|
Antinuclear Antibody
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human proteins (autoantigens). In some cases, antibodies to human antigens are produced. There are many subtypes of ANAs such as anti-Ro antibodies, anti-La antibodies, anti-Sm antibodies, anti-nRNP antibodies, anti-Scl-70 antibodies, anti-dsDNA antibodies, anti-histone antibodies, antibodies to nuclear pore complexes, anti-centromere antibodies and anti-sp100 antibodies. Each of these antibody subtypes binds to different proteins or protein complexes within the nucleus. They are found in many disorders including autoimmunity, cancer and infection, with different prevalences of antibodies depending on the condition. This allows the use of ANAs in the diagnosis of some autoimmune disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms. The cause of SLE is not clear. It is thought to involve a mixture of genetics combined with environmental factors. Among identical twins, if one is affected there is a 24% chance the other one will also develop the disease. Female sex hormones, sunlight, smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and certain infections are also believed to increase a person's risk. The mechanism involves an immune response by autoantibodies against a person's own tissues. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humoral Immunity
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it involves substances found in the humors, or body fluids. It contrasts with cell-mediated immunity. Humoral immunity is also referred to as antibody-mediated immunity. The study of the molecular and cellular components that form the immune system, including their function and interaction, is the central science of immunology. The immune system is divided into a more primitive innate immune system and an acquired or adaptive immune system of vertebrates, each of which contain both humoral and cellular immune elements. Humoral immunity refers to antibody production and the coinciding processes that accompany it, including: Th2 activation and cytokine production, germinal center formation and isotype switching, and affinity maturation an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the longest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titer
Titer (American English) or titre (British English) is a way of expressing concentration. Titer testing employs serial dilution to obtain approximate quantitative information from an analytical procedure that inherently only evaluates as positive or negative. The titre corresponds to the highest dilution factor that still yields a positive reading. For example, positive readings in the first 8 serial, twofold dilutions translate into a titer of 1:256 (i.e., 2−8). Titres are sometimes expressed by the denominator only, for example 1:256 is written 256. The term also has two other, conflicting meanings. In titration, the titer is the ratio of actual to nominal concentration of a titrant, e.g. a titer of 0.5 would require 1/0.5 = 2 times more titrant than nominal. This is to compensate for possible degradation of the titrant solution. Second, in textile engineering, titre is also a synonym for linear density. Etymology Titer has the same origin as the word "title", from the Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly a protein) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries. In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample to be tested are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme and then any unbound antibodies are removed. In the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's substrate is added. If there was binding, the subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change. Performing an ELISA involves at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
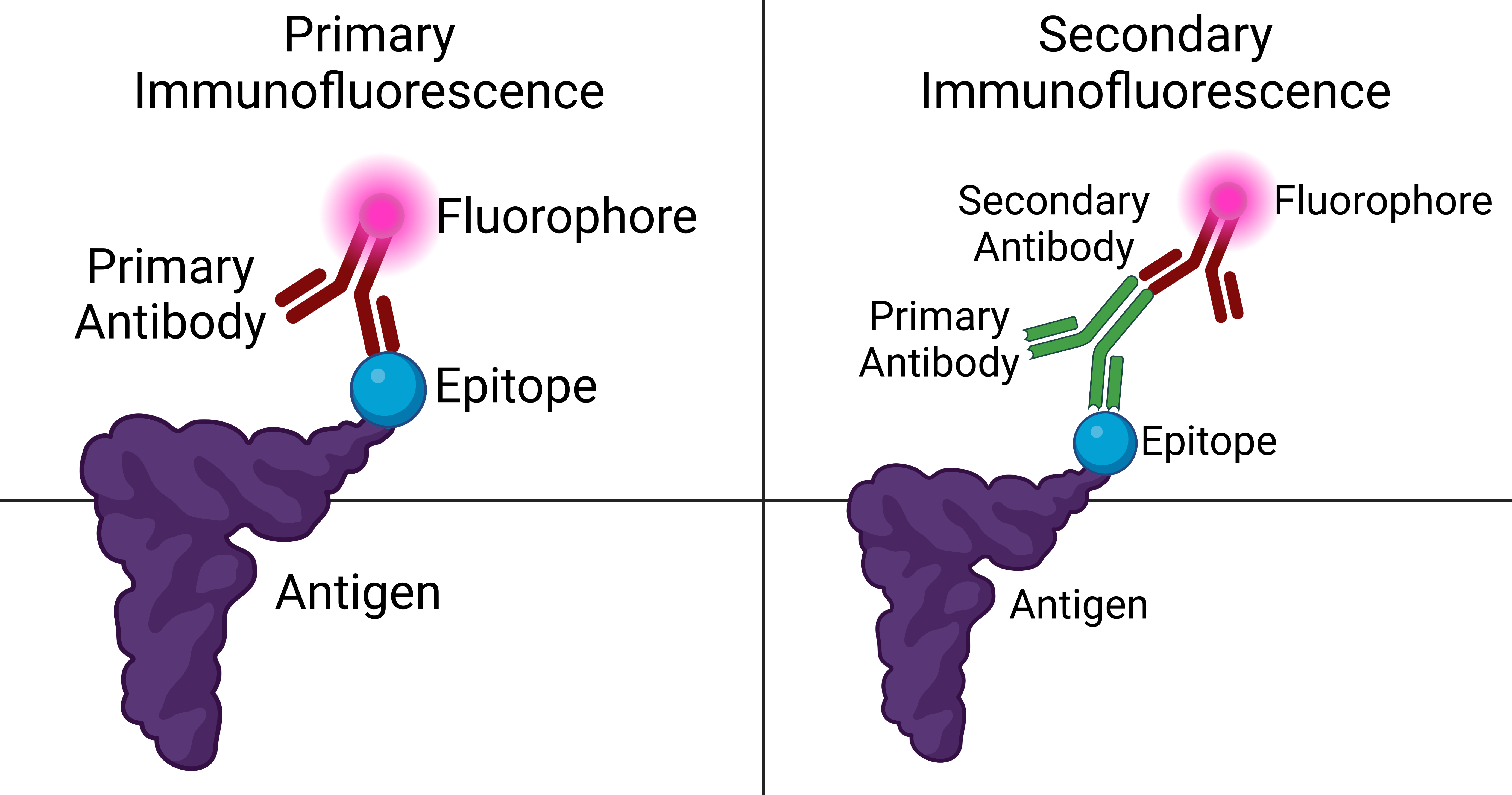
Indirect Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specific biomolecule targets within a cell, and therefore allows visualization of the distribution of the target molecule through the sample. The specific region an antibody recognizes on an antigen is called an epitope. There have been efforts in epitope mapping since many antibodies can bind the same epitope and levels of binding between antibodies that recognize the same epitope can vary. Additionally, the binding of the fluorophore to the antibody itself cannot interfere with the immunological specificity of the antibody or the binding capacity of its antigen. Immunofluorescence is a widely used example of immunostaining (using antibodies to stain proteins) and is a specific example of immunohistochemistry (the use of the antibody-antigen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Serum
Serum () is the fluid and solute component of blood which does not play a role in clotting. It may be defined as blood plasma without the clotting factors, or as blood with all cells and clotting factors removed. Serum includes all proteins not used in blood clotting; all electrolytes, antibodies, antigens, hormones; and any exogenous substances (e.g., drugs or microorganisms). Serum does not contain white blood cells (leukocytes), red blood cells (erythrocytes), platelets, or clotting factors. The study of serum is serology. Serum is used in numerous diagnostic tests as well as blood typing. Measuring the concentration of various molecules can be useful for many applications, such as determining the therapeutic index of a drug candidate in a clinical trial. To obtain serum, a blood sample is allowed to clot (coagulation). The sample is then centrifuged to remove the clot and blood cells, and the resulting liquid supernatant is serum. Clinical and laboratory uses The serum of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug-induced Lupus Erythematosus
Drug-induced lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disorder caused by chronic use of certain drugs. These drugs cause an autoimmune response (the body attacks its own cells) producing symptoms similar to those of systemic lupus erythematosus Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ... (SLE). There are 38 known medications to cause DIL but there are three that report the highest number of cases: hydralazine, procainamide, and quinidine. While the criteria for diagnosing DIL has not been thoroughly established, symptoms of DIL typically present as myalgia, muscle pain and arthralgia, joint pain. Generally, the symptoms recede after discontinuing use of the drugs. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of drug-induced lupus erythematosus include the following: * Joint pain (art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis, formerly known as lupoid hepatitis, plasma cell hepatitis, or autoimmune chronic active hepatitis, is a chronic, autoimmune disease of the liver that occurs when the body's immune system attacks liver cells, causing the liver to be inflamed. Common initial symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, muscle aches, or weight loss or signs of acute liver inflammation including fever, jaundice, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Individuals with autoimmune hepatitis often have no initial symptoms and the disease may be detected by abnormal liver function tests and increased protein levels during routine bloodwork or the observation of an abnormal-looking liver during abdominal surgery. Anomalous presentation of MHC class II receptors on the surface of liver cells, possibly due to genetic predisposition or acute liver infection, causes a cell-mediated immune response against the body's own liver, resulting in autoimmune hepatitis. This abnormal immune respons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a long-term inflammatory disorder which affects skin and the muscles. Its symptoms are generally a skin rash and worsening muscle weakness over time. These may occur suddenly or develop over months. Other symptoms may include weight loss, fever, lung inflammation, or light sensitivity. Complications may include calcium deposits in muscles or skin. The cause is unknown. Theories include that it is an autoimmune disease or a result of a viral infection. Dermatomyositis may develop as a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with several forms of malignancy. It is a type of inflammatory myopathy. Diagnosis is typically based on some combination of symptoms, blood tests, electromyography, and muscle biopsies. While no cure for the condition is known, treatments generally improve symptoms. Treatments may include medication, physical therapy, exercise, heat therapy, orthotics and assistive devices, and rest. Medications in the corticosteroids family are typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymyositis
Polymyositis (PM) is a type of chronic inflammation of the muscles (inflammatory myopathy) related to dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis. Its name means "inflammation of many muscles" ('' poly-'' + '' myos-'' + ''-itis''). The inflammation of polymyositis is mainly found in the endomysial layer of skeletal muscle, whereas dermatomyositis is characterized primarily by inflammation of the perimysial layer of skeletal muscles. Signs and symptoms The hallmark of polymyositis is weakness and/or loss of muscle mass in the proximal musculature, as well as flexion of the neck and torso. These symptoms can be associated with marked pain in these areas as well. The hip extensors are often severely affected, leading to particular difficulty in climbing stairs and rising from a seated position. The skin involvement of dermatomyositis is absent in polymyositis. Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) or other problems with esophageal motility occur in as many as 1/3 of patients. Low grad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |