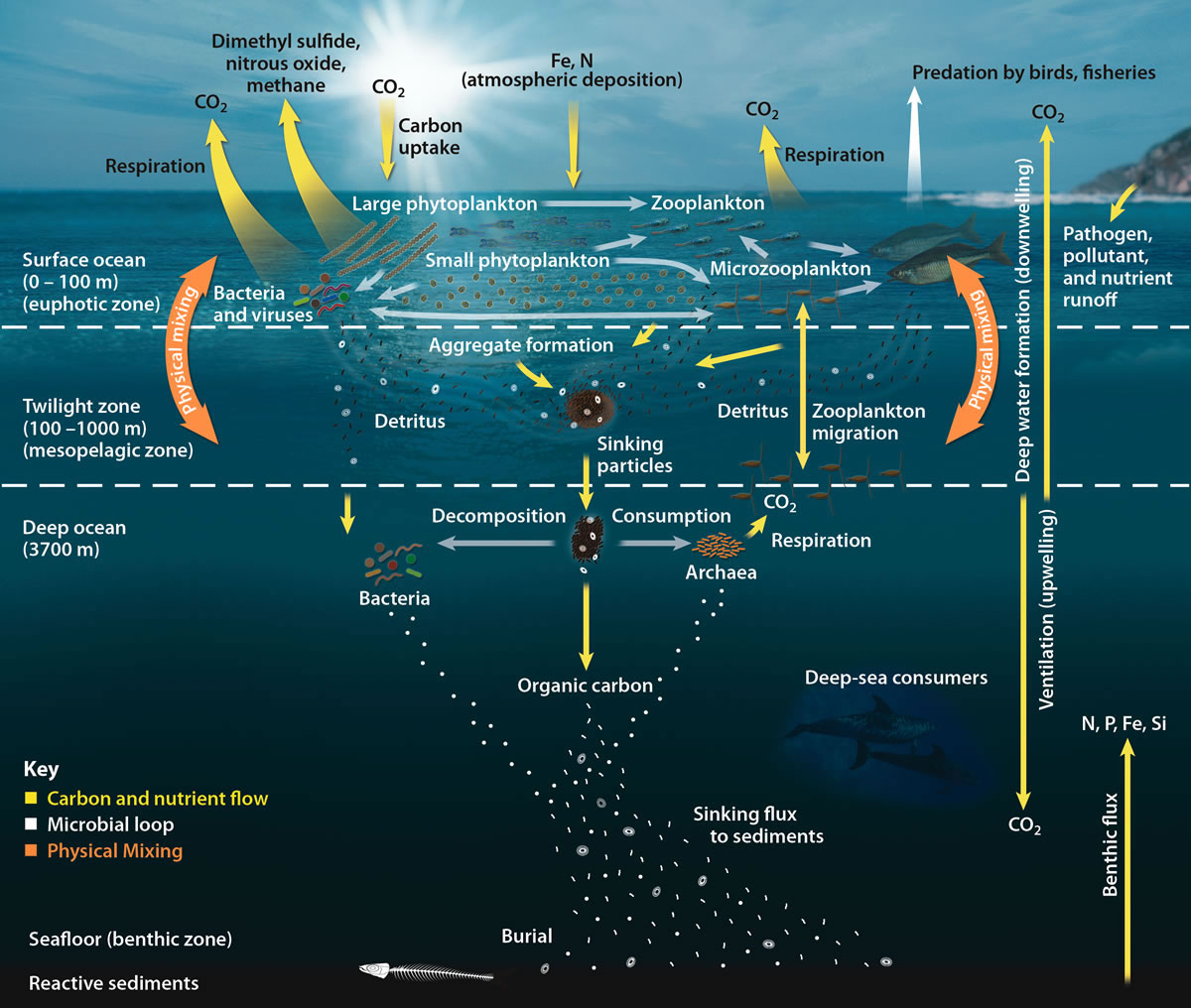
Biological Pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments.Sigman DM & GH Haug. 2006. The biological pump in the past. In: Treatise on Geochemistry; vol. 6, (ed.). Pergamon Press, pp. 491-528 In other words, it is a biologically mediated processes which result in the sequestering of carbon in the deep ocean away from the atmosphere and the land. The biological pump is the biological component of the "marine carbon pump" which contains both a physical and biological component. It is the part of the broader oceanic carbon cycle responsible for the cycling of organic matter formed mainly by phytoplankton during photosynthesis (soft-tissue pump), as well as the cycling of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) formed into shells by certain organisms such as plankton and mollusks (carbonate pump). Budget calculations of the biol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limnology
Limnology ( ; from Greek λίμνη, ''limne'', "lake" and λόγος, ''logos'', "knowledge") is the study of inland aquatic ecosystems. The study of limnology includes aspects of the biological, chemical, physical, and geological characteristics of fresh and saline, natural and man-made bodies of water. This includes the study of lakes, reservoirs, ponds, rivers, springs, streams, wetlands, and groundwater.Wetzel, R.G. 2001. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed. Academic Press () Water systems are often categorized as either running (lotic) or standing (lentic). Limnology includes the study of the drainage basin, movement of water through the basin and biogeochemical changes that occur en route. A more recent sub-discipline of limnology, termed landscape limnology, studies, manages, and seeks to conserve these ecosystems using a landscape perspective, by explicitly examining connections between an aquatic ecosystem and its drainage basin. Recently, the need to underst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geochemistry
Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the entire Solar System, and has made important contributions to the understanding of a number of processes including mantle convection, the formation of planets and the origins of granite and basalt. It is an integrated field of chemistry and geology. History The term ''geochemistry'' was first used by the Swiss-German chemist Christian Friedrich Schönbein in 1838: "a comparative geochemistry ought to be launched, before geognosy can become geology, and before the mystery of the genesis of our planets and their inorganic matter may be revealed." However, for the rest of the century the more common term was "chemical geology", and there was little contact between geologists and chemists. Geochemistry emerged as a separate discipline after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Oceanography
Biological oceanography is the study of how organisms affect and are affected by the physics, chemistry, and geology of the oceanographic system. Biological oceanography may also be referred to as ocean ecology, in which the root word of ecology is ''Oikos'' (oικoσ), meaning ‘house’ or ‘habitat’ in Greek. With that in mind, it is of no surprise then that the main focus of biological oceanography is on the microorganisms within the ocean; looking at how they are affected by their environment and how that affects larger marine creatures and their ecosystem.Lalli, Carol M., and Timothy R. Parsons. "Introduction." Biological Oceanography: An Introduction. First Edition ed. Tarrytown, New York: Pergamon, 1993. 7-21. Print. Biological oceanography is similar to marine biology, but is different because of the perspective used to study the ocean. Biological oceanography takes a bottom-up approach (in terms of the food web), while marine biology studies the ocean from a top-down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
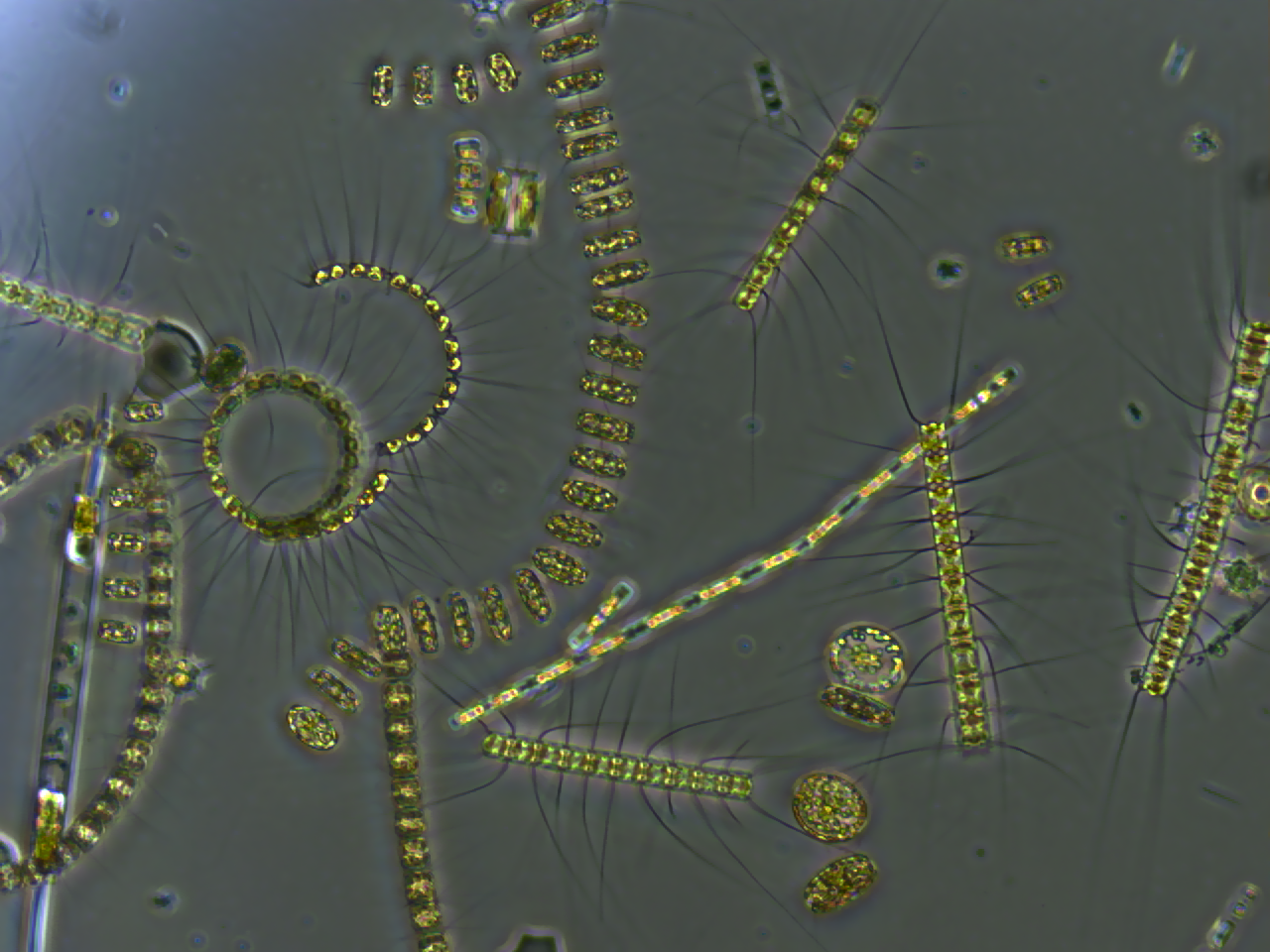
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermohaline Circulation
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The adjective ''thermohaline'' derives from '' thermo-'' referring to temperature and ' referring to salt content, factors which together determine the density of sea water. Wind-driven surface currents (such as the Gulf Stream) travel polewards from the equatorial Atlantic Ocean, cooling en route, and eventually sinking at high latitudes (forming North Atlantic Deep Water). This dense water then flows into the ocean basins. While the bulk of it upwells in the Southern Ocean, the oldest waters (with a transit time of about 1000 years) upwell in the North Pacific. Extensive mixing therefore takes place between the ocean basins, reducing differences between them and making the Earth's oceans a global system. The water in these circuits transport both energy (in the form of heat) and mass (dissolved solids and ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Ocean Water
Deep ocean water (DOW) is the name for cold, salty water found deep below the surface of Earth's oceans. Ocean water differs in temperature and salinity. Warm surface water is generally saltier than the cooler deep or polar waters; in polar regions, the upper layers of ocean water are cold and fresh. Deep ocean water makes up about 90% of the volume of the oceans. Deep ocean water has a very uniform temperature, around 0-3°C, and a salinity of about 3.5% or, as oceanographers state, 35 ppt (parts per thousand). In specialized locations such as the Natural Energy Laboratory of Hawaii (NELHA) ocean water is pumped to the surface from approximately 900 metres (2,952 feet) deep for applications in research, commercial and pre-commercial activities. DOW is typically used to describe ocean water at sub-thermal depths sufficient to provide a measurable difference in water temperature. When deep ocean water is brought to the surface, it can be used for a variety of things. Its most us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Ocean Atlas
The World Ocean Atlas (WOA) is a data product of the Ocean Climate Laboratory of the National Oceanographic Data Center (U.S.). The WOA consists of a climatology of fields of ''in situ'' ocean properties for the World Ocean. It was first produced in 1994 (based on the earlier ''Climatological Atlas of the World Ocean''), with later editions at roughly four year intervals in 1998, 2001, 2005, 2009, and 2013. Dataset The fields that make up the WOA dataset consist of objectively-analysed global grids at 1 ° spatial resolution. The fields are three-dimensional, and data are typically interpolated onto 33 standardised vertical intervalsStandardised intervals are at 0, 10, 20, 30, 50, 75, 100, 125, 150, 200, 250, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000, 1100, 1200, 1300, 1400, 1500, 1750, 2000, 2500, 3000, 3500, 4000, 4500, 5000, 5500 m from the surface (0 m) to the abyssal seafloor (5500 m). In terms of temporal resolution, averaged fields are produced for annual, seasonal and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remineralisation
In biogeochemistry, remineralisation (or remineralization) refers to the breakdown or transformation of organic matter (those molecules derived from a biological source) into its simplest inorganic forms. These transformations form a crucial link within ecosystems as they are responsible for liberating the energy stored in organic molecules and recycling matter within the system to be reused as nutrients by other organisms. Remineralisation is normally viewed as it relates to the cycling of the major biologically important elements such as carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. While crucial to all ecosystems, the process receives special consideration in aquatic settings, where it forms a significant link in the biogeochemical dynamics and cycling of aquatic ecosystems. Role in biogeochemistry The term "remineralization" is used in several contexts across different disciplines. The term is most commonly used in the medicinal and physiological fields, where it describes the develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxia (environmental)
Hypoxia refers to low oxygen conditions. Normally, 20.9% of the gas in the atmosphere is oxygen. The partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere is 20.9% of the total barometric pressure. In water, oxygen levels are much lower, approximately 7 ppm or 0.0007% in good quality water, and fluctuate locally depending on the presence of photosynthetic organisms and relative distance to the surface (if there is more oxygen in the air, it will diffuse across the partial pressure gradient). Atmospheric hypoxia Atmospheric hypoxia occurs naturally at high altitudes. Total atmospheric pressure decreases as altitude increases, causing a lower partial pressure of oxygen, which is defined as hypobaric hypoxia. Oxygen remains at 20.9% of the total gas mixture, differing from hypoxic hypoxia, where the percentage of oxygen in the air (or blood) is decreased. This is common in the sealed burrows of some subterranean animals, such as blesmols. Atmospheric hypoxia is also the basis of altitude tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stream Metabolism
Stream metabolism, often referred to as aquatic ecosystem metabolism in both freshwater (lakes, rivers, wetlands, streams, reservoirs) and marine ecosystems, includes gross primary productivity (GPP) and ecosystem respiration (ER) and can be expressed as net ecosystem production (NEP = GPP - ER). Analogous to metabolism within an individual organism, stream metabolism represents how energy is created (primary production) and used (respiration) within an aquatic ecosystem. In heterotrophic ecosystems, GPP:ER is 1 (ecosystem creating more energy than it is usingMost streams are heterotrophiA heterotrophic ecosystem often means that allochthonous (coming from outside the ecosystem) inputs of organic matter, such as leaves or debris fuel ecosystem respiration rates, resulting in respiration greater than production within the ecosystem. However, autochthonous (coming from within the ecosystem) pathways also remain important to metabolism in heterotrophic ecosystems. In an autotrophic ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |