|
Aortic Sac
The aortic sac or aortic bulb is a dilated structure in mammalian embryos, lined by endothelial cells and is the most distal part of the truncus arteriosus. It is the primordial vascular channel from which the aortic arches arise (and eventually the dorsal aortae) and is homologous to the ventral aorta of gill-bearing vertebrates. The aortic sac eventually forms right and left horns, which subsequently give rise to the brachiocephalic trunk and the proximal segment of the arch of aorta, respectively. Genes ''HAND2'' (''dHAND'') and ''HAND1'' (''eHAND'') are expressed during the development of the aortic bulb and the arteries which arise from it.Richard P. Harvey, Nadia Rosenthal (ed)Heart Development Gulf Professional Publishing, 1999; page 150-151. The protein encoded by these genes belong to the basic helix-loop-helix family of transcription factor In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Crest
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia. After gastrulation, neural crest cells are specified at the border of the neural plate and the non-neural ectoderm. During neurulation, the borders of the neural plate, also known as the neural folds, converge at the dorsal midline to form the neural tube. Subsequently, neural crest cells from the roof plate of the neural tube undergo an epithelial to mesenchymal transition, delaminating from the neuroepithelium and migrating through the periphery where they differentiate into varied cell types. The emergence of neural crest was important in vertebrate evolution because many of its structural derivatives are defining features of the vertebrate clade. Underlying the development of neural crest is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
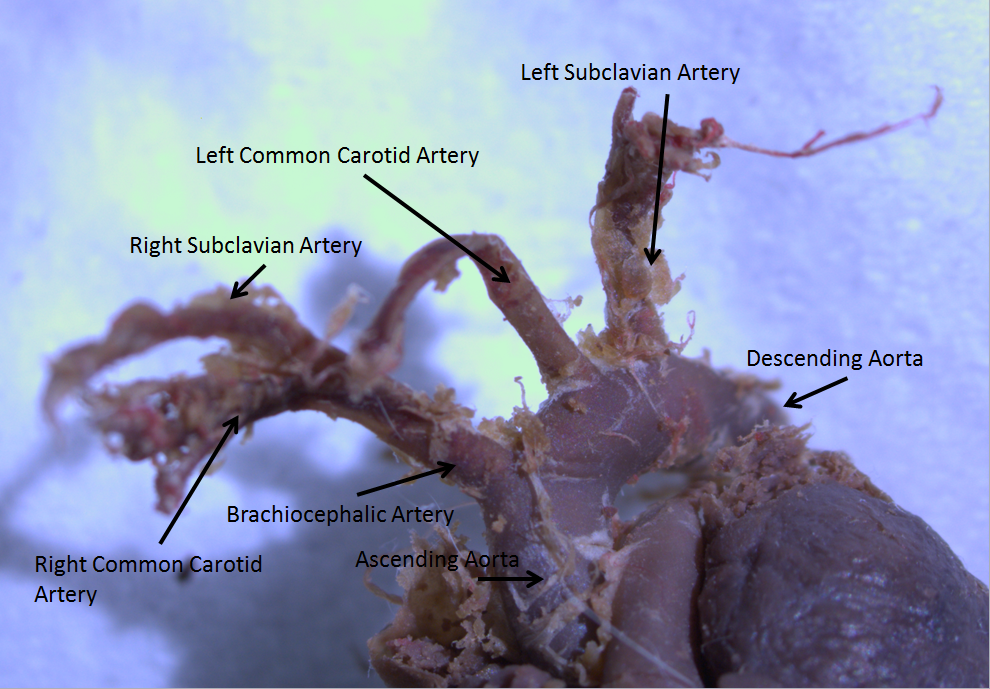
Brachiocephalic Trunk
The brachiocephalic artery (or brachiocephalic trunk or innominate artery) is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm and the head and neck. It is the first branch of the aortic arch. Soon after it emerges, the brachiocephalic artery divides into the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery. There is no brachiocephalic artery for the left side of the body. The left common carotid, and the left subclavian artery, come directly off the aortic arch. However, there are two brachiocephalic veins. Structure The brachiocephalic artery arises, on a level with the upper border of the second right costal cartilage, from the start of the aortic arch, on a plane anterior to the origin of the left carotid artery. It ascends obliquely upward, backward, and to the right to the level of the upper border of the right sternoclavicular articulation, where it divides into the right common carotid artery and right subclavian arteries. The artery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Helix-loop-helix
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College in 1963. They wanted to enable students in non-scientific fields to use computers. At the time, nearly all computers required writing custom software, which only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn. In addition to the program language, Kemeny and Kurtz developed the Dartmouth Time Sharing System (DTSS), which allowed multiple users to edit and run BASIC programs simultaneously on remote terminals. This general model became very popular on minicomputer systems like the PDP-11 and Data General Nova in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Hewlett-Packard produced an entire computer line for this method of operation, introducing the HP2000 series in the late 1960s and continuing sales into the 1980s. Many early video games trace their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HAND1
Heart- and neural crest derivatives-expressed protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HAND1'' gene. A member of the HAND subclass of basic Helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors, the Heart and neural crest-derived transcript-1 (''HAND1)'' gene is vital for the development and differentiation of three distinct embryological lineages including the cardiac muscle cells of the heart, trophoblast of the placenta, and yolk sac vasculogenesis. Most highly related to twist-like bHLH genes in amino acid identity and embryonic expression, HAND1 can form homo- and heterodimer combinations with multiple bHLH partners, mediating transcriptional activity in the nucleus. Function The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the basic helix-loop-helix family of transcription factors. This gene product is one of two closely related family members, the HAND proteins are expressed within the developing ventricular chambers, cardiac neural crest, endocardium (HAND2 onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HAND2
Heart- and neural crest derivatives-expressed protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HAND2'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the basic helix-loop-helix family of transcription factors. This gene product is one of two closely related family members, the HAND proteins Hand1 and Hand2, which are asymmetrically expressed in the developing ventricular chambers and play an essential role in cardiac morphogenesis. Working in a complementary fashion, they function in the formation of the right ventricle and aortic arch arteries, implicating them as mediators of congenital heart disease. In addition, this transcription factor plays an important role in limb and branchial arch development. In one study, it was found that a missense mutation of the Hand2 protein in patients with the congenital heart disease (CHD) Tetralogy of Fallot experienced significantly decreased Hand2 interactions with other key developmental genes such as GATA4 and NKX ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea. Structure The aorta begins at the level of the upper border of the second/third sternocostal articulation of the right side, behind the ventricular outflow tract and pulmonary trunk. The right atrial appendage overlaps it. The first few centimeters of the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk lies in the same pericardial sheath. and runs at first upward, arches over the pulmonary trunk, right pulmonary artery, and right main bronchus to lie behind the right second coastal cartilage. The right lung and sternum lies anterior to the aorta at this point. The aorta then passes posteriorly and to the left, anterior to the trachea, and arches over left main bronchus and left pulmonary artery, and reaches to the left side of the T4 vertebral body. Apart from T4 vertebral body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Aorta
The dorsal aortae are paired (left and right) embryological vessels which progress to form the descending aorta. The paired dorsal aortae arise from aortic arches that in turn arise from the aortic sac. The primary dorsal aorta is located deep to the lateral plate of mesoderm and move from lateral to medial position with development and eventually will fuse with the other dorsal aorta to form the descending aorta. Each primitive aorta anteriorly receives the vitelline vein from the yolk-sac, and is prolonged backward on the lateral aspect of the notochord under the name of the dorsal aorta. The dorsal aortae give branches to the yolk-sac, and are continued backward through the body-stalk as the umbilical arteries to the villi of the chorion The chorion is the outermost fetal membrane around the embryo in mammals, birds and reptiles (amniotes). It develops from an outer fold on the surface of the yolk sac, which lies outside the zona pellucida (in mammals), known as the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kit Kovacs
Kit Kovacs is a marine mammal researcher, best known for her work on biology, conservation and management of whales and seals. She is based at the Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI), Tromsø and is an Adjunct professor of biology, Marine Biology, at the University Centre in Svalbard (UNIS). Early life and education Kovacs was born in Germany and has Canadian citizenship. She received her H.B.Sc. (Biology) in 1979 from York University, Toronto, Canada. In 1982, she was awarded a Master of Science degree in Biology by the Lakehead University at Thunder Bay. Her doctorate (Ph.D) in Zoology was awarded by the University of Guelph (Guelph) in 1986. Research career Kovacs' teaching career, spanning over 12 years, started as an assistant professor at the University of Waterloo. She is now the senior research scientist for the Biodiversity Research Programme at the Centre for Ice Climate and Ecosystems (ICE) at the Norwegian Polar Institute, as well as a professor of biology at University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Arches
The aortic arches or pharyngeal arch arteries (previously referred to as branchial arches in human embryos) are a series of six paired embryological vascular structures which give rise to the great arteries of the neck and head. They are ventral to the dorsal aorta and arise from the aortic sac. The aortic arches are formed sequentially within the pharyngeal arches and initially appear symmetrical on both sides of the embryo, but then undergo a significant remodelling to form the final asymmetrical structure of the great arteries. Structure Arches 1 and 2 The ''first'' and ''second arches'' disappear early. A remnant of the 1st arch forms part of the maxillary artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. The ventral end of the second develops into the ascending pharyngeal artery, and its dorsal end gives origin to the stapedial artery, a vessel which typically atrophies in humans but persists in some mammals. The stapedial artery passes through the ring of the stapes and di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truncus Arteriosus
The truncus arteriosus is a structure that is present during embryonic development. It is an arterial trunk that originates from both ventricles of the heart that later divides into the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. Structure The truncus arteriosus and bulbus cordis are divided by the aorticopulmonary septum. The truncus arteriosus gives rise to the ascending aorta and the pulmonary trunk. The caudal end of the bulbus cordis gives rise to the smooth parts (outflow tract) of the left and right ventricles (aortic vestibule & conus arteriosus respectively). The cranial end of the bulbus cordis (also known as the conus cordis) gives rise to the aorta and pulmonary trunk with the truncus arteriosus. This makes its appearance in three portions. # Two distal ridge-like thickenings project into the lumen of the tube: the truncal and bulbar ridges. These increase in size, and ultimately meet and fuse to form a septum ( aorticopulmonary septum), which takes a spiral course toward the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)