|
Annie Royle Taylor
Hannah Royle Taylor (7 October 1855 – 9 September 1922), known as Annie Royle Taylor, was an English explorer and Evangelical missionary to China. She was the first Western woman known to have visited Tibet. She attempted to reach the "forbidden" city of Lhasa in 1892–1893. Early life She was a daughter of John Taylor, one of the directors of the Black Ball Line of packet ships. At the age of 13 she became converted to evangelical Christianity and determined to become a missionary, against her parents' wishes. After studying medicine and working in the slums of London and Brighton, she joined the China Inland Mission. (She was no relation to CIM founder Hudson Taylor.) She sailed to Shanghai in 1884 and was posted to Lanzhou on the borders of Tibet in 1886. Recalled from Lanzhou in 1888 because of poor health, she recuperated in Australia and determined to evangelise within Tibet. She described herself as a troublesome and unhealthy child. She was a "lone wolf...so bad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egremont, Merseyside
Egremont is an area of Wallasey, in the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral, Merseyside, England. Historically part of Cheshire and in the north east of the Wirral Peninsula, it is bordered by New Brighton to the north, Liscard to the west and Seacombe to the south. History Egremont was considered part of the Liscard township until the 1820s, when expansion of Liscard was deemed significant enough that it should be split into two townships. One of the earliest buildings in Egremont was the Liscard Manor House, also known as the 'Seabank'. Dating back to the 1790s, it was home to the influential Penkett and Maddock families. The area which grew up around Seabank was eventually to become the Mariners' home founded in 1892 by William Cliff. The name of the area was decided by one Captain Askew who built a house in the area as early as 1835 and named the village 'Egremont' after his Cumberland birthplace. Egremont Ferry was built in 1827 and was the longest pier on Merseyside until i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianshui
Tianshui is the second-largest cities in Gansu, city in Gansu list of Chinese provinces, Province, China. The city is located in the southeast of the province, along the upper reaches of the Wei River and at the boundary of the Loess Plateau and the Qinling, Qinling Mountains. As of the 2020 census, its population was 2,984,659 inhabitants, of which 1,212,791 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of the 2 urban districts of Qinzhou and Maiji District, Maiji. The city and its surroundings have played an important role in the early history of China, as still visible in the form of historic sites such as the Maijishan Grottoes. History state of Qin, Qin, whose House of Ying were the Qin dynasty, founding dynasty of the Early Imperial China, Chinese empire, developed from Quanqiu (present-day Li County, Gansu, Lixian) to the south. After the invasions of the Xirong, Rong which unseated the Western Zhou dynasty, Western Zhou, Qin recovered the territory of Tianshui from the nomad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Younghusband Expedition
