|
Anthony Cecil Capel Miers
Rear Admiral Sir Anthony Cecil Capel Miers, (11 November 1906 – 30 June 1985), known as "Crap Miers" and "Gamp", was a Royal Navy officer who served in the submarine service during the Second World War. Miers was a recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. He was allegedly responsible for two war crime incidents, while commanding , including the shooting of seven Germans in a life raft. Early life Born in 1906 in Inverness, Scotland, the son of an army captain killed in the First World War, Miers was educated at Stubbington House School in Gosport, Edinburgh Academy, and Wellington College. In 1924 he joined the Royal Navy as a special entry cadet and volunteered for the submarine service in 1929. He could be hot-tempered, and in 1933 was court martialled for striking a rating. Miers' career however continued, with his first submarine command (1936–7) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverness, Scotland
Inverness (; from the gd, Inbhir Nis , meaning "Mouth of the River Ness"; sco, Innerness) is a city in the Scottish Highlands. It is the administrative centre for The Highland Council and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands. Historically it served as the county town of the county of Inverness-shire. Inverness lies near two important battle sites: the 11th-century battle of Blàr nam Fèinne against Norway which took place on the Aird, and the 18th century Battle of Culloden which took place on Culloden Moor. It is the northernmost city in the United Kingdom and lies within the Great Glen (Gleann Mòr) at its northeastern extremity where the River Ness enters the Beauly Firth. At the latest, a settlement was established by the 6th century with the first royal charter being granted by Dabíd mac Maíl Choluim (King David I) in the 12th century. Inverness and Inverness-shire are closely linked to various influential clans, including Clan Mackintosh, Clan Fraser and Clan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverness
Inverness (; from the gd, Inbhir Nis , meaning "Mouth of the River Ness"; sco, Innerness) is a city in the Scottish Highlands. It is the administrative centre for The Highland Council and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands. Historically it served as the county town of the county of Inverness-shire. Inverness lies near two important battle sites: the 11th-century battle of Blàr nam Fèinne against Norway which took place on the Aird, and the 18th century Battle of Culloden which took place on Culloden Moor. It is the northernmost city in the United Kingdom and lies within the Great Glen (Gleann Mòr) at its northeastern extremity where the River Ness enters the Beauly Firth. At the latest, a settlement was established by the 6th century with the first royal charter being granted by Dabíd mac Maíl Choluim (King David I) in the 12th century. Inverness and Inverness-shire are closely linked to various influential clans, including Clan Mackintosh, Clan Fraser and Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
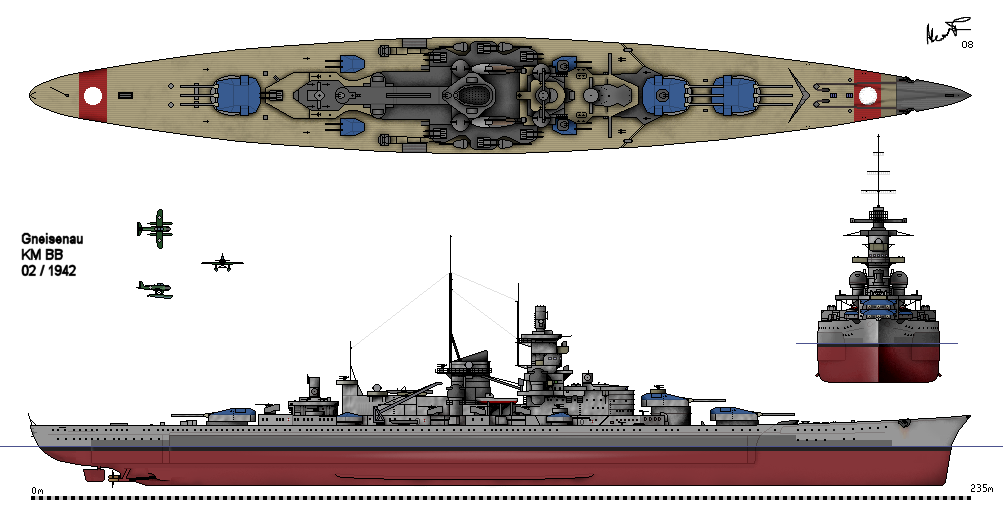
German Battleship Gneisenau
''Gneisenau'' () was a German capital ship, alternatively described as a battleship and battlecruiser, of Nazi Germany's '' Kriegsmarine''. She was the second vessel of her class, which included her sister ship, . The ship was built at the ''Deutsche Werke'' dockyard in Kiel; she was laid down on 6 May 1935 and launched on 8 December 1936. Completed in May 1938, the ship was armed with a main battery of nine 28 cm (11 in) C/34 guns in three triple turrets. Plans were approved, once construction had started, to replace these weapons with six 38 cm (15 in) SK C/34 guns in twin turrets, but as this would involve a lot of redesign, construction continued with the lower calibre guns. The intent was to make the upgrade in the winter of 1940–41, but the outbreak of World War II stopped this. ''Gneisenau'' and ''Scharnhorst'' operated together for much of the early portion of World War II, including sorties into the Atlantic to raid British merchant shipping. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
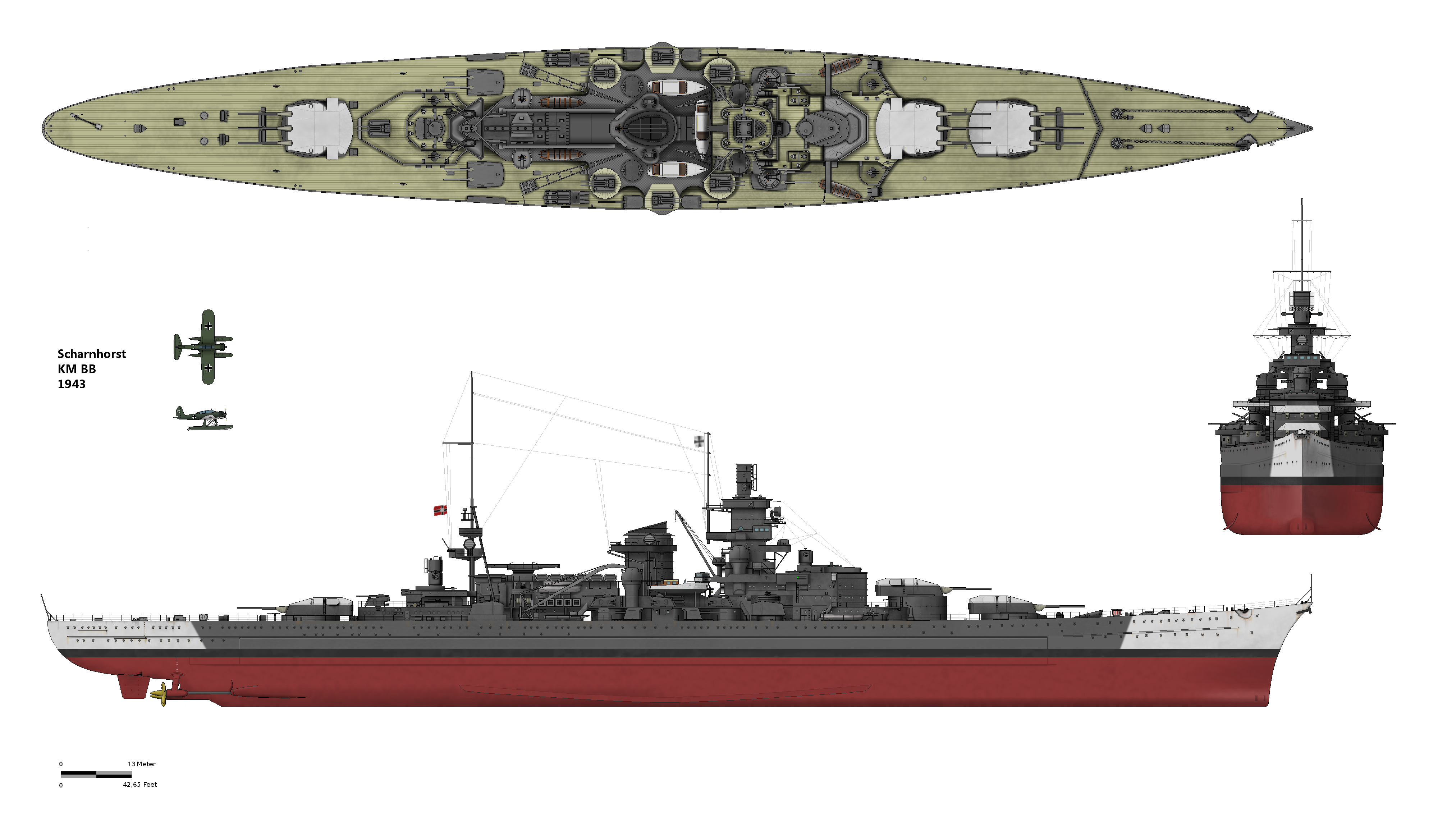
German Battleship Scharnhorst
''Scharnhorst'' was a German capital ship, alternatively described as a battleship or battlecruiser, of Nazi Germany's ''Kriegsmarine''. She was the lead ship of her class, which included her sister ship . The ship was built at the ''Kriegsmarinewerft'' dockyard in Wilhelmshaven; she was laid down on 15 June 1935 and launched a year and four months later on 3 October 1936. Completed in January 1939, the ship was armed with a main battery of nine 28 cm (11 in) C/34 guns in three triple turrets. Plans to replace these weapons with six 38 cm (15 in) SK C/34 guns in twin turrets were never carried out. ''Scharnhorst'' and ''Gneisenau'' operated together for much of the early portion of World War II, including sorties into the Atlantic to raid British merchant shipping. During her first operation, ''Scharnhorst'' sank the armed merchant in a short engagement (November 1939). ''Scharnhorst'' and ''Gneisenau'' participated in Operation Weserübung (April–Jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
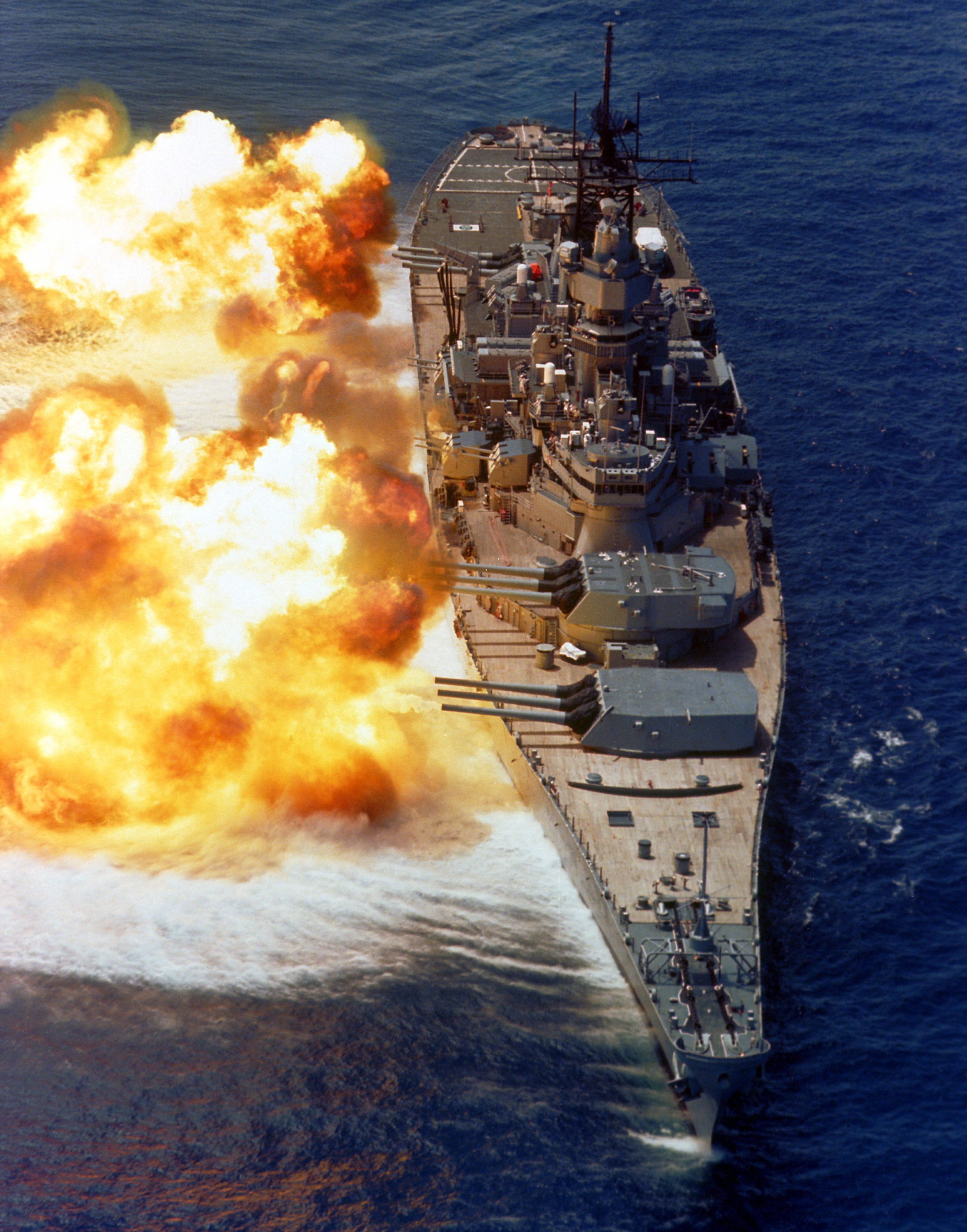
Battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1880s to describe a type of ironclad warship,Stoll, J. ''Steaming in the Dark?'', Journal of Conflict Resolution Vol. 36 No. 2, June 1992. now referred to by historians as pre-dreadnought battleships. In 1906, the commissioning of into the United Kingdom's Royal Navy heralded a revolution in the field of battleship design. Subsequent battleship designs, influenced by HMS ''Dreadnought'', were referred to as "dreadnoughts", though the term eventually became obsolete as dreadnoughts became the only type of battleship in common use. Battleships were a symbol of naval dominance and national might, and for decades the battleship was a major factor in both diplomacy and military strategy.Sondhaus, L. ''Naval Warfare 1815–1914'', . A global arms race in battleship cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depot Ship
A depot ship is an auxiliary ship used as a mobile or fixed base for submarines, destroyers, minesweepers, fast attack craft, landing craft, or other small ships with similarly limited space for maintenance equipment and crew dining, berthing and relaxation. Depot ships may be identified as tenders in American English. Depot ships may be specifically designed for their purpose or be converted from another purpose. Function Depot ships provide services unavailable from local naval base shore facilities. Industrialized countries may build naval bases with extensive workshops, warehouses, barracks, and medical and recreation facilities. Depot ships operating within such bases may provide little more than command staff offices,Lenton (1975) pp.391-394 while depot ships operating at remote bases may perform unusually diverse support functions. Some United States Navy submarine depot ships operating in the Pacific during World War II included sailors with Construction Battalion ratings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Long
Loch Long is a body of water in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. The Sea Loch extends from the Firth of Clyde at its southwestern end. It measures approximately in length, with a width of between . The loch also has an arm, Loch Goil, on its western side. Although it is fairly long, its name actually comes from the Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic for "ship lake". Prior to their defeat at the Battle of Largs in 1263, Viking raiders sailed up Loch Long to Arrochar, Argyll, Arrochar, and then dragged their longships 2 miles overland to Tarbet, Argyll, Tarbet and into Loch Lomond. Being inland, the settlements around Loch Lomond were more vulnerable to attack. Loch Long forms part of the coast of the Cowal peninsula and forms the entire western coastline of the Rosneath Peninsula. Loch Long was historically the boundary between Argyll and Dunbartonshire; however, in 1996 boundary redrawing meant that it moved wholly within the council area of Argyll and Bute. The steamboat ''Chancellor'' us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
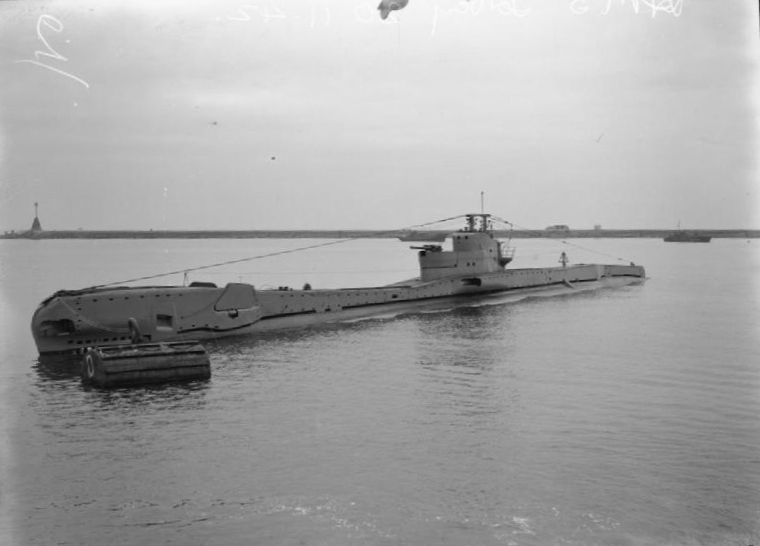
HMS Torbay
Five ships of the British Royal Navy have been named HMS ''Torbay'', after Torbay on the southwest English coast. * , an 80-gun second rate launched in 1693, rebuilt in 1719 and broken up in 1749. * HMS ''Torbay'' was previously , a 90-gun second rate launched in 1683, renamed ''Torbay'' in 1750 and sold in 1785. * , an launched in 1919. She was transferred to the Royal Canadian Navy in 1928 and renamed . She was sold in 1937. * , a T-class submarine launched in 1940 and sold in 1945. * , a nuclear submarine A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ... launched 1985 and decommissioned in 2017. {{DEFAULTSORT:Torbay Royal Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mentioned In Despatches
To be mentioned in dispatches (or despatches, MiD) describes a member of the armed forces whose name appears in an official report written by a superior officer and sent to the high command, in which their gallant or meritorious action in the face of the enemy is described. In some countries, a service member's name must be mentioned in dispatches as a condition for receiving certain decorations. United Kingdom, British Empire, and Commonwealth of Nations Servicemen and women of the British Empire or the Commonwealth who are mentioned in despatches (MiD) are not awarded a medal for their actions, but receive a certificate and wear an oak leaf device on the ribbon of the appropriate campaign medal. A smaller version of the oak leaf device is attached to the ribbon when worn alone. Prior to 2014, only one device could be worn on a ribbon, irrespective of the number of times the recipient was mentioned in despatches. Where no campaign medal is awarded, the oak leaf is worn direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Fleet
The Home Fleet was a fleet of the Royal Navy that operated from the United Kingdom's territorial waters from 1902 with intervals until 1967. In 1967, it was merged with the Mediterranean Fleet creating the new Western Fleet. Before the First World War, it consisted of the four Port Guard ships. In 1905 it was disestablished, and from 1905 to 1907 remaining ships at a lesser state of readiness were split into the reserve divisions (Devonport Division, Nore Division, and Portsmouth Division). During the First World War, it comprised some of the older ships of the Royal Navy. During the Second World War, it was the Royal Navy's main battle force in European waters. Pre-First World War In the first years of the 20th century, the Royal Navy had four 'Port Guard' ships, stationed in the major naval bases, partially to act as flagships for the admirals commanding at those ports. These vessels appear to have been stationed at the Nore, Portsmouth, and Plymouth, as well as one other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Martial
A court-martial or court martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of members of the armed forces subject to military law, and, if the defendant is found guilty, to decide upon punishment. In addition, courts-martial may be used to try prisoners of war for war crimes. The Geneva Conventions require that POWs who are on trial for war crimes be subject to the same procedures as would be the holding military's own forces. Finally, courts-martial can be convened for other purposes, such as dealing with violations of martial law, and can involve civilian defendants. Most navies have a standard court-martial which convenes whenever a ship is lost; this does not presume that the captain is suspected of wrongdoing, but merely that the circumstances surrounding the loss of the ship be made part of the official record. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

_Oak_Leaf_Cluster.jpg)