|
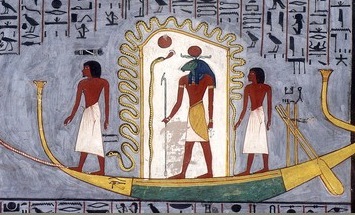
Anubis
Anubis (; grc, Ἄνουβις), also known as Inpu, Inpw, Jnpw, or Anpu in Ancient Egyptian (), is the god of funerary rites, protector of graves, and guide to the underworld, in ancient Egyptian religion, usually depicted as a canine or a man with a canine head. Like many ancient Egyptian deities, Anubis assumed different roles in various contexts. Depicted as a protector of graves as early as the First Dynasty (), Anubis was also an embalmer. By the Middle Kingdom (c. 2055–1650 BC) he was replaced by Osiris in his role as lord of the underworld. One of his prominent roles was as a god who ushered souls into the afterlife. He attended the weighing scale during the "Weighing of the Heart", in which it was determined whether a soul would be allowed to enter the realm of the dead. Anubis is one of the most frequently depicted and mentioned gods in the Egyptian pantheon; however, no relevant myth involved him. Anubis was depicted in black, a color that symbolized reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Pantheon
Ancient Egyptian deities are the God (male deity), gods and goddesses worshipped in ancient Egypt. The beliefs and rituals surrounding these gods formed the core of ancient Egyptian religion, which emerged sometime in prehistoric Egypt, prehistory. Deities represented natural phenomenon, natural forces and phenomena, and the Egyptians supported and appeased them through sacrifice, offerings and rituals so that these forces would continue to function according to ''maat'', or divine order. After the founding of the Egyptian state around 3100 BC, the authority to perform these tasks was controlled by the pharaoh, who claimed to be the gods' representative and managed the Egyptian temple, temples where the rituals were carried out. The gods' complex characteristics were expressed in Egyptian mythology, myths and in intricate relationships between deities: family ties, loose groups and hierarchies, and combinations of separate gods into one. Deities' diverse appearances in art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duat
The Duat ( egy, dwꜣt, Egyptological pronunciation "do-aht", cop, ⲧⲏ, also appearing as ''Tuat'', ''Tuaut'' or ''Akert'', ''Amenthes'', ''Amenti'', or ''Neter-khertet'') is the realm of the dead in ancient Egyptian mythology. It has been represented in hieroglyphs as a star-in-circle: 𓇽. The god Osiris was believed to be the lord of the underworld. He was the first mummy as depicted in the Osiris myth and he personified rebirth and life after death. The underworld was also the residence of various other gods along with Osiris. The geography of the ''Duat'' is similar in outline to the world the Egyptians knew: There are realistic features like rivers, islands, fields, lakes, mounds and caverns, but there were also fantastic lakes of fire, walls of iron, and trees of turquoise. In the ''Book of Two Ways'' (a Coffin Text) there is even a map-like image of the ''Duat''. Resident souls, gods, and demons The ''Duat'' was also a residence for various gods, including Osiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the List of rivers by length, longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Erit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Egyptian Gods
Ancient Egyptian deities were an integral part of ancient Egyptian religion and were worshipped for millennia. Many of them ruled over natural and social phenomena, as well as abstract concepts. These gods and goddesses appear in virtually every aspect of ancient Egyptian civilization, and more than 1,500 of them are known by name. Many Egyptian texts mention deities' names without indicating their character or role, while other texts refer to specific deities without even stating their name, so a complete list of them is difficult to assemble. Major deities Male *Aker – A god of the earth and the horizon *Amun – A creator god, patron deity of the city of Thebes, and the preeminent deity in Egypt during the New Kingdom *Anhur – A god of war and hunting *Anubis – God of the dead. Carries the dead to the judgement place of the Underworld *Aten – Sun disk deity who became the focus of the monolatrous or monotheistic Atenist belief system in the reign of Akhenaten *At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighing Scale
A scale or balance is a device used to measure weight or mass. These are also known as mass scales, weight scales, mass balances, and weight balances. The traditional scale consists of two plates or bowls suspended at equal distances from a fulcrum. One plate holds an object of unknown mass (or weight), while known masses are added to the other plate until static equilibrium is achieved and the plates level off, which happens when the masses on the two plates are equal. The perfect scale rests at neutral. A spring scale will make use of a spring of known stiffness to determine mass (or weight). Suspending a certain mass will extend the spring by a certain amount depending on the spring's stiffness (or spring constant). The heavier the object, the more the spring stretches, as described in Hooke's law. Other types of scales making use of different physical principles also exist. Some scales can be calibrated to read in units of force (weight) such as newtons instead of unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychopomp
Psychopomps (from the Greek word , , literally meaning the 'guide of souls') are supernatural creatures, spirits, entities, angels, demons or deities in many religions whose responsibility is to escort newly deceased souls from Earth to the afterlife. Their role is not to judge the deceased, but simply to guide them. Appearing frequently on funerary art, psychopomps have been depicted at different times and in different cultures as anthropomorphic entities, horses, deer, dogs, whip-poor-wills, ravens, crows, vultures, owls, sparrows, and cuckoos. In the case of birds, these are often seen in huge masses, waiting outside the home of the dying. Overview Ancient religion Classical examples of a psychopomp are the ancient Egyptian god Anubis, the deity Yama in Hinduism, the Greek ferryman Charon, the goddess Hecate, and god Hermes, the Roman god Mercury, the Norse Valkyries, the Aztec Xolotl, Slavic Morana and the Etruscan Vanth. Modern religion Heibai Wuchang, literally "Bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underworld. The concept of an underworld is found in almost every civilization and "may be as old as humanity itself". Common features of underworld myths are accounts of living people making journeys to the underworld, often for some heroic purpose. Other myths reinforce traditions that entrance of souls to the underworld requires a proper observation of ceremony, such as the ancient Greek story of the recently dead Patroclus haunting Achilles until his body could be properly buried for this purpose. Persons having social status were dressed and equipped in order to better navigate the underworld. A number of mythologies incorporate the concept of the soul of the deceased making its own journey to the underworld, with the dead needing to be taken a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Kingdom Of Egypt
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt (also known as The Period of Reunification) is the period in the history of ancient Egypt following a period of political division known as the First Intermediate Period. The Middle Kingdom lasted from approximately 2040 to 1782 BC, stretching from the reunification of Egypt under the reign of Mentuhotep II in the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Twelfth Dynasty. The kings of the Eleventh Dynasty ruled from Thebes and the kings of the Twelfth Dynasty ruled from el-Lisht. The concept of the Middle Kingdom as one of three golden ages was coined in 1845 by German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition evolved significantly throughout the 19th and 20th centuries. Some scholars also include the Thirteenth Dynasty of Egypt wholly into this period, in which case the Middle Kingdom would end around 1650 BC, while others only include it until Merneferre Ay around 1700 BC, last king of this dynasty to be attested in both Upper and Lower Egypt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embalming
Embalming is the art and science of preserving human remains by treating them (in its modern form with chemicals) to forestall decomposition. This is usually done to make the deceased suitable for public or private viewing as part of the funeral ceremony or keep them preserved for medical purposes in an anatomical laboratory. The three goals of embalming are sanitization, presentation, and preservation, with restoration being an important additional factor in some instances. Performed successfully, embalming can help preserve the body for a duration of many years. Embalming has a very long and cross-cultural history, with many cultures giving the embalming processes a greater religious meaning. Animal remains can also be embalmed by similar methods, but embalming is distinct from taxidermy. Embalming preserves the body intact, whereas taxidermy is the recreation of an animal's form often using only the creature's skin mounted on an anatomical form. History It is important to n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Dynasty Of Egypt
The First Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty I) covers the first series of Egyptian kings to rule over a unified Egypt. It immediately follows the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt, possibly by Narmer, and marks the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period, a time at which power was centered at Thinis. The date of this period is subject to scholarly debate about the Egyptian chronology. It falls within the early Bronze Age and is variously estimated to have begun anywhere between the 34th and the 30th centuriesBC. In a 2013 study based on radiocarbon dates, the beginning of the First Dynasty—the accession of Narmer (commonly known as Menes)—was placed at 3100BC give or take a century (3218–3035, with 95% confidence). The dynasty Information about this dynasty is derived from a few monuments and other objects bearing royal names, the most important being the Narmer Palette and Narmer Macehead, as well as Den and Qa'a king lists. No detailed records of the first two dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Deities
Ancient Egyptian deities are the God (male deity), gods and goddesses worshipped in ancient Egypt. The beliefs and rituals surrounding these gods formed the core of ancient Egyptian religion, which emerged sometime in prehistoric Egypt, prehistory. Deities represented natural phenomenon, natural forces and phenomena, and the Egyptians supported and appeased them through sacrifice, offerings and rituals so that these forces would continue to function according to ''maat'', or divine order. After the founding of the Egyptian state around 3100 BC, the authority to perform these tasks was controlled by the pharaoh, who claimed to be the gods' representative and managed the Egyptian temple, temples where the rituals were carried out. The gods' complex characteristics were expressed in Egyptian mythology, myths and in intricate relationships between deities: family ties, loose groups and hierarchies, and combinations of separate gods into one. Deities' diverse appearances in art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harcourt Brace
Harcourt () was an American publishing firm with a long history of publishing fiction and nonfiction for adults and children. The company was last based in San Diego, California, with editorial/sales/marketing/rights offices in New York City and Orlando, Florida, and was known at different stages in its history as Harcourt Brace, & Co. and Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. From 1919 to 1982, it was based in New York City. Houghton Mifflin acquired Harcourt in 2007. It incorporated the Harcourt name to form Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. As of 2012, all Harcourt books that have been re-released are under the Houghton Mifflin Harcourt name. The Harcourt Children's Books division left the name intact on all of its books under that name as part of HMH. In 2007 the U.S. Schools Education and Trade Publishing parts of Harcourt Education were sold by Reed Elsevier to Houghton Mifflin Riverdeep Group. Harcourt Assessment and Harcourt Education International were acquired by Pearson, the internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |