|
Anti-religious Campaign Of Communist Romania
The anti-religious campaign of Communist Romania was initiated by the People's Republic of Romania and continued by the Socialist Republic of Romania, which under the doctrine of Marxist–Leninist atheism took a hostile stance against religion and set its sights on the ultimate goal of an atheistic society, wherein religion would be recognized as the ideology of the bourgeoisie. Scope Romania's Communist government achieved an incredible degree of control (relative to the other Eastern Bloc nations) of the nation's largest religious community: the Romanian Orthodox Church. This control was used to foster political support for the regime as well as to manipulate Romania's image abroad. In Romania, more than 5,000 Orthodox Christian priests were imprisoned. The Orthodox archdiocese of Cluj contains biographies of 1,700 church personnel jailed. 1945–1965 Cultural background The Communist Party of the Soviet Union, in accordance with Marxist–Leninist interpretation of history, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Republic Of Romania
The Socialist Republic of Romania ( ro, Republica Socialistă România, RSR) was a Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist state that existed officially in Romania from 1947 to 1989. From 1947 to 1965, the state was known as the Romanian People's Republic (, RPR). The country was an Eastern Bloc state and a member of the Warsaw Pact with a dominant role for the Romanian Communist Party enshrined in its constitutions. Geographically, RSR was bordered by the Black Sea to the east, the Soviet Union (via the Ukrainian and Moldavian SSRs) to the north and east, Hungary and Yugoslavia (via SR Serbia) to the west, and Bulgaria to the south. As World War II ended, Romania, a former Axis member which had overthrown the Axis, was occupied by the Soviet Union, the sole representative of the Allies. On 6 March 1945, after mass demonstrations by communist sympathizers and political pressure from the Soviet representative of the Allied Control Commission, a new pro-Soviet government that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Army
uk, Радянська армія , image = File:Communist star with golden border and red rims.svg , alt = , caption = Emblem of the Soviet Army , start_date = 25 February 1946 , country = (1946–1991)' (1991–1992) , branch = , type = Army , role = Ground warfare, Land warfare , size = 3,668,075 active (1991) 4,129,506 reserve (1991) , command_structure = , garrison = , garrison_label = , nickname = "Red Army" , patron = , motto = ''За нашу Советскую Родину!(Za nashu Sovetskuyu Rodinu!)''"For our Soviet Motherland!" , colors = Red and yellow , colors_label = , march ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excommunication
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to end or at least regulate the communion of a member of a congregation with other members of the religious institution who are in normal communion with each other. The purpose of the institutional act is to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular, those of being in communion with other members of the congregation, and of receiving the sacraments. It is practiced by all of the ancient churches (such as the Catholic Church, Oriental Orthodox churches and the Eastern Orthodox churches) as well as by other Christian denominations, but it is also used more generally to refer to similar types of institutional religious exclusionary practices and shunning among other religious groups. The Amish have also been known to excommunicate members that were either seen or known for breaking rules, or questioning the church, a practice known as shun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Rite Catholic Churches
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous (''sui iuris'') particular churches of the Catholic Church, in full communion with the Pope in Holy See, Rome. Although they are distinct theologically, liturgically, and historically from the Latin Church, they are all in full communion with it and with each other. Eastern Catholics are a distinct minority within the Catholic Church; of the 1.3 billion Catholics in communion with the Pope, approximately 18 million are members of the eastern churches. The majority of the Eastern Catholic Churches are groups that, at different points in the past, used to belong to the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodox churches, or the historic Church of the East; these churches had various Schism in Christianity, schisms with the Catholic Church. The Eastern Catho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church
, native_name_lang = uk , caption_background = , image = StGeorgeCathedral Lviv.JPG , imagewidth = , type = Particular church (sui iuris) , alt = , caption = St. George's Cathedral in Lviv, mother church of Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church , abbreviation = UGCC , main_classification = Eastern Catholic , orientation = Eastern Christianity , theology = Catholic Theology , governance=Synod of the Ukrainian Catholic Church , polity = Episcopal , leader_title = Pope , leader_name = Francis , leader_title2 = Major Archbishop , leader_name2 = Sviatoslav Shevchuk , division_type = Parishes , division = 3993 , director = , fellowships = , associations = , area = Mainly: Ukraine Minority: Canada, the United States, Australia, France, the United Kingdom, Germany, Brazil, Poland, Lithuania and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (1922–1952) and Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union (1941–1953). Initially governing the country as part of a collective leadership, he consolidated power to become a dictator by the 1930s. Ideologically adhering to the Leninist interpretation of Marxism, he formalised these ideas as Marxism–Leninism, while his own policies are called Stalinism. Born to a poor family in Gori in the Russian Empire (now Georgia), Stalin attended the Tbilisi Spiritual Seminary before joining the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party. He edited the party's newspaper, ''Pravda'', and raised funds for Vladimir Lenin's Bolshevik faction via robberies, kidnappings and protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Review Of Politics
''The Review of Politics'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal in the fields of politics, philosophy, and history. It was founded in 1939 and is published by Cambridge University Press Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Pre .... References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Review of Politics, The Cambridge University Press academic journals English-language journals Political science journals Publications established in 1939 Quarterly journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Catholic Churches
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous (''sui iuris'') particular churches of the Catholic Church, in full communion with the Pope in Holy See, Rome. Although they are distinct theologically, liturgically, and historically from the Latin Church, they are all in full communion with it and with each other. Eastern Catholics are a distinct minority within the Catholic Church; of the 1.3 billion Catholics in communion with the Pope, approximately 18 million are members of the eastern churches. The majority of the Eastern Catholic Churches are groups that, at different points in the past, used to belong to the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodox churches, or the historic Church of the East; these churches had various Schism in Christianity, schisms with the Catholic Church. The Eastern Catho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniate Romanian Church
The Romanian Greek Catholic Church or Romanian Church United with Rome, Greek-Catholic ( la, Ecclesia Graeco-Catholica Romaniae; ro, Biserica Română Unită cu Roma, Greco-Catolică), sometimes called, in reference to its Byzantine Rite, the Romanian Byzantine Catholic Church is a ''sui iuris'' Eastern Catholic Church, in full union with the Catholic Church. It has the rank of a Major Archiepiscopal Church and it uses the Byzantine liturgical rite in the Romanian language. It is part of the Major Archiepiscopal Churches of the Catholic Church that are not distinguished with a patriarchal title. Cardinal Lucian Mureșan, Archbishop of Făgăraș and Alba Iulia, has served as the head of the Romanian Greek-Catholic Church since 1994. On December 16, 2005, as the ''Romanian Church United with Rome'', the Greek-Catholic church was elevated to the rank of a Major Archiepiscopal Church by Pope Benedict XVI, with Lucian Mureșan becoming its first major archbishop. Mureşan was ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Minority
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number of individuals is therefore the 'minority'. However, in terms of sociology, economics, and politics; a demographic which takes up the smallest fraction of the population is not necessarily the 'minority'. In the academic context, 'minority' and 'majority' groups are more appropriately understood in terms of hierarchical power structures. For example, in South Africa during Apartheid, white Europeans held virtually all social, economic, and political power over black Africans. For this reason, black Africans are the 'minority group', despite the fact that they outnumber white Europeans in South Africa. This is why academics more frequently use the term 'minority group' to refer to a category of people who experience relative disadvantage as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
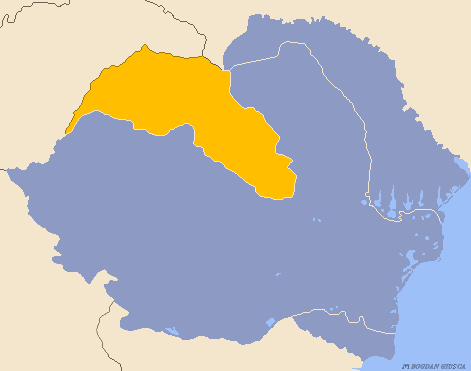
Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award, also known as the Vienna Diktat, was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all of Maramureș and part of Crișana, from Romania to Hungary. Background After World War I, the multiethnic Kingdom of Hungary was divided by the 1920 Treaty of Trianon to form several new nation states, but Hungary noted that the new state borders did not follow ethnic boundaries. The new nation state of Hungary was about a third the size of prewar Hungary, and millions of ethnic Hungarians were left outside the new Hungarian borders. Many historically-important areas of Hungary were assigned to other countries, and the distribution of natural resources was uneven. The various non-Hungarian populations generally saw the treaty as justice for their historically-marginalised nationalities, but the Hungarians considered the treaty to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania ( ro, Transilvania de Nord, hu, Észak-Erdély) was the region of the Kingdom of Romania that during World War II, as a consequence of the August 1940 territorial agreement known as the Second Vienna Award, became part of the Kingdom of Hungary. With an area of , the population was largely composed of both ethnic Romanians and Hungarians. In October 1944, Soviet and Romanian forces gained control of the territory, and by March 1945 Northern Transylvania returned to Romanian administration. After the war, this was confirmed by the Paris Peace Treaties of 1947. Background The region has a varied history. It was once the nucleus of the Kingdom of Dacia (82 BC–106 AD). In 106 AD the Roman Empire conquered the territory, systematically exploiting its resources. After the Roman legions withdrew in 271 AD, it was overrun by a succession of various tribes, bringing it under the control of the Carpi, Visigoths, Huns, Gepids, Avars, and Slavs. During the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)