The British expedition to Tibet, also known as the Younghusband expedition, began in December 1903 and lasted until September 1904. The expedition was effectively a temporary invasion by British Indian Armed Forces under the auspices of the Tibet Frontier Commission, whose purported mission was to establish diplomatic relations and resolve the dispute over the border between Tibet and Sikkim.Landon, P. (1905). ''The Opening of Tibet'' Doubleday, Page & Co, New York. In the nineteenth century, the British had conquered Burma and Sikkim, with the whole southern flank of Tibet coming under the control of the British Indian Empire. Tibet ruled by the Dalai Lama under the Ganden Phodrang government was a Himalayan state under the suzerainty of the Chinese Qing dynasty until the 1911 Revolution, after which a period of de facto Tibetan independence (1912-1951) followed. The invasion was intended to counter the Russian Empire's perceived ambitions in the East and was initiated la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh Museum Of Science And Art
The National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh, Scotland, was formed in 2006 with the merger of the new Museum of Scotland, with collections relating to Scottish antiquities, culture and history, and the adjacent Royal Scottish Museum (opened in 1866 as the Edinburgh Museum of Science and Art, renamed in 1904, and for the period between 1985 and the merger named the Royal Museum of Scotland or simply the Royal Museum), with international collections covering science and technology, natural history, and world cultures. The two connected buildings stand beside each other on Chambers Street, by the intersection with the George IV Bridge, in central Edinburgh. The museum is part of National Museums Scotland. Admission is free. The two buildings retain distinctive characters: the Museum of Scotland is housed in a modern building opened in 1998, while the former Royal Museum building was begun in 1861 and partially opened in 1866, with a Victorian Venetian Renaissance facade and a gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convention Of Calcutta
The Convention of Calcutta or Anglo-Chinese Convention of 1890, officially the Convention Between Great Britain and China Relating to Sikkim and Tibet, () was a treaty between Britain and Qing China relating to Tibet and the Kingdom of Sikkim. It was signed by Viceroy of India Lord Lansdowne and the Chinese Amban in Tibet, Sheng Tai, on 17March 1890 in Calcutta, India. The Convention recognized a British protectorate over Sikkim and demarcated the Sikkim–Tibet border. China is said to have negotiated the treaty without consulting Tibet, and the Tibetans refused to recognize it. China's inability to deliver on the treaty eventually necessitated a British expedition to Tibet in 1904, setting in motion a long chain of developments in the history of Tibet. Modern international law jurists state that the convention exposed the Chinese 'impotence' in Tibet. The boundary established between Sikkim and Tibet in the treaty still survives today, as part of the China–India border. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
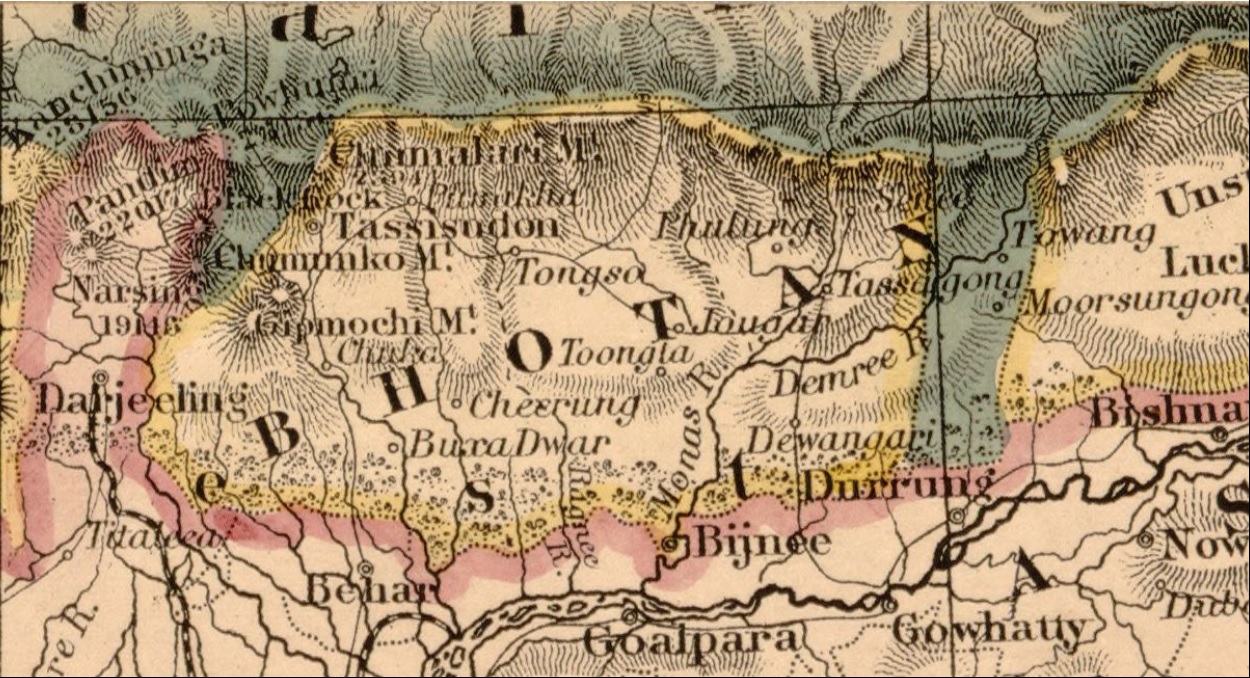
Chumbi Valley
The Chumbi Valley, called Dromo or Tromo in Tibetan, is a valley in the Himalayas that projects southwards from the Tibetan plateau, intervening between Sikkim and Bhutan. It is coextensive with the administrative unit Yadong County in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. The Chumbi Valley is connected to Sikkim to the southwest via the mountain passes of Nathu La and Jelep La. The valley is at an altitude of , and being on the south side of the Himalayas, enjoys a wetter and more temperate climate than most of Tibet. The valley supports some vegetation in the form of the Eastern Himalayan broadleaf forests and transitions to the Eastern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows in the north. The plant ''Pedicularis chumbica'' ( 春丕马先蒿) is named after the valley. The 1904 Younghusband Expedition of British India passed through the Chumbi Vally on its way to Lhasa. At the end of the expedition, the British took control of the Chumbi Valley in lieu of a war indemnity. Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rinchengang
Rinchengang : "By order of Military Control Commission freedom of movement is not being permitted to our Trade Agents even in the vicinity where the Trade Agencies are located. For example the I.T.A. Yatung was not permitted to go to Rinchengang, only six miles from Yatung..." : "Renqinggang, also known as Rinchengang, is located south of Sharsingma in Yadong counrty." () or Renqinggang () is a town in the Chumbi Valley and the headquarters of the Xia Yadong Township of Yadong County, Tibet region of China. It is in the valley of Amo Chu where the route from Sikkim's Jelep La pass meets Amo Chu. It is also close to the Bhutan–China border (Doklam area), which is currently in dispute. In December 2018, Rinchengang village had a population of around 550 people. The inhabitants are engaged in animal grazing or work as forest rangers. Some also carry supplies to Chinese border troops. In 2003, the governments of India and China agreed to use Rinchengang as a border trade ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Yatung
Old Yatung (), originally just "Yatung", with a native Tibetan spelling of Nyatong: "Miss nnie R.Taylor returned with the object of converting the Tibetan people, and now lives at the town of Nyatong, which by some is called Yatung." or Myatong, is a location 2 miles west of Rinchengang in the lower Chumbi Valley in the present day Yadong County of Tibet. It is in the valley of Yatung Chu, the river that flows down from Jelep La to join the Amo Chu river near Rinchengang. But according to travel writer John Easton, Yatung is actually a hill top location adjoining the valley, which has a historic Kagyu monastery. The monastery itself lies along the route from the Nathu La pass via Champithang. : arching from Champithangfor nearly two hours we marched ..., until we came to Old Yatung, perched on the buttress that divides the valley of the Amo Chu.... Yatung, to them he local Tibetans is merely a monastery, where the lamas live and the prayer flags flap. Yatung entered history a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Pioneer Mission 2
Tibetan may mean: * of, from, or related to Tibet * Tibetan people, an ethnic group * Tibetan language: ** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard ** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken dialect ** Tibetan pinyin, a method of writing Standard Tibetan in Latin script ** Tibetan script ** any other of the Tibetic languages Tibetan may additionally refer to: Culture * Old Tibetan, an era of Tibetan history * Tibetan art * Music of Tibet * Tibetan rug * Tibetan culture * Tibetan cuisine Religion * Tibetan Buddhism * Tibetan Muslims Other uses * Tibetan alphabet * Tibetan (Unicode block) * Tibetan name * Tibetan calendar * Tibetan Spaniel, a breed of dog * Tibetan Mastiff, a breed of dog See also * Tibetan Bells (other) * Traditional Tibetan medicine * Tibetan language (other) Tibetan language may refer to: * Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard * Lhasa Tibe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangding
Kangding (), also called Tachienlu and Dartsedo (; ), is a county-level city and the seat of Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Sichuan province of Southwest China. Kangding is on the bank of the Dadu River and has been considered the historical border between the Kham region of Tibet and the Sichuan region. Kangding's urban center is called Lucheng, which has around 134,000 inhabitants. Names Historically, the urban center was known by Chinese as Dajianlu (written also as Tachienlu or Tatsienlu) from the Chinese transliteration of the Tibetan name Dartsedo or Darzêdo. History Kangding was on the historical border between Tibet and the rest of China, from Kangding to the west lies Tibetan civilization where as to the east Han cultural areas; It was the capital of the Kingdom of Chakla. During its history, Kangding has witnessed many conflicts between Tibetan and Han polities. Kangding was for many centuries an important trading city where Han brick tea was carried by por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagchu Town
Nagqu, Nagchu in original Tibetan or Naqu (), also known as Nagchuka or Nagquka, is a town in northern Tibet, seat of the prefecture-level city of Nagqu, approximately by road north-east of the capital Lhasa, within the People's Republic of China. Nagqu railway station to the town's west sits on the Qingzang railway at . "Nagchu (...) is an important stop on both the road and railway line between Qīnghǎi and Tibet. In fact, this is where Hwy 317 ends as it joins the Qīnghǎi–Tibet Hwy (Hwy 109) on its way to Lhasa." At the time of the visit in 1950 of Thubten Jigme Norbu, the elder brother of Tenzin Gyatso the 14th Dalai Lama, Nagchukha was a small town with only a few clay huts but was also the headquarters of the District Officer, the Dzongpön. It was on the main caravan route coming from Amdo to Central Tibet. China is planning to build Nagqu Airport, the highest airport in the world at an altitude of . The construction is planned to start in 2011 and expected to take ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
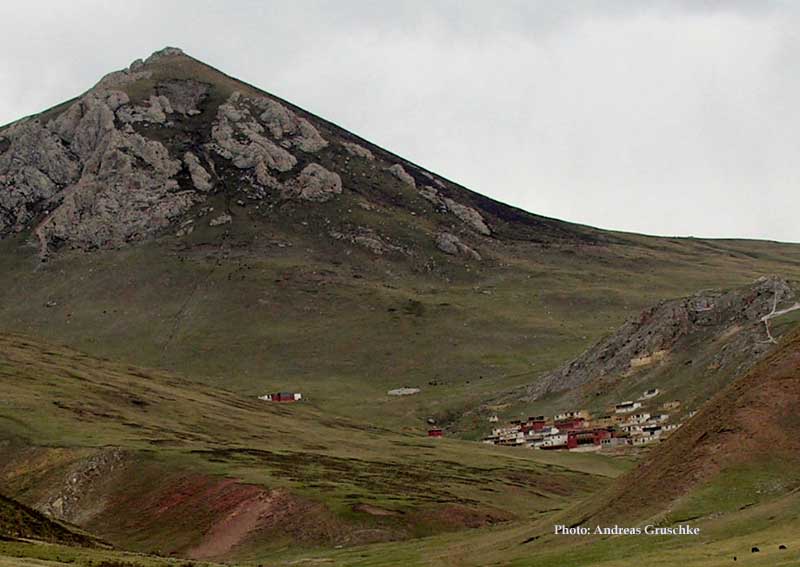
Gyêgu
Gyêgu Subdistrict, formerly a part of the Gyêgu town is a township-level division in Yushu, Yushu TAP, Qinghai, China. The name Gyêgu is still a common name for the Yushu city proper, which include Gyêgu subdistrict and three other subdistricts evolved from the former Gyêgu town. The four subdistricts altogether forms a modern town which developed from the old Tibetan trade mart called Jyekundo or Gyêgumdo in Tibetan and most Western sources. The town is also referred to as Yushu, synonymous with the prefecture of Yushu and the city of Yushu. Name The present name Gyêgu (; also spelled ''Jyegu'') is derived from Gyêgudo (, ZWPY: ''Gyêgumdo'', Wylie: ''skye dgu mdo'' or ''skye rgu mdo''; ). The Tibetan designation ''Gyêgumdo'' indicates that it is a place where one valley opens into another one (''mdo''), here formed by two tributaries of the Batang River, Za Qu (''rdza chu'') and Bai Qu (Bä Qu, ''dpal chu''). Since Gyêgu (''skye dgu'') also means men, mankind o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)