|
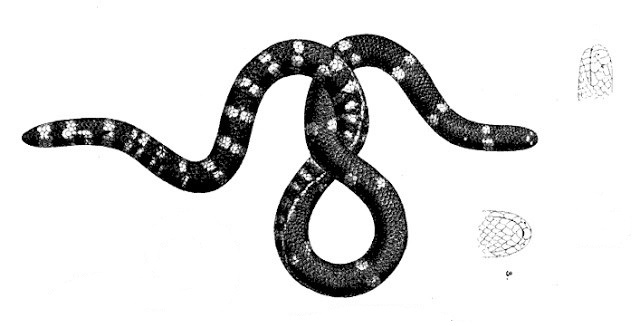
Anomochilus
The Anomochilidae, or anomochilids, are a monotypic family of snakes, created for the genus ''Anomochilus'', which currently contains three species. It is commonly called the dwarf pipe snake. Description Anomochilids are small snakes, with museum specimens measuring up to in total length (including tail). The eyes are reduced, and there are no teeth on the premaxiila, pterygoid, or palatine. A tracheal lung is absent. Anomochilids retain some pelvic elements, indicated externally by cloacal spurs. The tails are relatively short. Females have two well developed oviducts. Anomochilids have white or yellow patterns against a darker reddish background. Behaviour and habitat Anomochilids are probably fossorial. Diet Cranial and dentary morphology suggests that anomochilids probably eat small invertebrates. Reproduction One of the museum specimens of ''Anomochilus'' was found to contain four eggs, suggesting oviparity, but nothing else is known of anomochilid reproduction or behav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomochilus Weberi
''Anomochilus weberi'', commonly known as Weber's pipe snake or the Sumatran giant blind snake, is a species of snake in the family Anomochilidae. The species is endemic to Southeast Asia and Oceania. Etymology The specific name, ''weberi'', is in honor of German-Dutch zoologist Max Wilhelm Carl Weber van Bosse. Geographic range ''A. weberi'' is found in Indonesia, where it is known from Sumatra and Borneo, and in Malaysia, where it is known from Sabah. Habitat The preferred natural habitat of ''A. weberi'' is forest, at altitudes of . Description ''A. weberi'' has the following scalation: frontal quadrangular, nearly twice as large as the supraocular; no enlarged parietals; four upper labials, third largest and in contact with eye; dorsal scales in 21 rows; ventrals 244, scarcely larger than dorsal scales; anal divided; subcaudals 8. Dorsally Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomochilus Monticola
''Anomochilus monticola'', the mountain pipe snake, or Kinabalu giant blind snake, is a species of snake in the Anomochilidae family. It is endemic to northern Borneo and only known from Kinabalu Park (Sabah, Malaysia). It is known from altitudes of asl, characterized by montane forest. It presumably is fossorial A fossorial () animal is one adapted to digging which lives primarily, but not solely, underground. Some examples are badgers, naked mole-rats, clams, meerkats, and mole salamanders, as well as many beetles, wasps, and bees. Prehistoric eviden .... Description ''Anomochilus monticola'' grow to at least in snout–vent length. Head is not distinct from the stout body. The eyes are small, in diameter. Tail is short, just . The body has iridescent blue black ground colour. The dorsum is largely uniform in colour, but there is a pale horn coloured transverse bar across the snout. Ventrally, there are series of large pale horn coloured blotches. Chrome orange band en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomochilus Leonardi
:''Common names: Leonard's pipe snake, Leonard's burrowing snake, Malayan giant blind snake.'' ''Anomochilus leonardi'' is a species of snake in the family Anomochilidae. The species is endemic to Peninsular Malaysia. No subspecies are recognized . Geographic range ''A. leonardi'' is found in Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo (Sabah). Its type locality is Sungei Ngeram, near Merapoh, Pahang. Etymology The specific name, ''leonardi'', is in honor of G.R. Leonard, collector of the holotype.Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). ''The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. . (''Anomochilus leonardi'', p. 155). Reproduction ''A. leonardi'' is oviparous. Conservation status ''A. leonardi'' is listed as Least Concern (LC) on the IUCN The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodorus Willem Van Lidth De Jeude
Theodorus Willem van Lidth de Jeude (1 February 1853 – 29 May 1937) was a Dutch zoologist and herpetologist. He is not to be confused with his grandfather's brother, the Dutch veterinarian and zoologist Theodoor Gerard van Lidth de Jeude (1788–1863).Adler, K. (ed.) (2007) Contributions to the history of herpetology, Vol 2. SSAR Contributions to Herpetology, 389 pp. (p. 116) Life and career T.W. van Lidth de Jeude was born on 1 February 1853 in Helmond, about 15 km east of Eindhoven. He attended the University of Utrecht where his grandfather, T.G. van Lidth de Jeude, taught zoology and veterinary science. Theorodus Willem received his Ph.D. in 1882 for a thesis on coleopteran larvae. Between 1882 and 1884 he studied fishes in Naples and at Kralingen (near Rotterdam). In 1884, he became curator of Lower Vertebrates at the Rijksmuseum in Leiden. He retired from his curatorship in 1923 but kept working at the museum until 1931. T.W. von Lidth de Jeude died in Leiden on 29 May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Carl Wilhelm Weber
Max Carl Wilhelm Weber van Bosse or Max Wilhelm Carl Weber (5 December 1852, in Bonn – 7 February 1937, in Eerbeek) was a German-Dutch zoologist and biogeographer. Weber studied at the University of Bonn, then at the Humboldt University in Berlin with the zoologist Eduard Carl von Martens (1831–1904). He obtained his doctorate in 1877. Weber taught at the University of Utrecht then participated in an expedition to the Barents Sea. He became Professor of Zoology, Anatomy and Physiology at the University of Amsterdam in 1883. In the same year he received naturalised Dutch citizenship. His discoveries as leader of the Siboga Expedition led him to propose Weber's line, which encloses the region in which the mammalian fauna is exclusively Australasian, as an alternative to Wallace's Line. As is the case with plant species, faunal surveys revealed that for most vertebrate groups Wallace’s line was not the most significant biogeographic boundary. The Tanimbar Island group, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Cundall
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the third king of the United Kingdom of Israel. In the Books of Samuel, he is described as a young shepherd and harpist who gains fame by slaying Goliath, a champion of the Philistines, in southern Canaan. David becomes a favourite of Saul, the first king of Israel; he also forges a notably close friendship with Jonathan, a son of Saul. However, under the paranoia that David is seeking to usurp the throne, Saul attempts to kill David, forcing the latter to go into hiding and effectively operate as a fugitive for several years. After Saul and Jonathan are both killed in battle against the Philistines, a 30-year-old David is anointed king over all of Israel and Judah. Following his rise to power, David c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterygoid Bone
The pterygoid is a paired bone forming part of the palate of many vertebrates, behind the palatine bone In anatomy, the palatine bones () are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxillae, they comprise the hard palate. (''Palate'' is derived from the Latin ''pa ...s. It is a flat and thin lamina, united to the medial side of the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone, and to the perpendicular lamina of the palatine bone. Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olive Bown Goin
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' 'Montra', dwarf olive, or little olive. The species is cultivated in all the countries of the Mediterranean, as well as in Australia, New Zealand, North and South America and South Africa. ''Olea europaea'' is the type species for the genus ''Olea''. The olive's fruit, also called an "olive", is of major agricultural importance in the Mediterranean region as the source of olive oil; it is one of the core ingredients in Mediterranean cuisine. The tree and its fruit give their name to the plant family, which also includes species such as lilac, jasmine, forsythia, and the true ash tree. Thousands of cultivars of the olive tree are known. Olive cultivars may be used primarily for oil, eating, or both. Olives cultivated for consumption are gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylindrophiidae
The Cylindrophiidae are a monotypic Family (biology), family of secretive, semifossorial, non-venomous snakes containing the genus ''Cylindrophis'' found in southeastern Asia. These are burrowing snakes and most have a banded pattern on the belly. Currently, thirteen species are recognized, with no subspecies. Common names include Asian pipe snakes or Asian cylinder snakes. Geographic range ''Cylindrophis'' are found in southeastern Asia from Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand, and the Malay Archipelago, including Singapore, both peninsular Malaysia and Sarawak, and Indonesia, including the Greater Sunda Islands (Borneo [including Sarawak and Brunei]), Sumatra, and Java, as well as some of their offshore islands), Sulawesi, the Lesser Sunda Islands (Lombok, Komodo, Flores, Sumbawa, Timor [including Timor-Leste]), and east to the Maluku Islands (Halmahera, Wetar, Damar, Babar, and into the Tanimbar Archipelago). The eastern distributional limit, sometimes given as the Aru I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent islands such as the Simeulue, Nias, Mentawai, Enggano, Riau Islands, Bangka Belitung and Krakatoa archipelago. Sumatra is an elongated landmass spanning a diagonal northwest–southeast axis. The Indian Ocean borders the northwest, west, and southwest coasts of Sumatra, with the island chain of Simeulue, Nias, Mentawai, and Enggano off the western coast. In the northeast, the narrow Strait of Malacca separates the island from the Malay Peninsula, which is an extension of the Eurasian continent. In the southeast, the narrow Sunda Strait, containing the Krakatoa Archipelago, separates Sumatra from Java. The northern tip of Sumatra is near the Andaman Islands, while off the southeastern coast lie the islands of Bangka and Belitung, Karim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia ( ms, Semenanjung Malaysia; Jawi: سمننجڠ مليسيا), or the States of Malaya ( ms, Negeri-negeri Tanah Melayu; Jawi: نڬري-نڬري تانه ملايو), also known as West Malaysia or the Malaysian Peninsula, is the part of Malaysia that occupies the southern half of the Malay Peninsula in Southeast Asia and the nearby islands. Its area totals , which is nearly 40% of the total area of the country; the other 60% is in East Malaysia. For comparison, it is slightly larger than England (130,395 km2). It shares a land border with Thailand to the north and a maritime border with Singapore to the south. Across the Strait of Malacca to the west lies the island of Sumatra, and across the South China Sea to the east lie the Natuna Islands of Indonesia. At its southern tip, across the Strait of Johor, lies the island country of Singapore. Peninsular Malaysia accounts for the majority (roughly 81.3%) of Malaysia's population and economy; as of 2017, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |