|
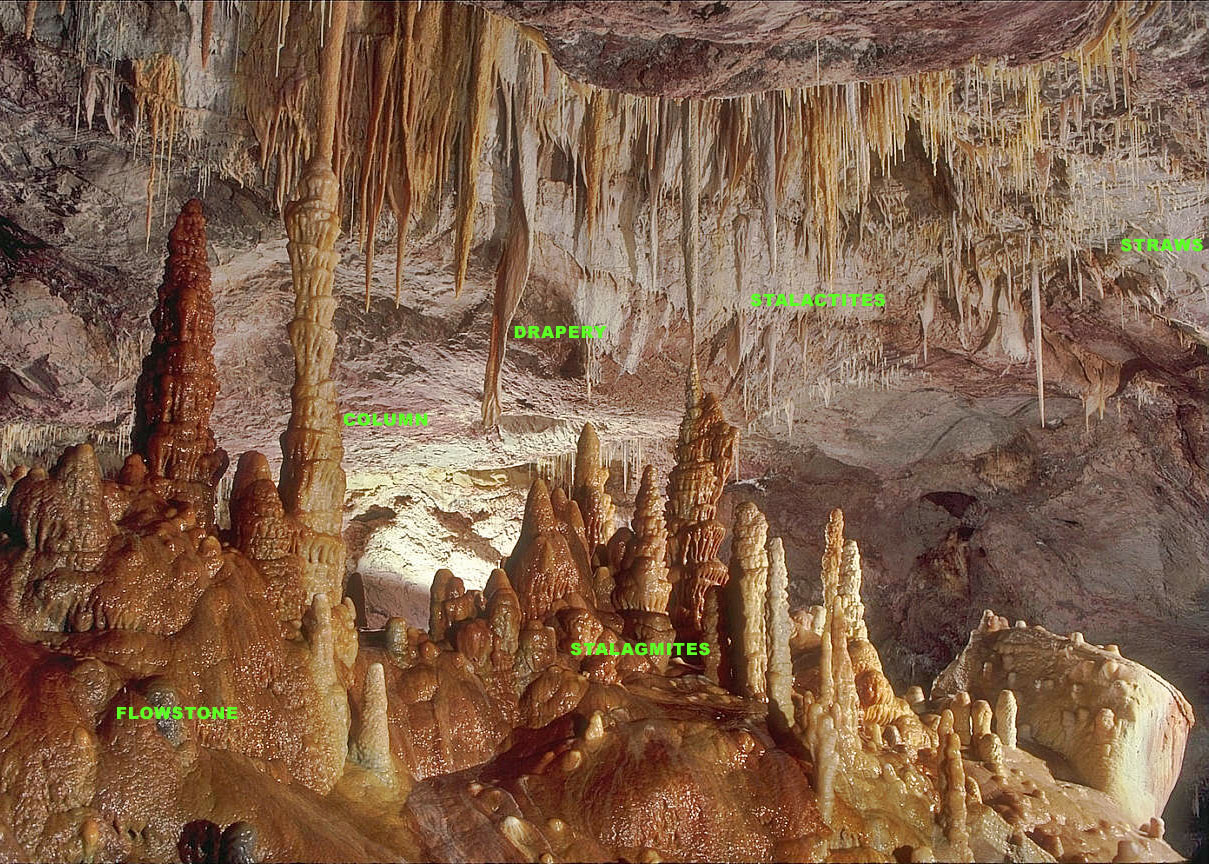
Anthodite
Anthodites (Greek ἄνθος ''ánthos'', "flower", ''-ode'', adjectival combining form, ''-ite'' adjectival suffix) are speleothems (cave formations) composed of long needle-like crystals situated in clusters which radiate outward from a common base. The "needles" may be quill-like or feathery. Most anthodites are made of the mineral aragonite (a variety of calcium carbonate, CaCO3), although some are composed of gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O). The term ''anthodite'' is first cited in the scientific literature in 1965 by Japanese researcher N. Kashima, who described "flower-like dripstone" composed of "an alternation of calcite and aragonite". Structure, composition and appearance The individual crystals of anthodites develop in a form described as "acicular" (needle-like) and often branch out as they grow. They usually grow downward from a cave's ceiling. Aragonite crystals are contrasted with those made of calcite (another variety of calcium carbonate) in that the latter tend to be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skyline Caverns
Skyline Caverns is a series of geologic caves and a tourist attraction located in Warren County, Virginia, south of Front Royal, Virginia, Front Royal. The caverns were discovered by Walter S. Amos, a retired geologist and mineralogist from Winchester, Virginia, on December 17, 1937. Skyline Caverns is open year-round, offering guided tours through the caverns. History Walter S. Amos was contracted by several private and government agencies to search for caves and caverns to open in conjunction with Skyline Drive. During his search, he came across a sinkhole that was located approximately where the parking lot is currently situated. Normally, sinkholes are created by the collapsing of a cavern roof, which takes the ground above with it. When he saw there was no water in the sinkhole, which meant there had to be a drain nearby, he believed he had discovered a cavern. Knowing this, Amos began to search the edges for some opening to the possible cave system below. He found this ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craighead Caverns
Craighead Caverns is an extensive cave system located in between Sweetwater and Madisonville, Tennessee. It is best known for containing the United States' largest and the world's second largest non- subglacial underground lake, The Lost Sea. In addition to the lake, the caverns contain an abundance of crystal clusters called anthodites, stalactites, stalagmites, and a waterfall. History Located in the foothills of the Great Smoky Mountains, the caverns are named after their former owner, a Cherokee Native American, Chief Craighead. The caverns were used by the Cherokee as a meeting place for their councils. During the American Civil War, the caves were mined by Confederate soldiers for saltpeter, a commodity necessary to the manufacture of gunpowder. The major cave and lake area was also used as a hideout for moonshiners, especially during the Prohibition era. In 1939, explorers found the fossilized remains of a Pleistocene jaguar. The persons who made the discovery w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speleothem
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety of forms, depending on their depositional history and environment. Their chemical composition, gradual growth, and preservation in caves make them useful paleoclimatic proxies. Chemical and physical characteristics More than 300 variations of cave mineral deposits have been identified. The vast majority of speleothems are calcareous, composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) minerals (calcite or aragonite). Less commonly, speleothems are made of calcium sulfate (gypsum or mirabilite) or opal. Speleothems of pure calcium carbonate or calcium sulfate are translucent and colorless. The presence of iron oxide or copper provides a reddish brown color. The presence of manganese oxide can create darker colors such as black or dark brown. Speleothems can also be brown d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helictite
A helictite is a speleothem (cave-formed mineral) found in a limestone cave that changes its axis from the vertical at one or more stages during its growth. Helictites have a curving or angular form that looks as if they were grown in zero gravity. They are most likely the result of capillary forces acting on tiny water droplets, a force often strong enough at this scale to defy gravity. Helictites are, perhaps, the most delicate of cave formations. They are usually made of needle-form calcite and aragonite. Helictite forms have been described in several types: ribbon helictites, saws, rods, butterflies, "hands", curly-fries, and "clumps of worms". They typically have radial symmetry. They can be easily crushed or broken by the slightest touch. Because of this, helictites are rarely seen within arm's reach in tourist caves. Timpanogos Cave National Monument in Utah has one of the largest collections of these formations in the world. Large numbers are also in the Jenolan Caves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helictite
A helictite is a speleothem (cave-formed mineral) found in a limestone cave that changes its axis from the vertical at one or more stages during its growth. Helictites have a curving or angular form that looks as if they were grown in zero gravity. They are most likely the result of capillary forces acting on tiny water droplets, a force often strong enough at this scale to defy gravity. Helictites are, perhaps, the most delicate of cave formations. They are usually made of needle-form calcite and aragonite. Helictite forms have been described in several types: ribbon helictites, saws, rods, butterflies, "hands", curly-fries, and "clumps of worms". They typically have radial symmetry. They can be easily crushed or broken by the slightest touch. Because of this, helictites are rarely seen within arm's reach in tourist caves. Timpanogos Cave National Monument in Utah has one of the largest collections of these formations in the world. Large numbers are also in the Jenolan Caves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Speleological Society
The National Speleological Society (NSS) is an organization formed in 1941 to advance the exploration, conservation, study, and understanding of caves in the United States. Originally headquartered in Washington D.C., its current offices are in Huntsville, Alabama. The organization engages in the research and scientific study, restoration, exploration, and protection of caves. It has more than 10,000 members in more than 250 grottos. History The Speleological Society of the District of Columbia (SSDC) was formed on May 6, 1939 by Bill Stephenson. In the fall of 1940, the officers of the SSDC drafted a proposed constitution that would transform the SSDC into the National Speleological Society. On January 24, 1941, Stephenson sent a letter to all members of the SSDC announcing that "on January 1 the Society was reorganized as a national organization." The New England Grotto was the first NSS Grotto. It was chartered in 1941 with Clay Perry as president and Ned Anderson as vice pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsomite
Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula MgSO4·7H2O. Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system as rarely found acicular or fibrous crystals, the normal form is as massive encrustations. It is colorless to white with tints of yellow, green and pink. The Mohs hardness is 2 to 2.5 and it has a low specific gravity of 1.67. It is readily soluble in water. It absorbs water from the air and converts to hexahydrate with the loss of one water molecule and a switch to monoclinic structure. Etymology It was first systematically described in 1806 for an occurrence near Epsom, Surrey, England, after which it was named. Discovery and occurrence Epsomite forms as encrustations or efflorescences on limestone cavern walls and mine timbers and walls, rarely as volcanic fumarole deposits, and as rare beds in evaporite layers such as those found in certain bodies of salt water. It occurs in association with melanterite, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Flower
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorganisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Cave
Wind Cave National Park is an American national park located north of the town of Hot Springs in western South Dakota. Established on January 3, 1903 by President Theodore Roosevelt, it was the sixth national park in the U.S. and the first cave to be designated a national park anywhere in the world. The cave is notable for its calcite formations known as boxwork, as well as its frostwork. Approximately 95 percent of the world's discovered boxwork formations are found in Wind Cave. The cave is recognized as the densest cave system in the world, with the greatest passage volume per cubic mile. Wind Cave is the seventh longest cave in the world with of explored cave passageways () and the third longest cave in the United States. Above ground, the park includes the largest remaining natural mixed-grass prairie in the United States. Origin of name The passages in the park are said to "breathe" as air continually moves into or out of them, equalizing the atmospheric pressure of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalagmite
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek , from , "dropping, trickling") is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically composed of calcium carbonate, but may consist of lava, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). The corresponding formation hanging down from the ceiling of a cave is a stalactite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground", another is that, as with ants in the pants, the mites go up and the tights (tites) come down. Formation and type Limestone stalagmites The most common stalagmites are speleothems, which usually form in limestone caves. Stalagmite formation occurs only under certain pH conditions within the cavern. They form through deposition of calcium carbonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frostwork
In geology, frostwork is a type of speleothem (cave formation) with acicular ("needle-like") growths almost always composed of aragonite (a polymorph of calcite) or calcite replaced aragonite. It is a variety of anthodite. Frostwork can also be made of opal or gypsum. In some caves frostwork may grow on top of cave popcorn or boxwork. In architecture frost-work or frostwork refers to a style of rustication carved with a vertically-oriented pattern evoking hanging pond-weed or algae, or icicles. It is mainly found in garden architecture, where water is to flow over or near the surface. "Rustication" Other decorative arts may use the term for other decorative patterns imitating frost or ice. Formation The origin of frostwork is somewhat controversial. Formation of ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)