|
Annexation
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act.: "Annexation means the forcible acquisition of territory by one State at the expense of another State. It is one of the principal modes of acquiring territory... in contrast to acquisition a) of terra nullius by means of effective occupation accompanied by the intent to appropriate the territory; b) by cession as a result of a treaty concluded between the States concerned (Treaties), or an act of adjudication, both followed by the effective peaceful transfer of territory; c) by means of prescription defined as the legitimization of a doubtful title to territory by passage of time and presumed acquiescence of the former sovereign; d) by accretion constituting the physical process by which new land is formed close to, or becomes attached to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annexation Of Crimea By The Russian Federation
In February and March 2014, Russia invaded and subsequently annexed the Crimean Peninsula from Ukraine. This event took place in the aftermath of the Revolution of Dignity and is part of the wider Russo-Ukrainian War. The events in Kyiv that ousted Ukrainian president Viktor Yanukovych on 22 February 2014 sparked pro-Russian demonstrations as of 23 February against the (prospected) new Ukrainian government. At the same time Russian president Vladimir Putin discussed Ukrainian events with security service chiefs remarking that "we must start working on returning Crimea to Russia". On 27 February, Russian troops captured strategic sites across Crimea, followed by the installation of the pro-Russian Aksyonov government in Crimea, the Crimean status referendum and the declaration of Crimea's independence on 16 March 2014. Although Russia initially claimed their military was not involved in the events, Putin later admitted that troops were deployed to "stand behind Crimea's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Occupation
Military occupation, also known as belligerent occupation or simply occupation, is the effective military control by a ruling power over a territory that is outside of that power's sovereign territory.Eyāl Benveniśtî. The international law of occupation. Princeton University Press, 2004. , , p. 43 The territory is then known as the ''occupied'' territory and the ruling power the ''occupant''. Occupation is distinguished from annexation and colonialism by its intended temporary duration. While an occupant may set up a formal military government in the occupied territory to facilitate its administration, it is not a necessary precondition for occupation. The rules of occupation are delineated in various international agreements, primarily the Hague Convention of 1907, the Geneva Conventions of 1949, as well as established state practice. The relevant international conventions, the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) Commentaries, and other treaties by military scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli–Palestinian Conflict
The Israeli–Palestinian conflict is one of the world's most enduring conflicts, beginning in the mid-20th century. Various attempts have been made to resolve the conflict as part of the Israeli–Palestinian peace process, alongside other efforts to resolve the broader Arab–Israeli conflict. Public declarations of claims to a Jewish homeland in Palestine, including the First Zionist Congress of 1897 and the Balfour Declaration of 1917, created early tensions in the region. Following World War I, the Mandate for Palestine included a binding obligation for the "establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people". Tensions grew into open sectarian conflict between Jews and Arabs. The 1947 United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was never implemented and provoked the 1947–1949 Palestine War. The current Israeli-Palestinian status quo began following Israeli military occupation of the Palestinian territories in the 1967 Six-Day War. Progress was made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
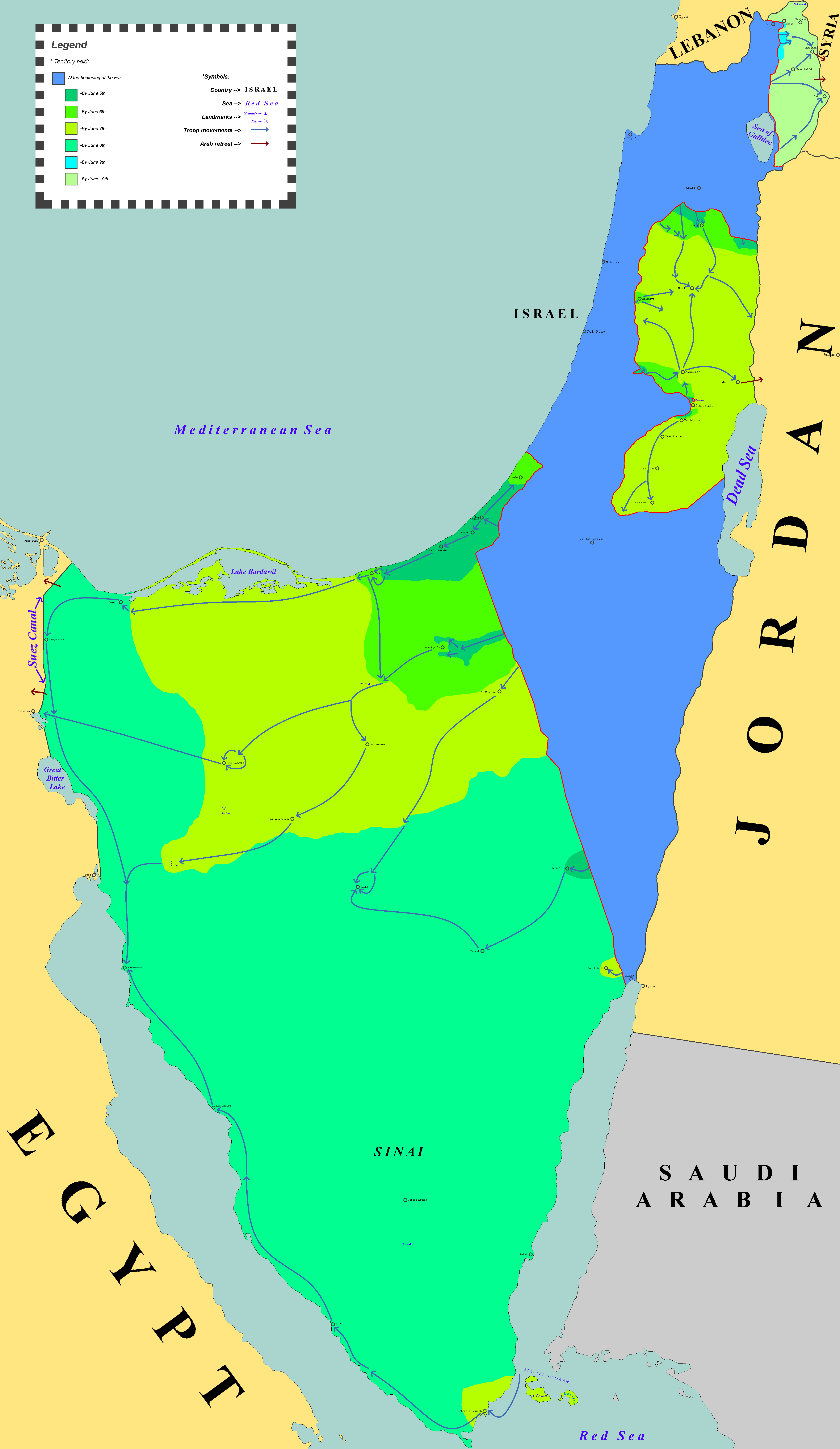
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967. Escalated hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours following the 1949 Armistice Agreements, which were signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt–Israel border. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimson Doctrine
The Stimson Doctrine is the policy of nonrecognition of states created as a result of a war of aggression. The policy was implemented by the United States government, enunciated in a note of January 7, 1932, to the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China, of non-recognition of international territorial changes imposed by force. The doctrine was an application of the principle of '' ex injuria jus non oritur''. Since the entry into force of the UN Charter, international law scholars have argued that states are under a legal obligation not to recognize annexations as legitimate, but this view is controversial and not supported by consistent state practice. Overview Named after Henry L. Stimson, United States Secretary of State in the Hoover administration (1929–1933), the policy followed Japan's unilateral seizure of Manchuria in northeastern China following action by Japanese soldiers at Mukden (now Shenyang), on September 18, 1931. The doctrine was also invoked by US Under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crime Of Aggression
A crime of aggression or crime against peace is the planning, initiation, or execution of a large-scale and serious act of aggression using state military force. The definition and scope of the crime is controversial. The Rome Statute contains an exhaustive list of acts of aggression that can give rise to individual criminal responsibility, which include invasion, military occupation, annexation by the use of force, bombardment, and military blockade of ports. Aggression is generally a leadership crime that can only be committed by those with the power to shape a state's policy of aggression, rather than those who carry it out. The philosophical basis for the wrongness of aggression is found in just war theory, in which waging a war without a just cause for self-defense is unjust. In the wake of the German invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II, Soviet jurist Aron Trainin made the first successful proposal to criminalize aggression. The Charter of the International Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
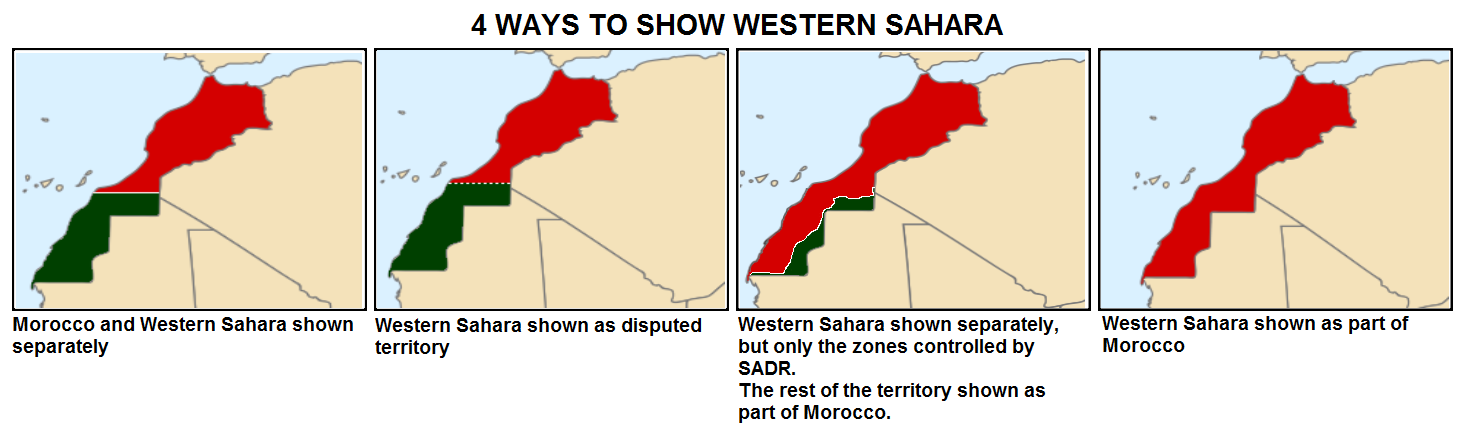
Western Sahara Conflict
The Western Sahara conflict is an ongoing conflict between the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic/Polisario Front and the Kingdom of Morocco. The conflict originated from an insurgency by the Polisario Front against Spanish colonial forces from 1973 to 1975 and the subsequent Western Sahara War against Morocco between 1975 and 1991. Today the conflict is dominated by unarmed civil campaigns of the Polisario Front and their self-proclaimed SADR state to gain fully recognized independence for Western Sahara. The conflict escalated after the withdrawal of Spain from the Spanish Sahara in accordance with the Madrid Accords. Beginning in 1975, the Polisario Front, backed and supported by Algeria, waged a 16-year-long war for independence against Mauritania and Morocco. In February 1976, the Polisario Front declared the establishment of the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, which was not admitted into the United Nations, but won limited recognition by a number of other states. Foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body, or institution that has the ultimate authority over other people in order to establish a law or change an existing law. In political theory, sovereignty is a substantive term designating supreme legitimate authority over some polity. In international law, sovereignty is the exercise of power by a state. ''De jure'' sovereignty refers to the legal right to do so; ''de facto'' sovereignty refers to the factual ability to do so. This can become an issue of special concern upon the failure of the usual expectation that ''de jure'' and ''de facto'' sovereignty exist at the place and time of concern, and reside within the same organization. Etymology The term arises from the unattested Vulgar Latin's ''*superanus'', (itself derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms. Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire and various Muslim conquests, to mention just a few. The Norman conquest of England provides an example: it built on cultural ties, led to the subjugation of the Kingdom of England to Norman control and brought William the Conqueror to the English throne in 1066. Conquest may link in some ways with colonialism. England, for example, experienced phases and areas of Anglo-Saxon, Viking and Franco-Norman colonisation and conquest. Methods of conquest The Ottomans used a method of gradual, non-military conquest in which they established suzerainty over their neighbours and then displaced their ruling dynasties. This concept was first systematized by Halil İnalcık. Conquests of this sort did no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cession
The act of cession is the assignment of property to another entity. In international law it commonly refers to land transferred by treaty. Ballentine's Law Dictionary defines cession as "a surrender; a giving up; a relinquishment of jurisdiction by a board in favor of another agency." In contrast with annexation, where property is forcibly seized, cession is voluntary or at least apparently so. Examples In 1790, the U.S. states of Maryland and Virginia both ceded land to create the District of Columbia, as specified in the U.S. Constitution of the previous year. The Virginia portion was given back in 1847, a process known as "retrocession". Following the First Opium War (18391842) and Second Opium War (18561860), Hong Kong (Treaty of Nanking) and Kowloon (Convention of Peking) were ceded by the Qing dynasty government of China to the United Kingdom; and following defeat in the First Sino-Japanese War, Taiwan was ceded to the Empire of Japan in 1895. Territory can also be ced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covenant Of The League Of Nations
The Covenant of the League of Nations was the charter of the League of Nations. It was signed on 28 June 1919 as Part I of the Treaty of Versailles, and became effective together with the rest of the Treaty on 10 January 1920. Creation Early drafts for a possible League of Nations began even before the end of the First World War. The London-based Bryce Group made proposals adopted by the British League of Nations Society, founded in 1915. Another group in the United States—which included Hamilton Holt and William B. Howland at the Century Association in New York City—had their own plan. This plan was largely supported by the League to Enforce Peace, an organization led by former U.S. President William Howard Taft. In December 1916, Lord Robert Cecil suggested that an official committee be set up to draft a covenant for a future league. The British committee was finally appointed in February 1918; it was led by Walter Phillimore (and became known as the Phillimore Committ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kellogg–Briand Pact
The Kellogg–Briand Pact or Pact of Paris – officially the General Treaty for Renunciation of War as an Instrument of National Policy – is a 1928 international agreement on peace in which signatory states promised not to use war to resolve "disputes or conflicts of whatever nature or of whatever origin they may be, which may arise among them". The pact was signed by Germany, France, and the United States on 27 August 1928, and by most other states soon after. Sponsored by France and the U.S., the Pact is named after its authors, United States Secretary of State Frank B. Kellogg and French foreign minister Aristide Briand. The pact was concluded outside the League of Nations and remains in effect. A common criticism is that the Kellogg–Briand Pact did not live up to all of its aims but has arguably had some success. It was unable to prevent the Second World War but was the base for trial and execution of Nazi leaders in 1946. Furthermore, declared wars became very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |