|
Anzû (mythology)
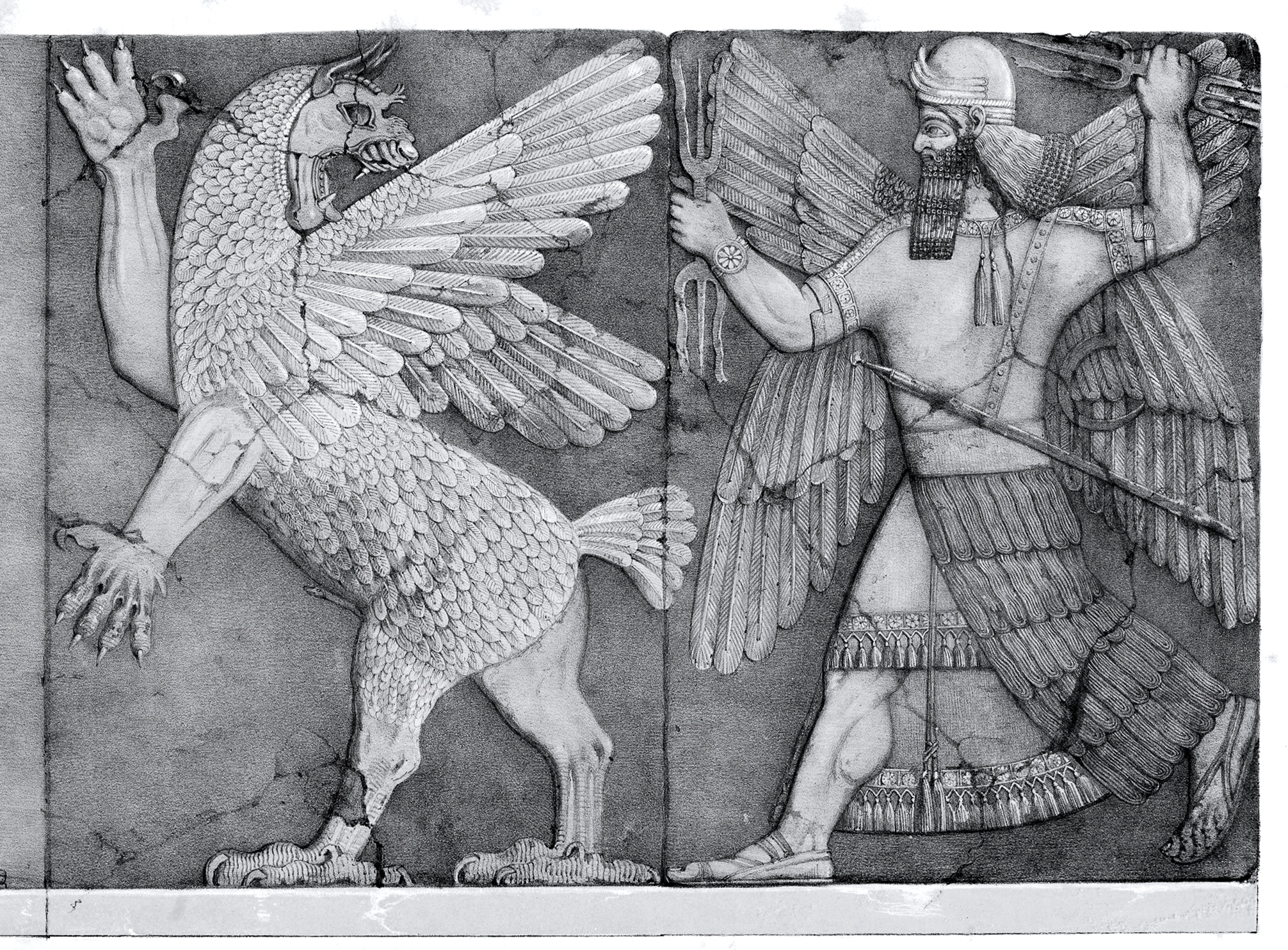
Anzû, also known as dZû and Imdugud ( Sumerian: ''AN.IM.DUGUD MUŠEN''), is a lesser divinity or monster in several Mesopotamian religions. He was conceived by the pure waters of the Apsu and the wide Earth, or as son of Siris. Anzû was depicted as a massive bird who can breathe fire and water, although Anzû is alternately depicted as a lion-headed eagle. Stephanie Dalley, in ''Myths from Mesopotamia'', writes that "the ''Epic of Anzu'' is principally known in two versions: an Old Babylonian version of the early second millennium C giving the hero as Ningirsu; and 'The Standard Babylonian' version, dating to the first millennium BC, which appears to be the most quoted version, with the hero as Ninurta". However, the Anzu character does not appear as often in some other writings, as noted below. Name The name of the mythological being usually called Anzû was actually written in the oldest Sumerian cuneiform texts as (''AN.IM.MIMUŠEN''; the cuneiform sign , or ''MUŠEN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaos Monster And Sun God
Chaos or CHAOS may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media Fictional elements * Chaos (''Kinnikuman'') * Chaos (''Sailor Moon'') * Chaos (''Sesame Park'') * Chaos (''Warhammer'') * Chaos, in ''Fabula Nova Crystallis Final Fantasy'' * Chaos, in ''Loom'' (video game) * Chaos, a character in the ''Sonic the Hedgehog'' series * Chaos, in ''The Power of Five'' * chaos, in ''Xenosaga'' * Chaos, in ''King of Cards'' * Chaos, in ''Nanatsu no Taizai'' Film and television * ''Chaos'' (2000 film), a Japanese mystery-thriller * ''Chaos'' (2001 film), a French comedy-drama * ''Chaos'' (2005 action film), an action thriller * ''Chaos'' (2005 horror film), an American horror film * ''Chaos'', a 2006 Polish film directed by Xawery Zulawski * ''Chaos'' (2008 film), a Hong Kong action thriller * ''Kaos'' (film) (''Chaos'' in the U.S.), a 1984 Italian film * ''Le Chaos'', a 2007 Arabic language film * ''CHAOS'' (TV series), 2011 * "Chaos", a 1986 episode of '' The Transformers'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Asmar Hoard
The Tell Asmar Hoard ( Early Dynastic I-II, ca. 2900–2550 BC) are a collection of twelve statues unearthed in 1933 at Eshnunna (modern Tell Asmar) in the Diyala Governorate of Iraq. Despite subsequent finds at this site and others throughout the greater Mesopotamian area, they remain the definitive example of the abstract style of Early Dynastic temple sculpture (2900 BC–2350 BC). Discovery In the late 1920s antique dealers in Baghdad were acquiring large quantities of unusual, high quality artifacts from the desert east of the Diyala River, just north of its confluence with the Tigris.Karen L. Wilson, ''Excavations in the Diyala Region'', i''Art Of The First Cities: The Third Millennium B.C. from the Mediterranean to the Indus'' ed. Joan Aruz (New York and London: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Yale University Press, 2003), 58. In 1929 the Oriental Institute at the University of Chicago obtained a concession to excavate the area. James Henry Breasted (1865–1935), the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asakku
In the Sumerian mythological poem ''Lugal-e'', Asag or Azag ( Sumerian: ), is a monstrous demon, so hideous that his presence alone makes fish boil alive in the rivers. He was said to be accompanied into battle by an army of rock demon offspring—born of his union with the mountains themselves. He was vanquished by the heroic Akkadian deity Ninurta, using Sharur, his enchanted talking mace, after seeking the counsel of his father, the god Enlil Enlil, , "Lord f theWind" later known as Elil, is an ancient Mesopotamian god associated with wind, air, earth, and storms. He is first attested as the chief deity of the Sumerian pantheon, but he was later worshipped by the Akkadians, Bab .... References External links Ninurta defeats the Asag—ETCSL tablet translation Mesopotamian demons {{MEast-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
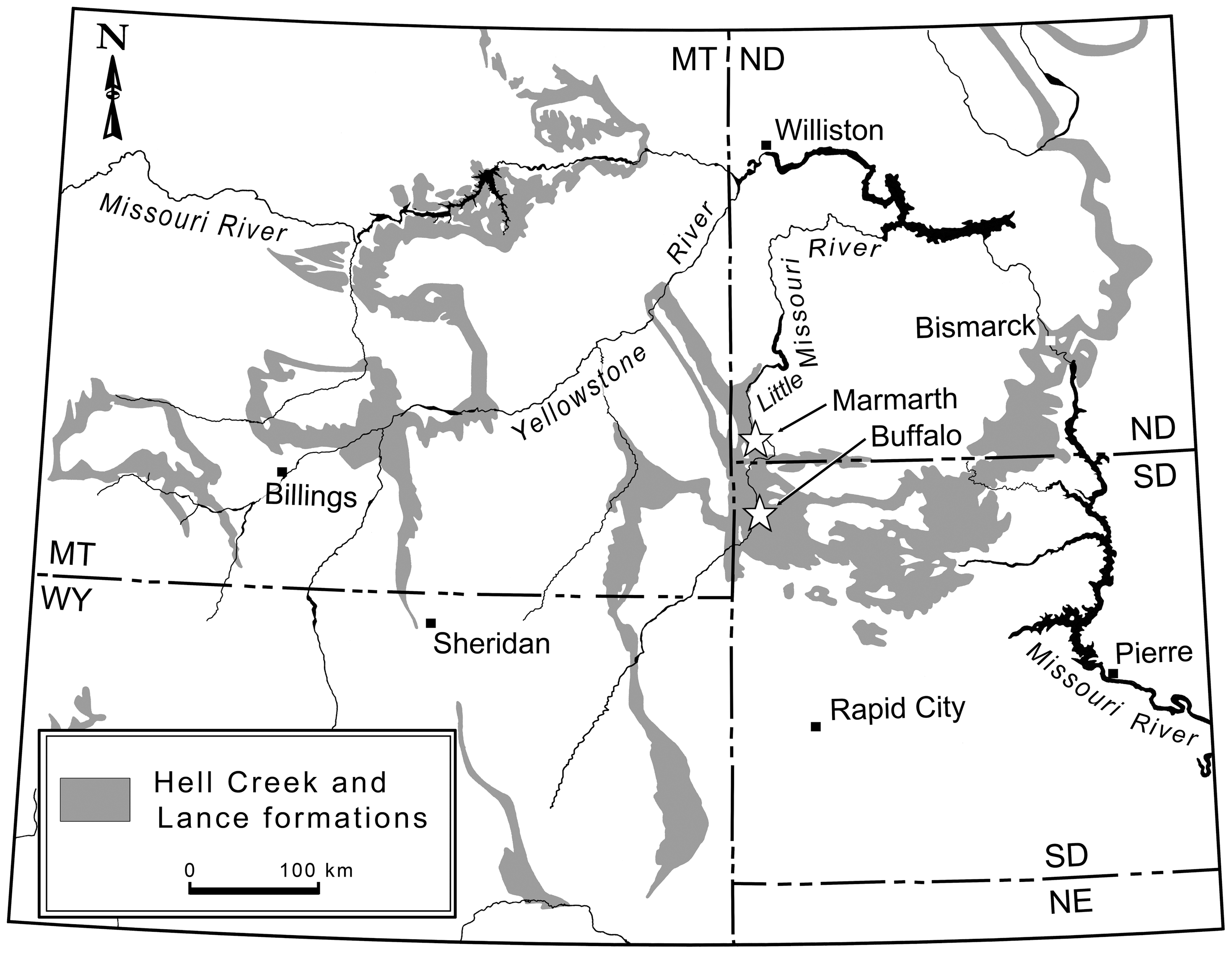
Anzu Wyliei
''Anzu'' (named for Anzû, a bird-like daemon in Ancient Mesopotamian religion) is a monospecific genus of caenagnathid dinosaur from North Dakota, South Dakota and Montana that lived during the Late Cretaceous (upper Maastrichtian stage, 67.2-66.0 Ma) in what is now the Hell Creek Formation. The type species and only species, ''Anzu wyliei'' is known from numerous skeletons that preserve cranial and postcranial elements. It was named in 2014 by Matthew C. Lamanna, Hans-Dieter Sues, Emma R. Schachner, and Tyler R. Lyson. It was named one of the "Top 10 New Species" for new species discovered in 2014 by the International Institute for Species Exploration in 2015. History of discovery Several large skeletons from the late Maastrichtian Hell Creek Formation of Montana and South Dakota were initially referred to as "cf. ''Chirostenotes''",Varricchio, D. J. (2001). Late Cretaceous Oviraptorosaur (Theropoda) dinosaurs from Montana. ''Mesozoic Vertebrate Life.'' D. H. Tanke and K. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claus Wilcke
Claus Wilcke (born 12 August 1939, in Bremen) is a German actor who has played Americans in the German TV shows ''Percy Stuart'' and ''I.O.B. Spezialauftrag''. He has also dubbed many American actors including Elvis Presley and Michael Landon for cinema and TV. He has won several German awards. Career Wilcke started as a stage actor. He passed a complete classic training and graduated. He was trained for stunts in London and played many sports such as fencing and riding. In 1958, he appeared for the first time on the big screen. After 20 feature films and three guest appearances in '' Jason King'', he was cast for ''Percy Stuart''. Nearly all of his stunts were done by himself because the insurance companies back then didn't hinder him. Later Wilcke played roles in numerous other German TV shows and on very many theatre stages all over Germany. He is also a very sought-after voice-over actor. In 2012, he had a cameo appearance in ''Iron Sky'' where he is the white-bearded polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugalbanda And The Anzud Bird
''Lugalbanda and the Anzu Bird'' is a Sumerian mythological account. The story is sometimes called ''The Return of Lugalbanda'' or ''Lugalbanda II'' being the second of two stories about the hero Lugalbanda. The first story is known as ''Lugalbanda in the Mountain Cave'', or sometimes ''Lugalbanda in the Wilderness''. They are part of a four-story cycle that describes the conflicts between Enmerkar, king of Unug (Uruk), and the king of Aratta. The texts are believed to be composed during the Ur III Period (21st century BCE), but almost all of the extant copies come from Isin-Larsa period (20th-18th centuries BCE). Nevertheless, a few fragmentary bilingual copies (Sumerian and Akkadian) from Nineveh suggest that the texts were still known during the first millennium.''ibid.'' p.135 Synopsis This story starts with Lugalbanda alone in the highlands of Lullubi. He finds the chick of the giant Anzû (or Anzud) bird, which is described as a lion-headed eagle, and decides to feed the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilgamesh, Enkidu, And The Netherworld
The ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' () is an epic poem from ancient Mesopotamia, and is regarded as the earliest surviving notable literature and the second oldest religious text, after the Pyramid Texts. The literary history of Gilgamesh begins with five Sumerian poems about Bilgamesh (Sumerian for "Gilgamesh"), king of Uruk, dating from the Third Dynasty of Ur (). These independent stories were later used as source material for a combined epic in Akkadian. The first surviving version of this combined epic, known as the "Old Babylonian" version, dates back to the 18th century BC and is titled after its incipit, ''Shūtur eli sharrī'' ("Surpassing All Other Kings"). Only a few tablets of it have survived. The later Standard Babylonian version compiled by Sîn-lēqi-unninni dates from the 13th to the 10th centuries BC and bears the incipit ''Sha naqba īmuru'' ("He who Saw the Abyss", in unmetaphoric terms: "He who Sees the Unknown"). Approximately two-thirds of this longer, twelve-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inanna
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, Divine law, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Sumer under the name "Inanna", and later by the Akkadian Empire, Akkadians, Babylonian religion, Babylonians, and Assyrians under the name Ishtar, (occasionally represented by the logogram ). She was known as the "Queen of heaven (antiquity), Queen of Heaven" and was the patron goddess of the Eanna temple at the city of Uruk, which was her main Cult (religious practice), cult center. She was associated with the planet Venus and her most prominent symbols included the Lion of Babylon, lion and the Star of Ishtar, eight-pointed star. Her husband was the god Dumuzid (later known as Tammuz) and her , or personal attendant, was the goddess Ninshubur (who later became conflated with the male deities Ilabrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marduk
Marduk (Cuneiform: dAMAR.UTU; Sumerian: ''amar utu.k'' "calf of the sun; solar calf"; ) was a god from ancient Mesopotamia and patron deity of the city of Babylon. When Babylon became the political center of the Euphrates valley in the time of Hammurabi (18th century BC), Marduk slowly started to rise to the position of the head of the Babylonian pantheon, a position he fully acquired by the second half of the second millennium BCE. In the city of Babylon, Marduk was worshipped in the temple Esagila. Marduk is associated with the divine weapon Imhullu. His symbolic animal and servant, whom Marduk once vanquished, is the dragon Mušḫuššu. "Marduk" is the Babylonian form of his name. The name ''Marduk'' was probably pronounced ''Marutuk''. The etymology of the name ''Marduk'' is conjectured as derived from ''amar-Utu'' ("immortal son of Utu" or "bull calf of the sun god Utu"). The origin of Marduk's name may reflect an earlier genealogy, or have had cultural ties to the anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tablet Of Destinies (mythic Item)
In Mesopotamian mythology, the Tablet of Destinies ( sux, ; akk, ṭup šīmātu, ṭuppi šīmāti, script=Latn, italic=yes) was envisaged as a clay tablet inscribed with cuneiform writing, also impressed with cylinder seals, which, as a permanent legal document, conferred upon the god Enlil his supreme authority as ruler of the universe. Other mention In the Sumerian poem '' Ninurta and the Turtle'' it is the god Enki, rather than Enlil, who holds the Tablet, as Enki has stolen it and brought it to the ''Abzu''. Both this poem and the Akkadian Anzû poem also share concern of the theft of the tablet by the bird Imdugud (Sumerian) or Anzû (Akkadian).. In the Babylonian '' Enuma Elish'', Tiamat bestows this tablet on Kingu and gives him command of her army. In the end, the Tablet always returns to Enlil. See also *List of Mythological Objects Mythological objects encompass a variety of items (e.g. weapons, armor, clothing) found in mythology, legend, folklore, tall tal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkadian Literature
Akkadian literature is the ancient literature written in the Akkadian language (Assyrian and Babylonian dialects) in Mesopotamia (Assyria and Babylonia) during the period spanning the Middle Bronze Age to the Iron Age (roughly the 23rd to 6th centuries BC). Drawing on the traditions of Sumerian literature, the Babylonians compiled a substantial textual tradition of mythological narrative, legal texts, scientific works, letters and other literary forms. Literature in Akkadian society Most of what we have from the Babylonians was inscribed in cuneiform with a metal stylus on tablets of clay, called ''laterculae coctiles'' by Pliny the Elder; papyrus seems to have been also employed, but it has perished. There were libraries in most towns and temples; an old Sumerian proverb averred that "he who would excel in the school of the scribes must rise with the dawn." Women as well as men learned to read and write, and in Semitic times, this involved a knowledge of the extinct Sumer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



