|
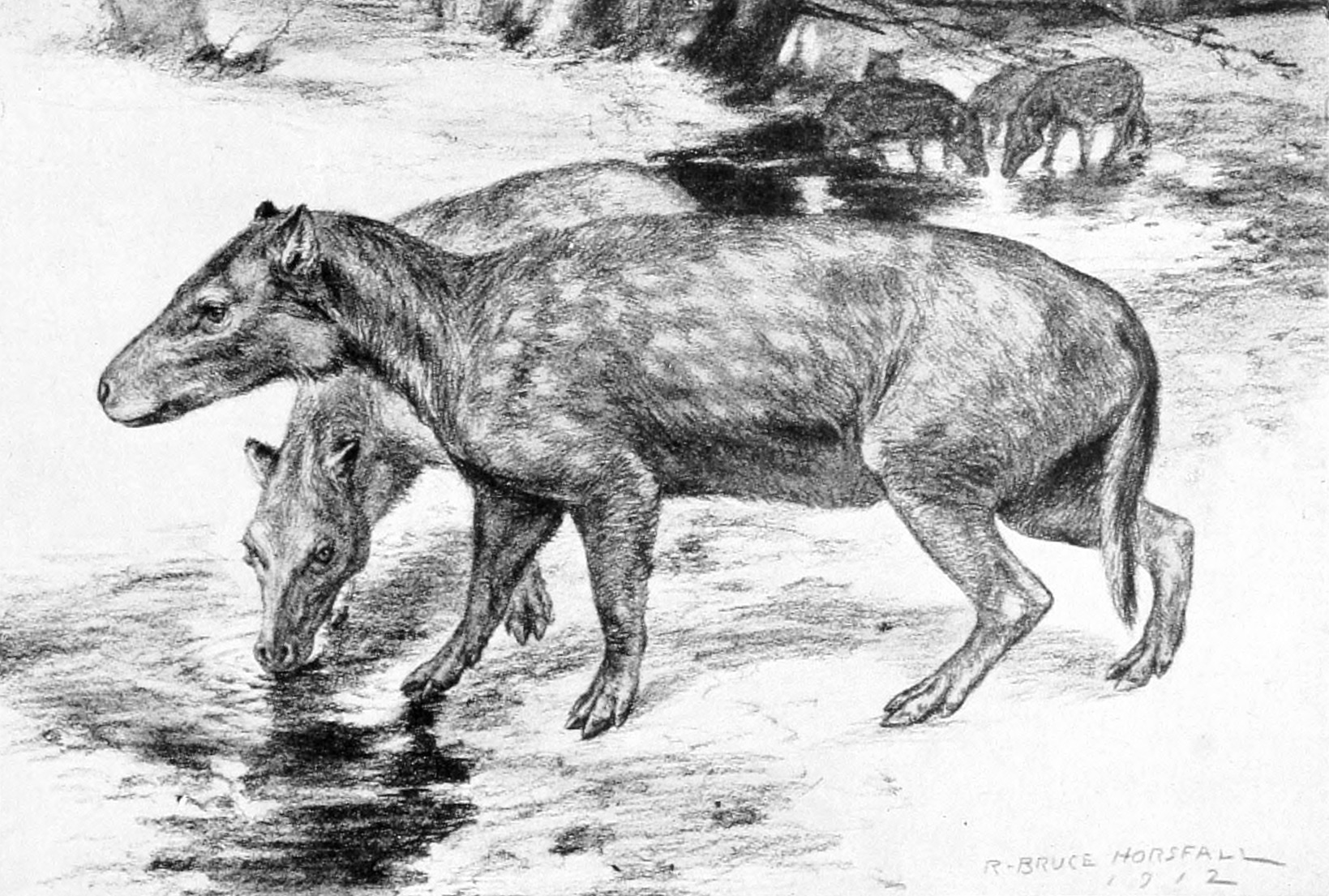
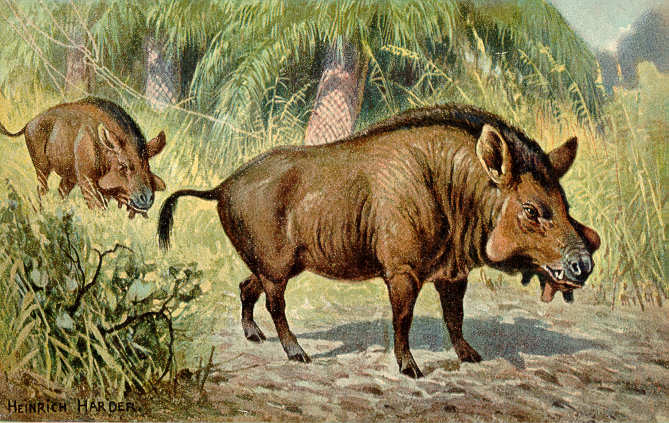
Anthracotheres
Anthracotheriidae is a paraphyletic family of extinct, hippopotamus-like artiodactyl ungulates related to hippopotamuses and whales. The oldest genus, ''Elomeryx'', first appeared during the middle Eocene in Asia. They thrived in Africa and Eurasia, with a few species ultimately entering North America during the Oligocene. They died out in Europe and Africa during the Miocene, possibly due to a combination of climatic changes and competition with other artiodactyls, including pigs and true hippopotamuses. The youngest genus, ''Merycopotamus'', died out in Asia during the late Pliocene. The family is named after the first genus discovered, ''Anthracotherium'', which means "coal beast", as the first fossils of it were found in Paleogene-aged coal beds in France. Fossil remains of the anthracothere genus were discovered by the Harvard University and Geological Survey of Pakistan joint research project (Y-GSP) in the well-dated middle and late Miocene deposits of the Pothohar Plateau i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracotherium
''Anthracotherium'' (from el, ἄνθραξ , 'coal' and el, θηρίον 'beast') was a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulate mammals, characterized by having 44 teeth, with five semi-crescentic cusps on the crowns of the upper molars. The genus ranged from the middle Eocene period until the early Miocene, having a distribution throughout Eurasia. Material subjectively assigned to ''Anthracotherium'' from Pakistan suggests the last species died out soon after the start of the Miocene. Description The genus typifies the family Anthracotheriidae, if only because it is the most thoroughly studied. In many respects, especially the anatomy of the lower jaw, ''Anthracotherium'', as with the other members of the family, is allied to the hippopotamus, of which it is probably an ancestral form. Anthracotheres, together with hippos, are grouped with cetaceans in the clade Whippomorpha. Etymology The genus name stems from the fact that the holotype and other first specimens were ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiodactyl
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippopota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merycopotamus
''Merycopotamus'' is an extinct genus of Asian anthracothere that appeared during the Middle Miocene, and died out in the Late Pliocene. At the height of the genus' influence, species ranged throughout southern Asia. With the extinction of the last species, ''M. dissimilis'', the lineage of anthracotheres came to an end. ''Merycopotamus'' was closely related to the anthracothere genus ''Libycosaurus'', which, unlike the former, never left Africa Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area .... In fact, some African fossils originally placed in ''Merycopotamus'', but are now referred to ''Libycosaurus''. References Anthracotheres Miocene even-toed ungulates Pliocene even-toed ungulates Piacenzian extinctions Neogene mammals of Asia Fossil taxa described in 1847 P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbunodon
''Microbunodon'' was a genus of extinct artiodactyl mammals in the family Anthracotheriidae. It lived between the upper Eocene and the lower Pliocene (about 35–5 million years ago). Its fossil remains have been found in Europe and Asia. Description ''Microbunodon'', unlike most of its close relatives, was small in size and with a slight build. Its weight did not exceed 20–25 kilograms and the skull was about 20–30 centimeters long. ''Microbunodon'' was slim with long legs and a short snout with long prominent canine teeth in males, similar to a saber-toothed cat. It was characterized by a fused mandibular symphysis, with a ventral ridge-like prominence. Classification The genus ''Microbunodon'' was established by Deperet in 1908 to accommodate a species previously described by Georges Cuvier in 1822 and attributed to the genus ''Anthracotherium'', as ''A. minimum'', from the Oligocene superior of France. The type species, ''Microbunodon minimum'', lived in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaggermeryx
''Jaggermeryx'' is an extinct genus of semiaquatic anthracothere, ungulates related to hippopotamuses, from the Early Miocene Moghara Formation in Egypt. The genus was named after Mick Jagger. Etymology Its genus name, ''Jaggermeryx'' is derived from ''Jagger'', after Mick Jagger, and ''meryx'', the Greek word means ruminant, which is common suffix for genus name of artiodactyls. Species name, ''naida'' is derived from ''Naias'', the Greek word means water nymph. It was named after Mick Jagger, lead singer for The Rolling Stones, because of its oversized lips. There was some debate among the team as to whether it should instead be named after Angelina Jolie. "Some of my colleagues suggested naming the new species after Hollywood star Angelina Jolie, because she also has famous lips," said lead author Ellen Miller. It was eventually settled to name the species after Jagger when co-author Gregg Gunnell sided with Miller. Discovery The first fossils of the species were desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elomeryx
''Elomeryx'' is an extinct genus of artiodactyl ungulate, and is among the earliest known anthracotheres. The genus was extremely widespread, first being found in Asia in the middle Eocene, in Europe during the latest Eocene, and having spread to North America by the early Oligocene. It is closely related to cows, pigs, deer, cetaceans, and possibly hippopotamuses. ''Elomeryx'' was about in body length, and had a long, vaguely horse-like head. It had small tusks which it used to uproot plants, and spoon-shaped incisors ideal for pulling and cropping water plants. ''Elomeryx'' had five-toed hind legs and four-toed front legs, resulting in wide feet which made it easier to walk on soft mud. It probably had similar habits to the modern hippopotamus The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbunodontinae
The microbunodontines were an extinct subfamily of anthracotheres that were predominately a Paleogene group of Eurasian artiodactyls. The group died out at the end of the Late Miocene. It comprised the genera '' Anthracokeryx'', '' Geniokeryx'', ''Microbunodon ''Microbunodon'' was a genus of extinct artiodactyl mammals in the family Anthracotheriidae. It lived between the upper Eocene and the lower Pliocene (about 35–5 million years ago). Its fossil remains have been found in Europe and Asia. Descr ...'', and possibly '' Etruscotherium''. They are different from the other anthracothere lineages by their smaller size, slenderer limbs and male specimens having laterally compressed, longer canines. They were originally classified as members of the other subfamily of anthracotheres, Anthracotheriinae but recent phylogenetic studies have found them to be their own clade sister to Bothriodontinae. References Anthracotheres Mammal subfamilies Eocene first appearances [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothriodontinae
The bothriodontines are a paraphyletic assemblage of anthracotheres that originated from Eurasia in the late middle Eocene (Bartonian). The group can be distinguished from other anthracothere lineages by their upper molars with the mesostyle that is occupied by the transverse valley, selenodont cusps, ventrally concave symphysis, elongated muzzles, with presence of a diastema between the canine and first premolar. The size range of the group ranged from small, basal forms to larger and more derived forms. During their evolution, the bothriodontines undergone a trend from evolving from small basal forms such as '' Qatraniodon'' into larger taxa such as ''Libycosaurus'' and ''Merycopotamus ''Merycopotamus'' is an extinct genus of Asian anthracothere that appeared during the Middle Miocene, and died out in the Late Pliocene. At the height of the genus' influence, species ranged throughout southern Asia. With the extinction of th ...''. Some genera the snouts became even more e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracotheriinae
The anthracotheriines are an extinct subfamily of anthracotheres that comprised Paleogene to early Neogene North American and Eurasian artiodactyls. The group contained the genera ''Anthracotherium'', '' Heptacodon'', and '' Paenanthracotherium'', as well as possibly '' Myaingtherium'' and '' Siamotherium''. They were small to large sized anthracotheres, and when compared to the other two subfamilies, Microbunodontinae and Bothriodontinae The bothriodontines are a paraphyletic assemblage of anthracotheres that originated from Eurasia in the late middle Eocene (Bartonian). The group can be distinguished from other anthracothere lineages by their upper molars with the mesostyle tha ..., anthracotheriines are found to occupy a primitive, basal position in the family. References Anthracotheres Mammal subfamilies Eocene first appearances {{paleo-eventoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bugtitherium
''Bugtitherium'' is an extinct genus of anthracothere found in late Oligocene ( Chattian) deposits in the Bugti Hills of Baluchistan, Pakistan. Incisor teeth that Pilgrim (1908) referred to ''Bugtitherium'' were recognized as instead belonging to the giant paraceratheriid ''Paraceratherium ''Paraceratherium'' is an extinct genus of hornless rhinoceros. It is one of the largest terrestrial mammals that has existed and lived from the early to late Oligocene epoch (34–23 million years ago). The first fossils were discovered ...''.Cooper, C. F. (1924). "On the Skull and Dentition of Paraceratherium bugtiense: A Genus of Aberrant Rhinoceroses from the Lower Miocene Deposits of Dera Bugti". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 212 (391–401): 369–394. doi:10.1098/rstb.1924.0009. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q55606097 Oligocene mammals of Asia Anthracotheres Prehistoric even-toed ungulate genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracothema
''Anthracothema'' was a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulate mammals that lived in Myanmar during the late Eocene. Taxonomy Ducrocq (1999) and Tsubamoto et al. (2002) considered ''Anthracothema'' a synonym of ''Anthracotherium ''Anthracotherium'' (from el, ἄνθραξ , 'coal' and el, θηρίον 'beast') was a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulate mammals, characterized by having 44 teeth, with five semi-crescentic cusps on the crowns of the upper molars. The ...''. However, Lihoreau et al. (2004) and Scherler et al. (2018) rejected the synonymy, with the latter recovering it as sister to '' Myaingtherium'' and '' Siamotherium''.Laureline Scherler; Fabrice Lihoreau; Damien Becker (2018). "To split or not to split Anthracotherium? A phylogeny of Anthracotheriinae (Cetartiodactyla: Hippopotamoidea) and its palaeobiogeographical implications". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. Online edition. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zly052. References Anthracotheres Eocen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracohyus
''Anthracohyus'' was a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulate mammal belonging to Anthracotheriidae that lived in Asia during the middle to late Eocene. Taxonomy ''Anthracohyus'' is treated as a junior synonym of ''Anthracotherium ''Anthracotherium'' (from el, ἄνθραξ , 'coal' and el, θηρίον 'beast') was a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulate mammals, characterized by having 44 teeth, with five semi-crescentic cusps on the crowns of the upper molars. The ...'' by Tsubamoto et al. (2002) based on similarities in dental morphology.Tsubamoto T, Takai M, Egi N, Shigehara N, Tun ST, Aung AK, Soe Aung Naing, Thein T. 2002. The Anthracotheriidae (Mammalia; Artiodactyla) from the Eocene Pondaung Formation (Myanmar) and comments on some other anthracotheres from the Eocene of Asia. Paleontol Res. 6:363–384. However, this synonymy was rejected by Lihoreau and Ducrocq (2007).Lihoreau F, Ducrocq S. 2007. Family Anthracotheriidae. In: Prothero DR, Foss SE, editors. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |