|
Anti-Sacrilege Act
The Anti-Sacrilege Act (1825–1830) was a French law against blasphemy and sacrilege passed in April 1825 under King Charles X. The death penalty provision of the law was never applied, but a man named François Bourquin was sentenced to perpetual forced labour for sacrilegial burglary; the law was later revoked at the beginning of the July Monarchy under King Louis-Philippe. The draft bill In April 1824, King Louis XVIII's government, headed by the Ultra-royalist Jean-Baptiste, Comte de Villèle, introduced a first draft of the law into Parliament. The elections of December 1823, conducted under restricted census suffrage, had produced a heavy ultraroyalist majority in the Chamber of Deputies, which was therefore dubbed '' Chambre retrouvée'' (in reference to the ultra-royalist ''Chambre introuvable'' elected after the Restoration). Despite this majority, the bill failed as it was not accepted by the Chamber of Peers. After the accession of Charles X in September of the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Law
The Law of France refers to the legal system in the French Republic, which is a civil law legal system primarily based on legal codes and statutes, with case law also playing an important role. The most influential of the French legal codes is the Napoleonic Civil Code, which inspired the civil codes of Europe and later across the world. The Constitution of France adopted in 1958 is the supreme law in France. European Union law is becoming increasingly important in France, as in other EU member states. In academic terms, French law can be divided into two main categories: private law (''Droit privé'') and public law (''droit public''). This differs from the traditional common law concepts in which the main distinction is between criminal law and civil law. Private law governs relationships between individuals. It includes, in particular: * Civil law ('). This branch refers to the field of private law in common law systems. This branch encompasses the fields of inheritance la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
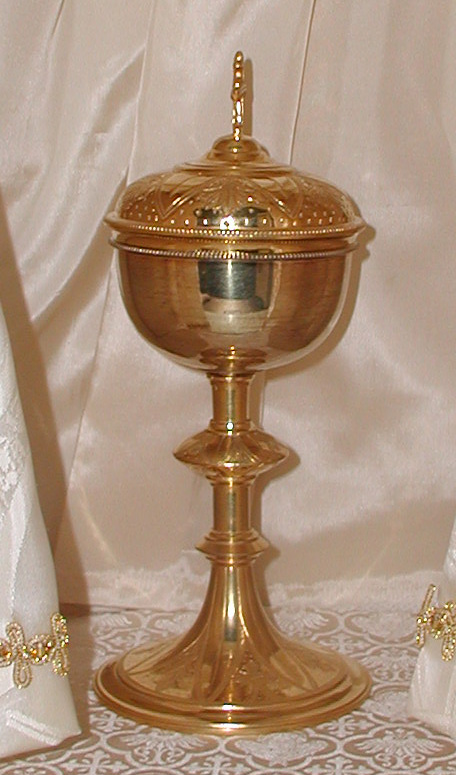
Ciborium (container)
A ciborium (plural ciboria; Medieval Latin ''ciborium'' (drinking cup), from the Ancient Greek κιβώριον ''kibōrion'', a type of drinking-cupOED.) is a vessel, normally in metal. It was originally a particular shape of drinking cup in Ancient Greece and Rome, but the word later came to refer to a large covered cup designed to hold hosts for, and after, the Eucharist, thus the counterpart (for the bread) of the chalice (for the wine). The word is also used for a large canopy over the altar of a church, which was a common feature of Early Medieval church architecture, now relatively rare. History The ancient Greek word referred to the cup-shaped seed vessel of the Egyptian water-lily ''nelumbium speciosum'' and came to describe a drinking cup made from that seed casing, or in a similar shape. These vessels were particularly common in ancient Egypt and the Greek East. The word "'ciborium'" was also used in classical Latin to describe such cups, although the only examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Paul Royer-Collard
Pierre Paul Royer-Collard (21 June 1763 – 2 September 1845) was a French statesman and philosopher, leader of the Doctrinaires group during the Bourbon Restoration (1814–1830). Biography Early life He was born at Sompuis, near Vitry-le-François (in modern-day Marne), the son of Anthony Royer, a small businessman. His mother, Angélique Perpétue Collard, had a reputation for strong character and great piety. His younger brother, Antoine-Athanase Royer-Collard, was a physician and pioneer in the field of psychiatry, at one point serving as chief physician at Charenton Asylum. Royer-Collard was sent at 12 to the college of Chaumont of which his uncle, Father Paul Collard, was director. He subsequently followed his uncle to Saint-Omer, where he studied mathematics. Career At the outbreak of the French Revolution, to which he was passionately sympathetic, he was practising at the Parisian bar. He was returned by his section, the Island of Saint-Louis, to the Commune, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amable Guillaume Prosper Brugière, Baron De Barante
Amable Guillaume Prosper Brugière, baron de Barante (June 10, 1782November 22, 1866) was a French statesman and historian. Associated with the center-left, he was described in France as the first man to call himself, "without any embarrassment or restriction, a Liberal." Life Barante was born at Riom, Puy-de-Dôme, the son of an advocate. At the age of sixteen he entered the École Polytechnique at Paris, and at twenty obtained his first appointment in the civil service. His abilities secured him rapid promotion, and in 1806 he obtained the post of auditor to the council of state. After being employed in several political missions in Germany, Poland, and Spain, during the next two years, he became prefect of Vendée. At the time of the return of Napoleon I he held the prefecture of Nantes, and this post he immediately resigned. On the second restoration of the Bourbons he was made councillor of state and secretary-general of the ministry of the interior. After filling for sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctrinaires
During the Bourbon Restoration (1814–1830) and the July Monarchy (1830–1848), the Doctrinals (french: doctrinaires) were a group of French royalists who hoped to reconcile the monarchy with the French Revolution and power with liberty. Headed by Royer-Collard, these liberal royalists were in favor of a constitutional monarchy, but with a heavily restricted census suffrage—Louis XVIII, who had been restored to the throne, had granted a Charter to the French with a Chamber of Peers and a Chamber of Deputies elected under tight electoral laws (only around 100,000 Frenchmen had at the time the right to vote). The Doctrinaires were a centrist, as well as a conservative-liberal group, but at that time, ''liberal'' was considered to be the mainstream political left, so the group was considered a centre-left group. During the July Monarchy, they were an intellectual and political group within the Resistance Party. Led by the Duke of Broglie and François Guizot, the Doct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberalism
Liberalism is a political and moral philosophy based on the rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostility to autocracy, cultural distaste for conservatism and for tradition in general, tolerance, and ... individualism". John Dunn. ''Western Political Theory in the Face of the Future'' (1993). Cambridge University Press. . Liberals espouse various views depending on their understanding of these principles. However, they generally support private property, market economies, individual rights (including civil rights and human rights), liberal democracy, secularism, rule of law, economic and political freedom, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of assembly, and freedom of religion. Liberalism is frequently cited as the dominant ideology of modern times.Wolfe, p. 23.Adams, p. 11. Liberalism became a distinct movement in the Age of Enlightenment, gaining popularity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Gabriel Ambroise De Bonald
Louis Gabriel Ambroise, Vicomte de Bonald (2 October 1754 – 23 November 1840) was a French counter-revolutionary philosopher and politician. He is mainly remembered for developing a theoretical framework from which French sociology would emerge. Life Early life and education Bonald came from an ancient noble family of Provence. Louis was born in the chateau of Le Monna, a modest estate that served as the family seat; the only son in his family, Louis was heir to the family estate. Le Monna is situated just east of the market town of Millau, overlooking the Dourbie river. His father, Antoine Sébastien de Bonald, died when Louis was four years old and the young boy would be brought up by his pious mother Anne ''née'' de Boyer du Bosc de Périe. Like many in the provincial nobility of the time, Anne was influenced by the Jansenists and brought up her son with a stern Catholic piety. De Bonald was tutored at Le Monna until the age of eleven, when he was sent to boar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterrevolutionary
A counter-revolutionary or an anti-revolutionary is anyone who opposes or resists a revolution, particularly one who acts after a revolution in order to try to overturn it or reverse its course, in full or in part. The adjective "counter-revolutionary" pertains to movements that would restore the state of affairs, or the principles, that prevailed during a prerevolutionary era. Definition A counter-revolution is opposition or resistance to a revolutionary movement. It can refer to attempts to defeat a revolutionary movement before it takes power, as well as attempts to restore the old regime after a successful revolution. Europe France The word "counter-revolutionary" originally referred to thinkers who opposed themselves to the 1789 French Revolution, such as Joseph de Maistre, Louis de Bonald or, later, Charles Maurras, the founder of the '' Action française'' monarchist movement. More recently, it has been used in France to describe political movements that reject t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comte De Breteuil
''Comte'' is the French, Catalan and Occitan form of the word 'count' (Latin: ''comes''); ''comté'' is the Gallo-Romance form of the word 'county' (Latin: ''comitatus''). Comte or Comté may refer to: * A count in French, from Latin ''comes'' * A county in France, that is, the territory ruled by a count * La Comté, a commune in the Pas-de-Calais département of France * Comté cheese, a French cheese from Franche-Comté People with the surname * Alfred Comte (1895–1965), Swiss aviation pioneer * Auguste Comte (1798–1857), French philosopher * Charles Comte (1782–1837), French lawyer, journalist and political writer * Claudine le Comte (born 1950), Belgian fencer * Fabienne Comte, French statistician * Fernando Compte (1930–2013), founder and first president of the International Sambo Federation * Ferran Soriano i Compte (born 1967), Spanish CEO of various football clubs, including Manchester City F.C. * Harry Comte (1909—1945), Australian rules footballer * Louis Comte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre-Denis, Comte De Peyronnet
Pierre-Denis, comte de Peyronnet (9 October 1778, in Bordeaux – 2 January 1854) was the president of the Bordeaux Court in France in 1815, Minister of Justice from 1821 to 1828 and four times Minister of Interior. Opposed to Napoleon's Empire, he rallied himself to the Bourbons during the Restoration. An Ultra-royalist, he supported the Anti-Sacrilege Act, the 1827 law restricting press freedom and the ''loi du droit d'aînesse''. Life The Count of Peyronnet's father had bought a charge of secretary to the King, thus conferring himself a noble title. He was guillotined during the Terror. After law studies, Pierre-Denis de Peyronnet was received as a lawyer in 1796. On 26 October 1815, he was named president of the first instance Court of Bordeaux, and then, a year later, public prosecutor in Bourges. The Count of Peyronnet was elected deputy on 13 November 1820, and established himself in Paris. Nominated general prosecutor at the Royal Court of Rouen, he was then called fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like '' liberté, égalité, fraternité'' reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day. Its causes are generally agreed to be a combination of social, political and economic factors, which the ''Ancien Régime'' proved unable to manage. In May 1789, widespread social distress led to the convocation of the Estates General, which was converted into a National Assembly in June. Continuing unrest culminated in the Storming of the Bastille on 14 July, which led to a series of radical measures by the Assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to * the French word for " ancient, old" ** Société des anciens textes français * the French for "former, senior" ** Virelai ancien ** Ancien Régime ** Ancien Régime in France {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |