|
Ann Dinham
Ann Dinham (17 March 1827 – 2 May 1882); born Ann Orchard, and later Ann Riddiford and Ann Foster, was keeping an inn in Abergavenny, Monmouthshire in 1851 with her husband, William, when she was convicted of inciting a burglary and sentenced to be transported to Tasmania for ten years. In Tasmania, she married John Foster, a wealthy businessman, magistrate and member of the Tasmanian Legislative Council. After his death, she took their five surviving children to be educated in England, and was thus one of the few Australian convicts to return to her native land. Early life Dinham was born in the Gloucestershire town of Wotton-under-Edge on 17 March 1827. Her father, James Orchard, is described in the 1851 census as a "Dealer in Marine Stores", a term applied to traders in second-hand goods and "rag and bone men". Her mother, Elizabeth, died in 1839, when Dinham was about 12 years old and her father remarried before the end of that year. The 1841 census shows Dinham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
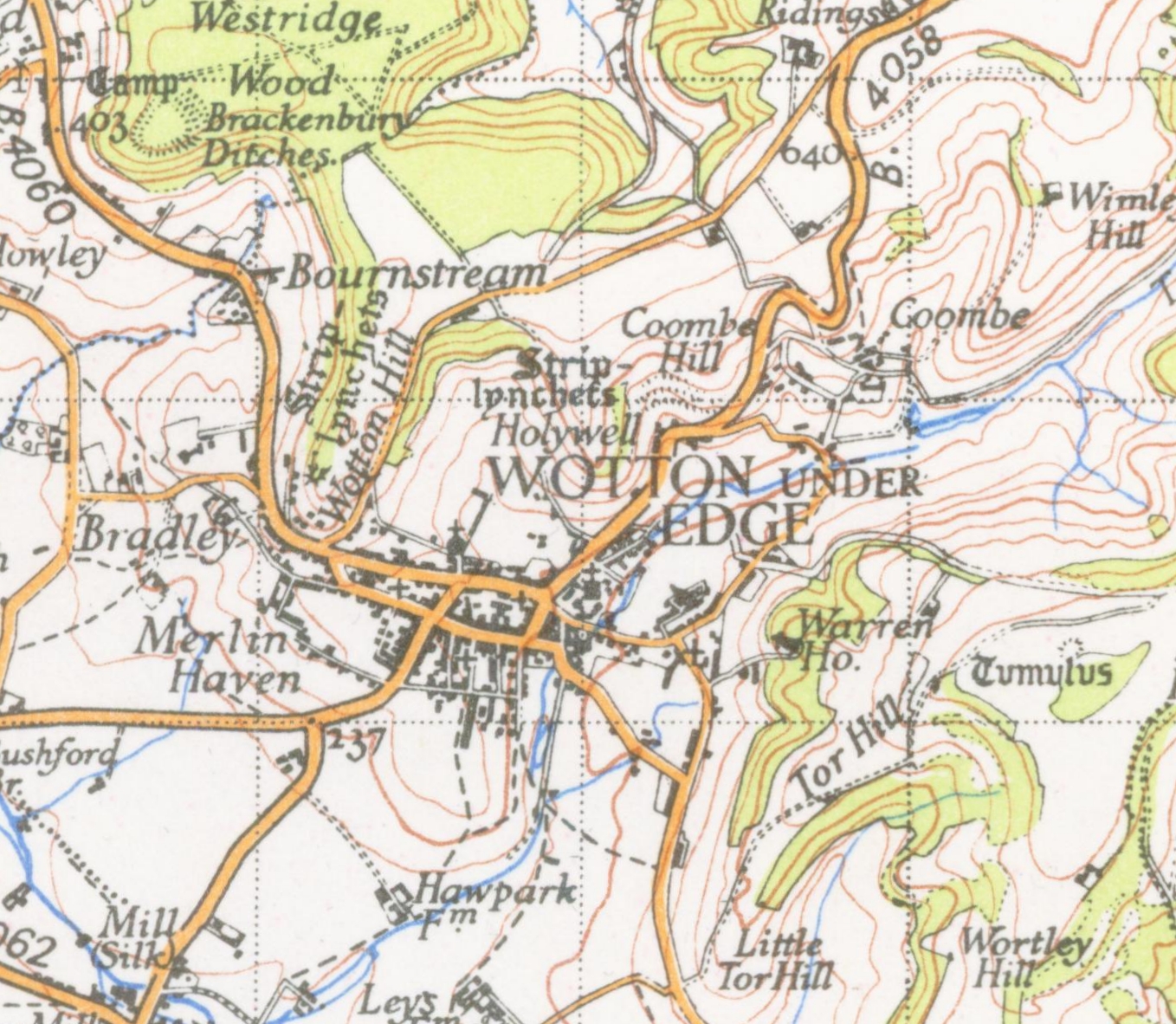
Wotton-under-Edge
Wotton-under-Edge is a market town within the Stroud district of Gloucestershire, England. Located near the southern fringe of the Cotswolds, the Cotswold Way long-distance footpath passes through the town. Standing on the B4058, Wotton is about from the M5 motorway. The nearest railway station is Cam and Dursley, away by road, on the Bristol to Birmingham line. History The first record of the town is in an Anglo-Saxon Royal Charter of King Edmund I, who in AD 940 leased four hides of land in ''Wudetun'' to Eadric. The name ''Wudetun'' means the enclosure, homestead or village (''tun'') in or near the wood (''wude''). The "Edge" refers to the limestone escarpment of the Cotswold Edge which includes the hills of Wotton Hill and Tor Hill that flank the town. In the 1086 Domesday Book listing, Wotton was in the hundred of Dudstone. Kingswood Abbey was founded in 1139, but all that remains is a 16th-century Cistercian gatehouse. Nearby historical buildings include the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the east and southeast, Missouri to the south, Nebraska to the west, South Dakota to the northwest, and Minnesota to the north. During the 18th and early 19th centuries, Iowa was a part of French Louisiana and Spanish Louisiana; its state flag is patterned after the flag of France. After the Louisiana Purchase, people laid the foundation for an agriculture-based economy in the heart of the Corn Belt. In the latter half of the 20th century, Iowa's agricultural economy transitioned to a diversified economy of advanced manufacturing, processing, financial services, information technology, biotechnology, and green energy production. Iowa is the 26th most extensive in total area and the 31st most populous of the 50 U.S. states, with a populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Mercury (Hobart)
''The'' ''Mercury'' is a daily newspaper, published in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, by Davies Brothers Pty Ltd (DBL), a subsidiary of News Corp Australia, itself a subsidiary of News Corp. The weekend issues of the paper are called ''Mercury on Saturday '' and ''Sunday Tasmanian''. The current editor of ''The'' ''Mercury'' is Craig Warhurst. History The newspaper was started on 5 July 1854 by George Auber Jones and John Davies. Two months subsequently (13 September 1854) John Davies became the sole owner. It was then published twice weekly and known as the ''Hobarton Mercury''. It rapidly expanded, absorbing its rivals, and became a daily newspaper in 1858 under the lengthy title ''The Hobart Town Daily Mercury''. In 1860 the masthead was reduced to ''The Mercury'' and in 2006 it was further shortened to simply ''Mercury''. With the imminent demise of the ( Launceston) ''Daily Telegraph'', ''The Mercury'', from March 1928, used the opportunity to increase their penetration th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campbell Town, Tasmania
Campbell Town is a town in Tasmania, Australia, on the Midland Highway. At the 2021 census, the town had a population of 823. History Traditional owners of the Campbell Town area The traditional custodians of the Campbell Town area were the Tyerrernotepanner (chera-noti-pahner) Clan of the North Midlands Nation. The Tyerrernotepanner were a nomadic people who traversed country from the Central Plateau to the Eastern Tiers but were recorded as inhabiting 'resorts' around present day Campbell Town, lagoons near present-day Cleveland and Conara and the southern banks of the South Esk River. The colonial name for this clan was the Stony Creek Tribe, named after a small southern tributary of the South Esk at Llewellyn. The Tyerrernotepanner called the Campbell Town area ''norerytymonerler'' or ''parndokenne''. Their name for the hills above Campbell Town ( the Campbell Town Tier) was ''Lukargener Purntobebenner'' and the Elizabeth River was ''parndokennerlyerpinder''. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelian Bay Cemetery
Cornelian Bay Cemetery is a cemetery in Cornelian Bay, Tasmania, Australia. It is the oldest cemetery in Tasmania that remains in use. History The cemetery location, a section of the former Government Farm site, was selected in the late 1860s, amidst concern about risks to health posed by several cemeteries close to the centre of the city of Hobart. These issues led to legislation in 1870 to close those cemeteries three months after a new cemetery could be opened, and funding for the cemetery's establishment was allocated the same year. The cemetery layout was designed by surveyor E. J. Burgess, who won a design competition for the task. It was formally opened by Governor Charles Du Cane on 22 July 1872. As some of the older cemeteries were cleared, the remains of those interred there were reburied at Cornelian Bay. A crematorium (the Derwent Chapel) opened in 1935. It was replaced with a new facility (the Wellington Chapel) in 1993. The cemetery was closed for new burials in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kensal Green Cemetery
Kensal Green Cemetery is a cemetery in the Kensal Green area of Queens Park in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea in London, England. Inspired by Père Lachaise Cemetery in Paris, it was founded by the barrister George Frederick Carden.The Founding of Kensal Green Cemetery Accessed 7 February 2014 The cemetery opened in 1833 and comprises of grounds, including two conservation areas, adjoining a canal. The cemetery is home to at least 33 species of bird and other wildlife. This distinctive cemetery has memorials ranging from large s housing the rich and famous to many distinctive smaller graves and includes special areas dedicated to the very young. It has three ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brighton
Brighton () is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the City of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located south of London. Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze Age, Roman and Anglo-Saxon periods. The ancient settlement of "Brighthelmstone" was documented in the ''Domesday Book'' (1086). The town's importance grew in the Middle Ages as the Old Town developed, but it languished in the early modern period, affected by foreign attacks, storms, a suffering economy and a declining population. Brighton began to attract more visitors following improved road transport to London and becoming a boarding point for boats travelling to France. The town also developed in popularity as a health resort for sea bathing as a purported cure for illnesses. In the Georgian era, Brighton developed as a highly fashionable seaside resort, encouraged by the patronage of the Prince Regent, later King George IV, who spent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Fatal Shore
''The Fatal Shore: The Epic of Australia's Founding'' by Robert Hughes is a history of the early years of British colonisation of Australia, and especially the history and social effects of Britain's convict transportation system. It also addresses the historical, political and sociological reasons that led to British settlement. It was first published in 1986. Hughes was an Australian man who became an internationally well-known art critic, living in Europe and then New York, where he became art critic for ''Time'' magazine. Hughes's interest in Australia's convict era began in the early 1970s, when he was filming a TV documentary about the history of Australian art that took him to Port Arthur in Tasmania. Awards * 1987 Duff Cooper Prize. * 1988 WH Smith Literary Award. Publication history ''The Fatal Shore'' was originally published in 1986 by Alfred A. Knopf in the United States and by William Collins in the UK, and subsequently published in paperback the UK by Collins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Hughes (critic)
Robert Studley Forrest Hughes AO (28 July 19386 August 2012) was an Australian-born art critic, writer, and producer of television documentaries. He was described in 1997 by Robert Boynton of ''The New York Times'' as "the most famous art critic in the world." Hughes earned widespread recognition for his book and television series on modern art, '' The Shock of the New'', and for his longstanding position as art critic with ''TIME'' magazine. He is also known for his best seller ''The Fatal Shore'' (1986), a study of the British convict system in early Australian history. Known for his contentious critiques of art and artists, Hughes was generally conservative in his tastes, although he did not belong to a particular philosophical camp. His writing was noted for its power and elegance. Early life Hughes was born in Sydney, in 1938. His father and paternal grandfather were lawyers. Hughes's father, Geoffrey Forrest Hughes, was a pilot in the First World War, with later caree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Surgeon
A naval surgeon, or less commonly ship's doctor, is the person responsible for the health of the ship's company aboard a warship. The term appears often in reference to Royal Navy's medical personnel during the Age of Sail. Ancient uses Specialised crew members capable of providing medical care have been a feature of military vessels for at least two thousand years. The second-century Roman Navy under Emperor Hadrian included a surgeon aboard each of its triremes, with the position earning twice a regular officer's pay. Royal Navy During the Age of Sail, the Royal Navy carried trained medical officers aboard its warships, who usually learned their trade before coming on board ship. They were generally called surgeons. The Navy Board qualified surgeons through an examination at the Barber-Surgeons' Company and they were responsible to the Sick and Wounded Board under the Navy Board. Surgeons were required to keep two logbooks detailing treatments and procedures carried out under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hobart
Hobart ( ; Nuennonne/Palawa kani: ''nipaluna'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian island state of Tasmania. Home to almost half of all Tasmanians, it is the least-populated Australian state capital city, and second-smallest if territories are taken into account, before Darwin, Northern Territory. Hobart is located in Tasmania's south-east on the estuary of the River Derwent, making it the most southern of Australia's capital cities. Its skyline is dominated by the kunanyi/Mount Wellington, and its harbour forms the second-deepest natural port in the world, with much of the city's waterfront consisting of reclaimed land. The metropolitan area is often referred to as Greater Hobart, to differentiate it from the City of Hobart, one of the five local government areas that cover the city. It has a mild maritime climate. The city lies on country which was known by the local Mouheneener people as nipaluna, a name which includes surrounding features such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |