|
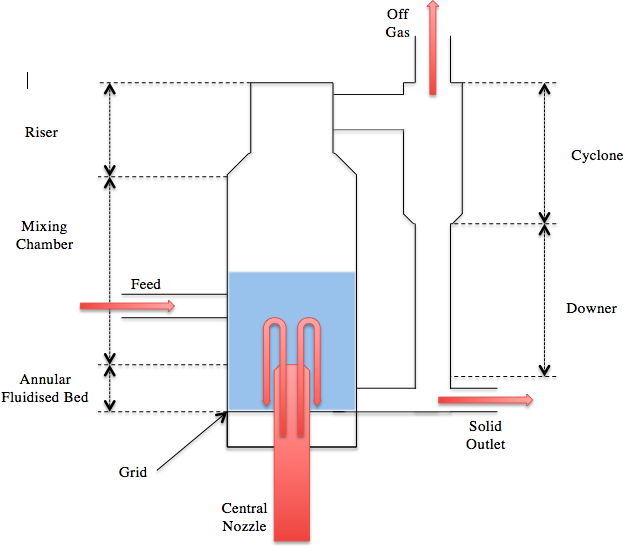
Annular Fluidized Bed
Fluidisation is a phenomenon whereby solid particulate is placed under certain conditions to cause it to behave like a fluid. A fluidized bed is a system conceived to facilitate the fluidisation. Fluidized beds have a wide range of applications including but not limited to: assisting with chemical reactions, heat transfer, mixing and drying. A recent concept devised and patented by Outotec, '' "An annular fluidized bed consists of a large central nozzle surrounded be a stationary fluidized" .'' History * Fritz Winkler created the first fluidised bed in 1922 for coal gasification. * The next advancement in fludizied bed was the Circulating fluidised bed produced in 1942 for catalytic cracking of organic oils. * Finally in the early 1990s annular fluidised beds was conceptualised and its current uses are:Outotec Fluidization technology 2011, viewed 13 October 2013, www.outotec.com :* Waste heat boiler pilot plant (1992) :* Circored direct reduction plant (1996) :* Ore prehea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
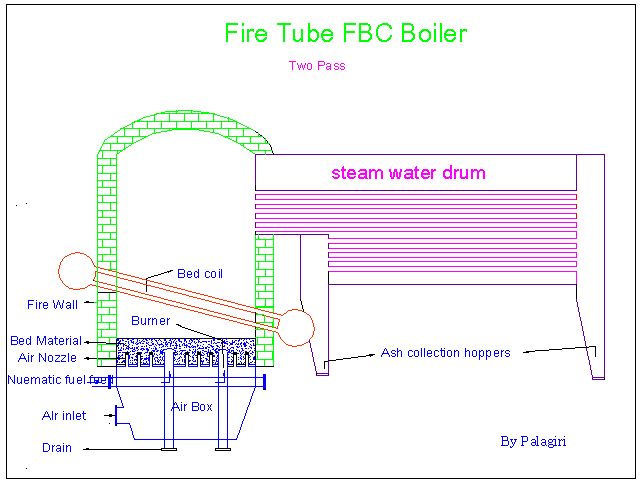
Fluidized Bed Combustion
Fluidized bed combustion (FBC) is a combustion technology used to burn solid fuels. In its most basic form, fuel particles are suspended in a hot, bubbling fluidity bed of ash and other particulate materials (sand, limestone etc.) through which jets of air are blown to provide the oxygen required for combustion or gasification. The resultant fast and intimate mixing of gas and solids promotes rapid heat transfer and chemical reactions within the bed. FBC plants are capable of burning a variety of low-grade solid fuels, including most types of coal, coal waste and woody biomass, at high efficiency and without the necessity for expensive fuel preparation (e.g., pulverising). In addition, for any given thermal duty, FBCs are smaller than the equivalent conventional furnace, so may offer significant advantages over the latter in terms of cost and flexibility. FBC reduces the amount of sulfur emitted in the form of SO''x'' emissions. Limestone is used to precipitate out sulfate du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, Convection (heat transfer), thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species (mass transfer in the form of advection), either cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have distinct characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system. Heat conduction, also called diffusion, is the direct microscopic exchanges of kinetic energy of particles (such as molecules) or quasiparticles (such as lattice waves) through the boundary between two systems. When an object is at a different temperature from another body or its surroundings, heat flows so that the body and the surroundings reach the same temperature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outotec
Outotec Oyj (Outokumpu Technology prior to 24 April 2007) was a Finnish company, headquartered in Espoo, aimed at providing technologies and services for the metal and mineral processing industries. In 2020 Outotec merged with Metso Minerals and new company is called Metso Outotec. The firm concentrated on producing machines and methods which facilitate the various stages of extractive metallurgy and mineral processing from ore through to pure metal or mineral, including the grinding and physical separation of ores and the smelting and leaching of base and precious metals. The company also provides engineering and after-sales services for its products. Outotec was previously a wholly owned business area of Outokumpu, having been established in the late 1940s, but it was spun off as a separate entity in June 2006 when the parent company decided to concentrate on its primary concern of stainless steel. A listing on the Helsinki Stock Exchange followed shortly afterwards, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclonic Separation
Cyclonic separation is a method of removing particulates from an air, gas or liquid stream, without the use of filters, through vortex separation. When removing particulate matter from liquid, a hydrocyclone is used; while from gas, a gas cyclone is used. Rotational effects and gravity are used to separate mixtures of solids and fluids. The method can also be used to separate fine droplets of liquid from a gaseous stream. A high speed rotating (air)flow is established within a cylindrical or conical container called a cyclone. Air flows in a helical pattern, beginning at the top (wide end) of the cyclone and ending at the bottom (narrow) end before exiting the cyclone in a straight stream through the center of the cyclone and out the top. Larger (denser) particles in the rotating stream have too much inertia to follow the tight curve of the stream, and thus strike the outside wall, then fall to the bottom of the cyclone where they can be removed. In a conical system, as the ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drying
Drying is a mass transfer process consisting of the removal of water or another solvent by evaporation from a solid, semi-solid or liquid. This process is often used as a final production step before selling or packaging products. To be considered "dried", the final product must be solid, in the form of a continuous sheet (e.g., paper), long pieces (e.g., wood), particles (e.g., cereal grains or corn flakes) or powder (e.g., sand, salt, washing powder, milk powder). A source of heat and an agent to remove the vapor produced by the process are often involved. In bioproducts like food, grains, and pharmaceuticals like vaccines, the solvent to be removed is almost invariably water. Desiccation may be synonymous with drying or considered an extreme form of drying. In the most common case, a gas stream, e.g., air, applies the heat by convection and carries away the vapor as humidity. Other possibilities are vacuum drying, where heat is supplied by conduction or radiation (or microwave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixing (process Engineering)
In industrial process engineering, mixing is a unit operation that involves manipulation of a heterogeneous physical system with the intent to make it more homogeneous. Familiar examples include pumping of the water in a swimming pool to homogenize the water temperature, and the stirring of pancake batter to eliminate lumps (deagglomeration). Mixing is performed to allow heat and/or mass transfer to occur between one or more streams, components or phases. Modern industrial processing almost always involves some form of mixing.Ullmann, Fritz (2005). Ullmann's Chemical Engineering and Plant Design, Volumes 1–2. John Wiley & Sons. http://app.knovel.com/hotlink/toc/id:kpUCEPDV02/ullmanns-chemical-engineering Some classes of chemical reactors are also mixers. With the right equipment, it is possible to mix a solid, liquid or gas into another solid, liquid or gas. A biofuel fermenter may require the mixing of microbes, gases and liquid medium for optimal yield; organic nitration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reactions (Men In Trees)
''Men in Trees'' is an American romantic comedy-drama television series starring Anne Heche as relationship coach Marin Frist, which premiered on September 12, 2006, on ABC. The series is set in the fictional town of Elmo, Alaska, and concerns Marin Frist's misadventures in relationships. The premise showed at least superficial similarities to the HBO television series ''Sex and the City'' (on which series creator Jenny Bicks was a co-executive producer), which also featured a romantically oriented female writer. The protagonist's apparent "fish-out-of-water" feeling in a remote, small Alaskan town can be likened to CBS's ''Northern Exposure''. The protagonists in both series were New Yorkers thrust into small town Alaskan societies. Filming for the series was based in Squamish, British Columbia, Canada. Five episodes of the first production season, which had not yet been shown on ABC, debuted in New Zealand on the TV2 network in June and July 2007. The five carryover episodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluidized Bed Reactor
A fluidized bed reactor (FBR) is a type of reactor device that can be used to carry out a variety of multiphase chemical reactions. In this type of reactor, a fluid (gas or liquid) is passed through a solid granular material (usually a catalyst) at high enough speeds to suspend the solid and cause it to behave as though it were a fluid. This process, known as fluidization, imparts many important advantages to an FBR. As a result, FBRs are used for many industrial applications. Basic principles The solid substrate material (the catalytic material upon which chemical species react) in the fluidized bed reactor is typically supported by a porous plate, known as a distributor.Howard, J. R. (1989). ''Fluidized Bed Technology: Principles and Applications.'' New York, NY: Adam Higler. The fluid is then forced through the distributor up through the solid material. At lower fluid velocities, the solids remain in place as the fluid passes through the voids in the material. This is know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluidized Bed
A fluidized bed is a physical phenomenon that occurs when a solid particulate substance (usually present in a holding vessel) is under the right conditions so that it behaves like a fluid. The usual way to achieve a fluidize bed is to pump pressurized fluid into the particles. The resulting medium then has many properties and characteristics of normal fluids, such as the ability to free-flow under gravity, or to be pumped using fluid technologies. The resulting phenomenon is called fluidization. Fluidized beds are used for several purposes, such as fluidized bed reactors (types of chemical reactors), solids separation, fluid catalytic cracking, fluidized bed combustion, heat or mass transfer or interface modification, such as applying a coating onto solid items. This technique is also becoming more common in aquaculture for the production of shellfish in integrated multi-trophic aquaculture systems. Properties A fluidized bed consists of fluid-solid mixture that exhibits fluid-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |