|
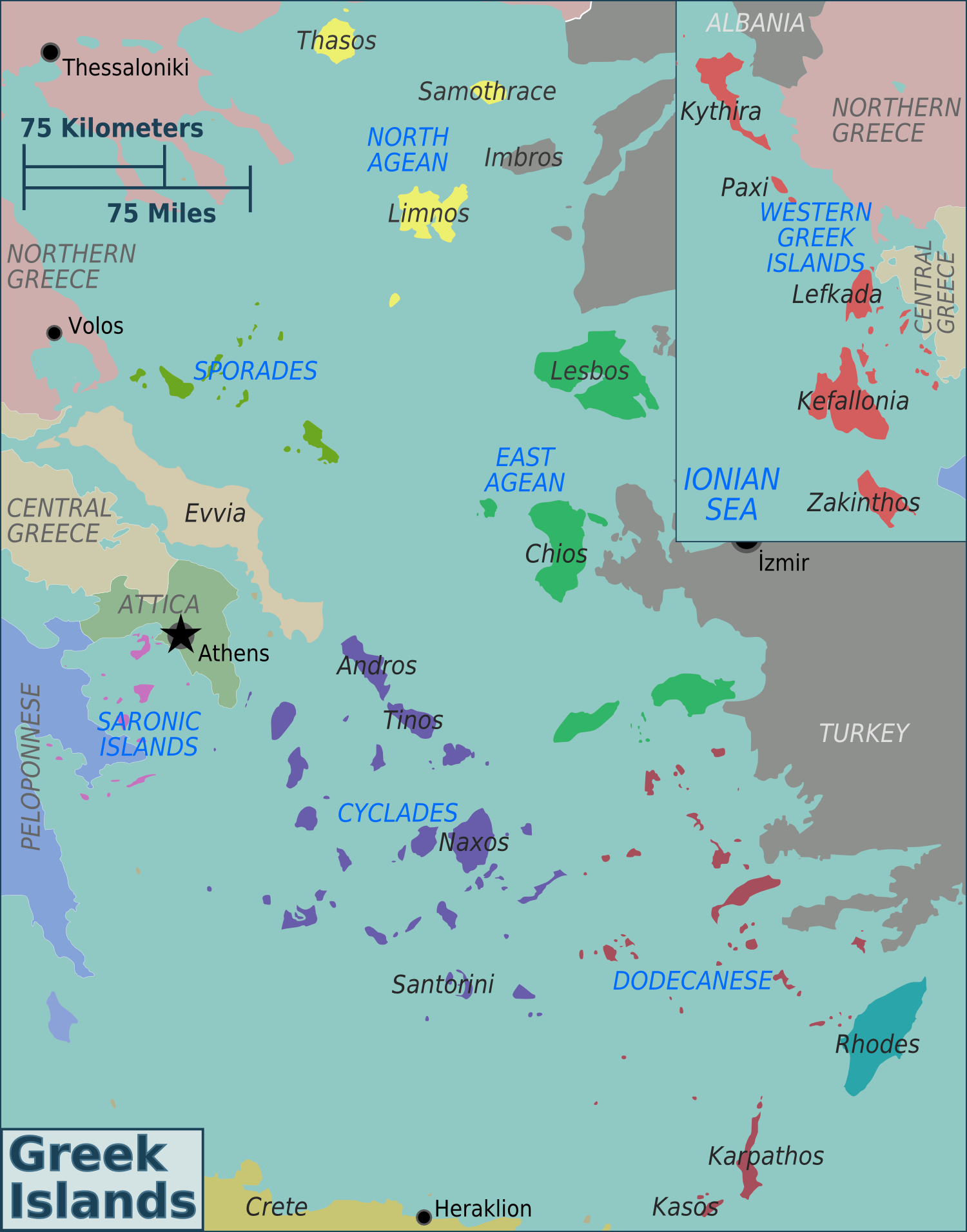
Antipsara
Antipsara ( el, ќСќљѕДќѓѕИќ±ѕБќ±) is a small Greek island in the Aegean Sea. Antipsara had 4 inhabitants according to the 2011 census.ќ¶ќХќЪ ќ±ѕАќњѕДќµќїќµѕГќЉќђѕДѕЙќљ ќЬќЯќЭќЩќЬќЯќ• ѕАќїќЈќЄѕЕѕГќЉќњѕН ќ±ѕАќњќ≥ѕБќ±ѕЖќЃѕВ 2011ї, ѕГќµќї. 10833 (ѕГќµќї. 359 ѕДќњѕЕ pdf) It lies about west of the larger island Psara Psara ( el, ќ®ќ±ѕБќђ, , ; known in ancient times as /, /) is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea. Together with the small island of Antipsara (Population 4) it forms the municipality of Psara. It is part of the Chios regional unit, which is part of ..., from which its name is derived. Geographic conditions make it inaccessible from the north and west side. Evidence exists of settlement in ancient Greek and Roman times. During Ottoman rule the island served as a port. Nowadays, tourist trips to the island originate from Psara in the summer months. The small church of St John (ќЖќ≥ќєќњѕВ ќЩѕЙќђќљќљќЈѕВ) on the eastern side is visited in August by pilgrims. Wildlife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islands Of Greece
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227. The largest Greek island by area is Crete, located at the southern edge of the Aegean Sea. The second largest island is Euboea or Evvia, which is separated from the mainland by the 60m-wide Euripus Strait, and is administered as part of the Central Greece region. After the third and fourth largest Greek islands, Lesbos and Rhodes, the rest of the islands are two-thirds of the area of Rhodes, or smaller. The Greek islands are traditionally grouped into the following clusters: the Argo-Saronic Islands in the Saronic Gulf near Athens; the Cyclades, a large but dense collection occupying the central part of the Aegean Sea; the North Aegean islands, a loose grouping off the west coast of Turkey; the Dodecanese, another loose collection in the southeast between Crete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psara
Psara ( el, ќ®ќ±ѕБќђ, , ; known in ancient times as /, /) is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea. Together with the small island of Antipsara (Population 4) it forms the municipality of Psara. It is part of the Chios regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean region. The only town of the island and seat of the municipality is also called Psara. Psara had 448 inhabitants according to the 2011 census. It has a small port linking to the island of Chios and other parts of Greece. It was also the site of the Psara massacre, in which thousands of Greeks on the island were massacred by Ottoman troops during the Greek War of Independence in 1824. Geography Psara lies northwest of Chios, from the northwestern point of the island of Chios and east-northeast of Athens. The length and width of the island are about and the area is . The highest point on the island is "Profitis Ilias" (). The municipality has total area of . Flag The modern flag of Psara is based largely on the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chios (regional Unit)
Chios ( el, ќ†ќµѕБќєѕЖќµѕБќµќєќ±ќЇќЃ ќµќљѕМѕДќЈѕДќ± ќІќѓќњѕЕ, ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of North Aegean. The capital of the regional unit is the town of Chios. The regional unit consists of the islands of Chios, Psara, Oinousses and some smaller uninhabited islands (including Antipsara), all in the Aegean Sea. Administration The regional unit Chios is subdivided into 3 municipalities. These are (number as in the map in the infobox): * Chios (1) * Oinousses (2) * Psara (3) Prefecture As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the regional unit Chios was created out of the former prefecture Chios ( el, ќЭќњќЉѕМѕВ ќІбљґќњѕЕ). The prefecture had the same territory as the present regional unit. At the same time, the municipalities were reorganised, according to the table below. See also * List of settlements in the Chios regional unit This is a list of settlements in Chios regional unit in Greece: * Agio Gala * Agios Geor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
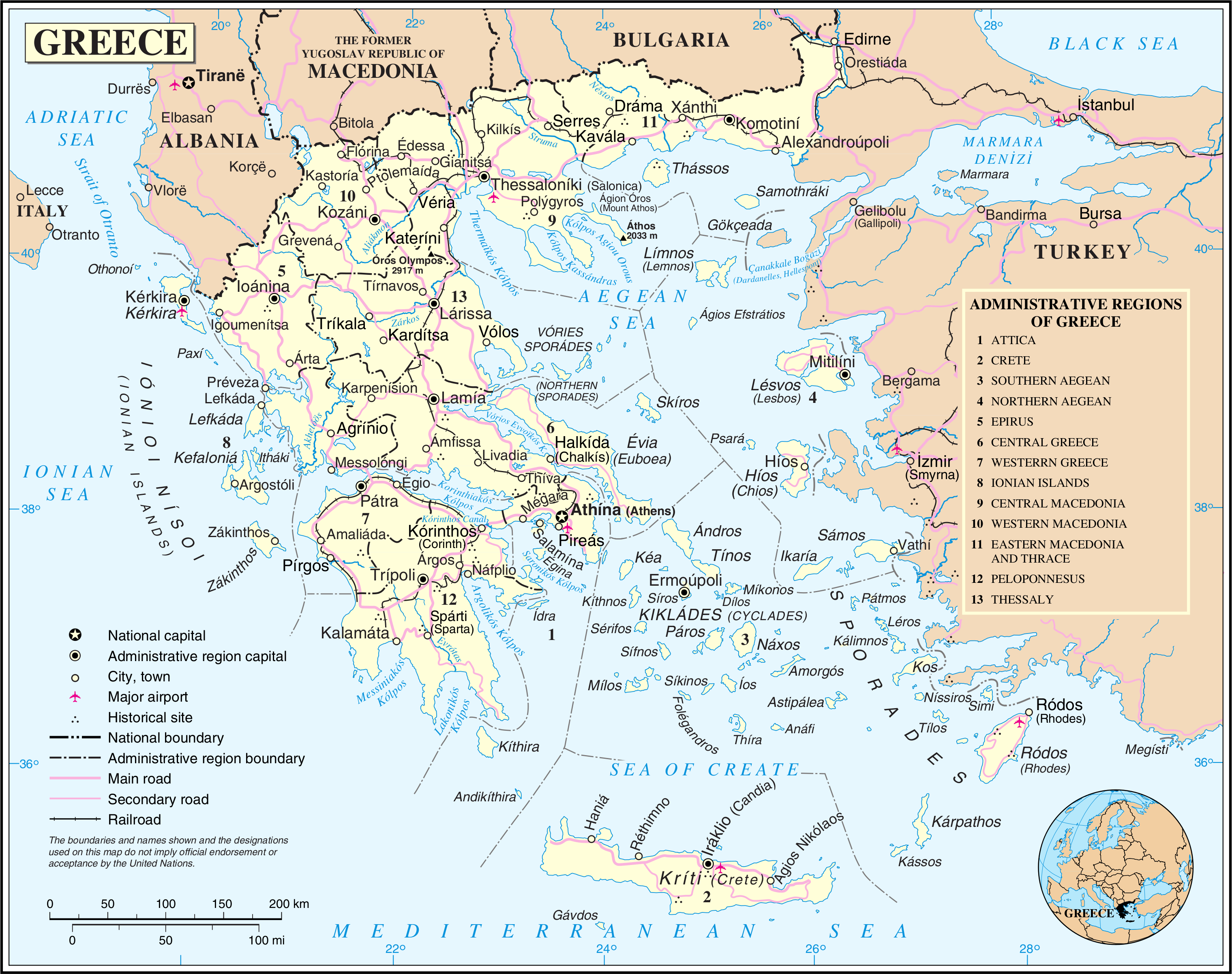
Modern Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece ( el, ѕАќµѕБќєѕЖќ≠ѕБќµќєќµѕВ, translit=perif√©ries) are the country's thirteen first-level administrative entities, each comprising several second-level units, originally known as prefectures and, since 2011, as regional units. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the prefectures (Law 1622/1986). ќЭ.1622/86 "ќ§ќњѕАќєќЇќЃ ќСѕЕѕДќњќіќєќњќѓќЇќЈѕГќЈ - ќ†ќµѕБќєѕЖќµѕБќµќєќ±ќЇќЃ ќСќљќђѕАѕДѕЕќЊќЈ - ќФќЈќЉќњќЇѕБќ±ѕДќєќЇѕМѕВ ќ†ѕБќњќ≥ѕБќ±ќЉќЉќ±ѕДќєѕГќЉѕМѕВ", (ќ¶ќХќЪ 92/ѕД.ќСќД/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad historicalвАУgeographical regions (ќ≥ќµѕЙќ≥ѕБќ±ѕЖќєќЇќђ ќіќєќ±ќЉќµѕБќѓѕГќЉќ±ѕДќ±), which, however, was often arbitrary; not all of the pre-1986 traditional historical-geographic regions had official administrative bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Aegean
The North Aegean Region ( el, ќ†ќµѕБќєѕЖќ≠ѕБќµќєќ± ќТќњѕБќµќѓќњѕЕ ќСќєќ≥ќ±ќѓќњѕЕ, translit=Perif√©ria Vor√≠ou Ey√©ou, ) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece, and the smallest of the thirteen by population. It comprises the islands of the north-eastern Aegean Sea, called the North Aegean islands, except for Thasos and Samothrace, which belong to the Greek region of Eastern Macedonia and Thrace, and Imbros and Tenedos, which belong to Turkey. Administration The North Aegean region was established in the 1987 administrative reform. With the 2010 Kallikratis plan, its powers and authority were redefined and extended. Along with the Southern Aegean region, it is supervised by the Decentralized Administration of the Aegean based at Piraeus. The capital of the region is situated in Mytilene on the island of Lesbos. Until the Kallikratis reform, the region consisted of the three prefectures of Samos, Chios and Lesbos. Since 1 January 2011 it is divided into fiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Units Of Greece
The 74 regional units of Greece Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ... ( el, ѕАќµѕБќєѕЖќµѕБќµќєќ±ќЇќ≠ѕВ ќµќљѕМѕДќЈѕДќµѕВ, ; sing. , ) are the country's Seventy-four second-level administrative units. They are divisions of the country's 13 regions, and are further divided into municipalities. They were introduced as part of the Kallikratis administrative reform on 1 January 2011 and are comparable in area and, in the mainland, coterminous with the 'pre-Kallikratis' prefectures of Greece. List References {{Articles on second-level administrative divisions of European countries Regional units Greece transport-related lists Subdivisions of Greece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring thousands of islands. The country consists of nine traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western civilization, being the birthplace of democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major scientific and mathematical p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: ќСќєќ≥ќ±ќѓќњ ќ†ќ≠ќїќ±ќ≥ќњѕВ: "Eg√©o P√©lagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some 215,000 square kilometres. In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea and the Black Sea by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639m to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea. The Aegean Islands can be divided into several island groups, including the Dodecanese, the Cyclades, the Sporades, the Saronic islands and the North Aegean Islands, as well as Crete and its surrounding islands. The Dodecanese, located to the southeast, includes the islands of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Shag
The European shag or common shag (''Gulosus aristotelis'') is a species of cormorant. It is the only member of the monotypic genus ''Gulosus''. It breeds around the rocky coasts of western and southern Europe, southwest Asia and north Africa, mainly wintering in its breeding range except for the northernmost birds. In Britain this seabird is usually referred to as simply the shag. The scientific genus name derives from the Latin for glutton. The species name ''aristotelis'' commemorates the Greek philosopher Aristotle. Taxonomy The European shag was formerly classified within the genus '' Phalacrocorax'', but a 2014 study found it to be significantly more diverged than the clade containing '' Phalacrocorax'' and '' Urile'', but basal to the clade containing '' Nannopterum'' and '' Leucocarbo'', and thus classified it in its own genus, ''Gulosus''. The IOC followed this classification in 2021. ''Gulosus'' is thought to have split from the ''Nannopterum''-''Leucocarbo'' clade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleonora's Falcon
Eleonora's falcon (''Falco eleonorae'') is a medium-sized falcon. It belongs to the hobby group, a rather close-knit number of similar falcons often considered a subgenus ''Hypotriorchis''. The sooty falcon is sometimes considered its closest relative, but while they certainly belong to the same lineage, they do not seem to be close sister species. The English name and the species name ''eleonorae'' commemorate Eleanor of Arborea, Queen or Lady-Judge () and national heroine of Sardinia, who in 1392, under the jurisdiction conferred by the Carta de Logu, became the first ruler in history to grant protection to hawk and falcon nests against illegal hunters. The genus name ''falco'' is from Late Latin ''falx'', ''falcis'', a sickle, referring to the claws of the bird. Description Eleonora's falcon is a bird of prey, long with an wingspan. It is shaped like a large Eurasian hobby or a small slender peregrine falcon, with its long pointed wings, long tail and slim body. There a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cory's Shearwater
Cory's shearwater (''Calonectris borealis'') is a large shearwater in the seabird family Procellariidae. It breeds colonially of rocky islands in the eastern Atlantic. Outside the breeding season it ranges widely in the Atlantic. It was formerly considered to be conspecific with Scopoli's shearwater. Taxonomy Cory's shearwater was formally described in 1881 by the American ornithologist Charles B. Cory from a specimen collected off Chatham Island, Massachusetts. He coined the binomial name ''Puffinus borealis''. Cory's shearwater is now placed in the genus '' Calonectris'' that was introduced in 1915 by the ornithologists Gregory Mathews and Tom Iredale. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek ''kalos'' meaning "good" or "noble" with the genus name ''Nectris'' that was used for shearwaters by the German naturalist Heinrich Kuhl in 1820. The name ''Nectris'' comes from the Ancient Greek ''nƒУktris'' meaning "swimmer". The specific epithet ''borealis'' is Latin and means "north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |