|
Anti–Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Antibody
Anti-''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' antibodies (ASCAs) are antibodies against antigens presented by the cell wall of the yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. These antibodies are directed against oligomannose sequences α-1,3 Man (α-1,2 Man α-1,2 Man)n (n = 1 or 2). ASCAs and perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (pANCAs) are the two most useful and often discriminating biomarkers for colitis. ASCA tends to recognize Crohn's disease more frequently, whereas pANCA tend to recognize ulcerative colitis. ASCA antibodies react to a yeast protein with mannans, a 200-kDa glycoprotein. Diseases Diseases in which ASCA are found include the following: * Behçet's disease - The association with ASCA is not generally strong, but increased in patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. * Coeliac disease * Colitis ** Ulcerative colitis-familial. ** Microscopic colitis *** Collagenous colitis * Crohn's disease Intestinal yeast and ASCA positive Intestinal yeast infections are seen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
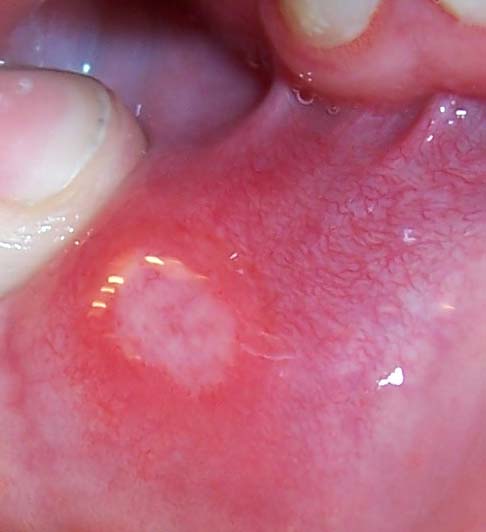
Crohn's Disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer. While the precise causes of Crohn's disease (CD) are unknown, it is believed to be caused by a combination of environmental, immune, and bacterial factors in genetically susceptible individuals. It results in a chronic inflammatory disorder, in which the body's immune system defends the gastrointestinal tract, possibly targeting microbial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOD2
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2 (NOD2), also known as caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 15 (CARD15) or inflammatory bowel disease protein 1 (IBD1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NOD2'' gene located on chromosome 16. NOD2 plays an important role in the immune system. It recognizes bacterial molecules ( peptidoglycans) and stimulates an immune reaction. NOD2 is an intracellular pattern recognition receptor, which is similar in structure to resistant proteins of plants and recognizes molecules containing the specific structure called muramyl dipeptide (MDP) that is found in certain bacteria. Structure The C-terminal portion of the protein contains a leucine-rich repeat domain that is known to play a role in protein–protein interactions. The middle part of the protein is characterized by a NOD domain involved in protein self-oligomerization. The N-terminal portion contains two CARD domains known to play a role in apo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD69
CD69 (Cluster of Differentiation 69) is a human transmembrane C-Type lectin protein encoded by the gene. It is an early activation marker that is expressed in hematopoietic stem cells, T cells, and many other cell types in the immune system. It is also implicated in T cell differentiation as well as lymphocyte retention in lymphoid organs. Function The activation of T lymphocytes and Natural Killer (NK) cells, both in vivo and in vitro, induces expression of CD69. This molecule, which appears to be the earliest inducible cell surface glycoprotein acquired during lymphoid activation, is involved in lymphocyte proliferation and functions as a signal-transmitting receptor in lymphocytes, including natural killer (NK) cells, and platelets (Cambiaggi et al., 1992) upplied by OMIM Structure and ligands The gene encoding CD69 is located in the NK gene complex on chromosome 6 and chromosome 12 in mice and humans respectively. Activation signaling pathways in lymphocytes, NK cells, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD25
Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain (also called CD25) is the human protein encoded by the ''IL2RA'' gene. The interleukin 2 (IL2) receptor alpha (IL2RA) and beta (IL2RB) chains, together with the common gamma chain (IL2RG), constitute the high-affinity IL2 receptor. Homodimeric alpha chains (IL2RA) result in low-affinity receptor, while homodimeric beta (IL2RB) chains produce a medium-affinity receptor. Normally an integral-membrane protein, soluble IL2RA has been isolated and determined to result from extracellular proteolysis. Alternately-spliced IL2RA mRNAs have been isolated, but the significance of each is currently unknown. Description It is a type I transmembrane protein present on activated T cells, activated B cells, some thymocytes, myeloid precursors, and oligodendrocytes. Though IL2RA has been used as a marker to identify CD4+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in mice, it has been found that a large proportion of resting memory T cells constitutively express IL2RA in humans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes
Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) are mature lymphocytes that circulate in the blood, rather than localising to organs (such as the spleen or lymph nodes). They comprise T cells, NK cells and B cells B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or .... References Lymphocytes {{lymphatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lectin
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that are highly specific for sugar groups that are part of other molecules, so cause agglutination of particular cells or precipitation of glycoconjugates and polysaccharides. Lectins have a role in recognition at the cellular and molecular level and play numerous roles in biological recognition phenomena involving cells, carbohydrates, and proteins. Lectins also mediate attachment and binding of bacteria, viruses, and fungi to their intended targets. Lectins are ubiquitous in nature and are found in many foods. Some foods, such as beans and grains, need to be cooked, fermented or sprouted to reduce lectin content. Some lectins are beneficial, such as CLEC11A, which promotes bone growth, while others may be powerful toxins such as ricin. Lectins may be disabled by specific mono- and oligosaccharides, which bind to ingested lectins from grains, legumes, nightshade plants, and dairy; binding can prevent their attachment to the carbohy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannan-binding Lectin
Mannose-binding lectin (MBL), also called mannan-binding lectin or mannan-binding protein (MBP), is a lectin that is instrumental in innate immunity as an opsonin and via the lectin pathway. Structure MBL has an oligomeric structure (400-700 kDa), built of subunits that contain three presumably identical peptide chains of about 30 kDa each. Although MBL can form several oligomeric forms, there are indications that dimers and trimers are biologically inactive as an opsonin and at least a tetramer form is needed for activation of complement. Genes and polymorphisms Human MBL2 gene is located on chromosome 10q11.2-q21. Mice have two homologous genes, but in human the first of them was lost. A low level expression of an MBL1 pseudogene 1 (MBL1P1) was detected in liver. The pseudogene encodes a truncated 51-amino acid protein that is homologous to the MBLA isoform in rodents and some primates. Structural mutations in exon 1 of the human MBL2 gene, at codon 52 (Arg to Cys, allele D), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C Albicans En
C, or c, is the third letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''cee'' (pronounced ), plural ''cees''. History "C" comes from the same letter as "G". The Semites named it gimel. The sign is possibly adapted from an Egyptian hieroglyph for a staff sling, which may have been the meaning of the name ''gimel''. Another possibility is that it depicted a camel, the Semitic name for which was ''gamal''. Barry B. Powell, a specialist in the history of writing, states "It is hard to imagine how gimel = "camel" can be derived from the picture of a camel (it may show his hump, or his head and neck!)". In the Etruscan language, plosive consonants had no contrastive voicing, so the Greek ' Γ' (Gamma) was adopted into the Etruscan alphabet to represent . Already in the Western Greek alphabet, Gamma first took a '' form in Early Etruscan, then '' in Classical Etru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coeliac Disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barley. Classic symptoms include gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhoea, abdominal distention, malabsorption, loss of appetite, and among children failure to grow normally. This often begins between six months and two years of age. Non-classic symptoms are more common, especially in people older than two years. There may be mild or absent gastrointestinal symptoms, a wide number of symptoms involving any part of the body, or no obvious symptoms. Coeliac disease was first described in childhood; however, it may develop at any age. It is associated with other autoimmune diseases, such as Type 1 diabetes mellitus and Hashimoto's thyroiditis, among others. Coeliac disease is caused by a reaction to gluten, a group of various prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S Cerevisiae Under DIC Microscopy
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ess'' (pronounced ), plural ''esses''. History Origin Northwest Semitic šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative (as in 'ip'). It originated most likely as a pictogram of a tooth () and represented the phoneme via the acrophonic principle. Ancient Greek did not have a phoneme, so the derived Greek letter sigma () came to represent the voiceless alveolar sibilant . While the letter shape Σ continues Phoenician ''šîn'', its name ''sigma'' is taken from the letter '' samekh'', while the shape and position of ''samekh'' but name of ''šîn'' is continued in the '' xi''. Within Greek, the name of ''sigma'' was influenced by its association with the Greek word (earlier ) "to hiss". The original name of the letter "sigma" may have been ''san'', but due to the compli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscopic Colitis
Microscopic colitis refers to two related medical conditions which cause diarrhea: collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis. Both conditions are characterized by the presence of chronic non-bloody watery diarrhea, normal appearances on colonoscopy and characteristic histopathology findings of inflammatory cells. Signs and symptoms The main symptom is persistent non-bloody watery diarrhea, which may be profuse. People may also experience abdominal pain, fecal incontinence, and unintentional weight loss. Microscopic colitis is the diagnosis in around 10% of cases investigated for chronic non-bloody diarrhea. Associated conditions A higher incidence of autoimmune diseases, for example arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome, thyroid disorders, and celiac disease, has been reported in people with microscopic colitis. Associations with various drugs have been found, especially proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and non-steroidal anti-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |