|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme 2
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is an enzyme that can be found either attached to the membrane of cells (mACE2) in the intestines, kidney, testis, gallbladder, and heart or in a soluble form (sACE2). Both membrane bound and soluble ACE2 are integral parts of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) that exists to keep the body's blood pressure in check. While mACE2 does not appear to factor into the harmful phase of RAAS (the increase of blood pressure), its existence is vital in order for the enzyme ADAM17 to cleave its extracellular domain to create soluble ACE2 (sACE2). Soluble ACE2 lowers blood pressure by catalyzing the hydrolysis of angiotensin II (a vasoconstrictor peptide) into angiotensin (1–7) (a vasodilator) which in turns binds to MasR receptors creating localized vasodilation and hence decreasing blood pressure. This decrease in blood pressure makes the entire process a promising drug target for treating cardiovascular diseases. mACE2 also ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Center For Biotechnology Information
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland, and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by US Congressman Claude Pepper. The NCBI houses a series of databases relevant to biotechnology and biomedicine and is an important resource for bioinformatics tools and services. Major databases include GenBank for DNA sequences and PubMed, a bibliographic database for biomedical literature. Other databases include the NCBI Epigenomics database. All these databases are available online through the Entrez search engine. NCBI was directed by David Lipman, one of the original authors of the BLAST sequence alignment program and a widely respected figure in bioinformatics. GenBank NCBI had responsibility for making available the GenBank DNA seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADAM17
A disintegrin and metalloprotease 17 (ADAM17), also called TACE (''tumor necrosis factor-α-converting enzyme''), is a 70-kDa enzyme that belongs to the ADAM protein family of disintegrins and metalloproteases. Chemical characteristics ADAM17 is an 824-amino acid polypeptide. Function ADAM17 is understood to be involved in the processing of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) at the surface of the cell, and from within the intracellular membranes of the trans-Golgi network. This process, which is also known as 'shedding', involves the cleavage and release of a soluble ectodomain from membrane-bound pro-proteins (such as pro-TNF-α), and is of known physiological importance. ADAM17 was the first 'sheddase' to be identified, and is also understood to play a role in the release of a diverse variety of membrane-anchored cytokines, cell adhesion molecules, receptors, ligands, and enzymes. Cloning of the TNF-α gene revealed it to encode a 26 kDa type II transmembrane pro- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
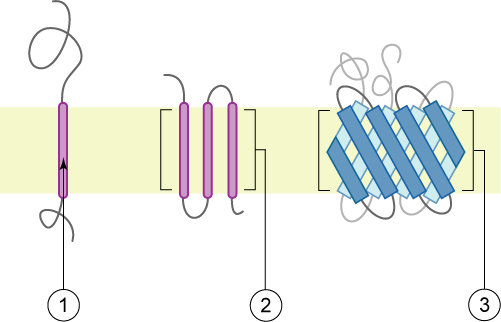
Transmembrane Domain
A transmembrane domain (TMD) is a membrane-spanning protein domain. TMDs generally adopt an alpha helix topological conformation, although some TMDs such as those in porins can adopt a different conformation. Because the interior of the lipid bilayer is hydrophobic, the amino acid residues in TMDs are often hydrophobic, although proteins such as membrane pumps and ion channels can contain polar residues. TMDs vary greatly in length, sequence, and hydrophobicity, adopting organelle-specific properties. Functions of transmembrane domains Transmembrane domains are known to perform a variety of functions. These include: * Anchoring transmembrane proteins to the membrane. *Facilitating molecular transport of molecules such as ions and proteins across biological membranes; usually hydrophilic residues and binding sites in the TMDs help in this process. *Signal transduction across the membrane; many transmembrane proteins, such as G protein-coupled receptors, receive extracellular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes including apoptosis, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or misfolded proteins in cells. Consequently, abnormality in the regulation of proteolysis can cause disease. Proteolysis can also be used as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, and it may also be used in industry, for example in food proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins. Background The concept of the domain was first proposed in 1973 by Wetlaufer aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type I Membrane Protein
A single-pass membrane protein also known as single-spanning protein or bitopic protein is a transmembrane protein that spans the lipid bilayer only once. These proteins may constitute up to 50% of all transmembrane proteins, depending on the organism, and contribute significantly to the network of interactions between different proteins in cells, including interactions via transmembrane alpha helices. They usually include one or several water-soluble domains situated at the different sides of biological membranes, for example in single-pass transmembrane receptors. Some of them are small and serve as regulatory or structure-stabilizing subunits in large multi-protein transmembrane complexes, such as photosystems or the respiratory chain. A 2013 estimate identified about 1300 single-pass membrane proteins in the human genome. Topology-based classification Bitopic proteins are classified into 4 types, depending on their transmembrane topology and location of the transmembrane heli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid Transporter
An amino acid transporter is a membrane transport protein that transports amino acids. They are mainly of the solute carrier family. Families There are several families that function in amino acid transport, some of these include: TC# 2.A.3- Amino Acid-Polyamine-Organocation (APC) Superfamily TC# 2.A.18- Amino Acid/Auxin Permease (AAAP) Family TC# 2.A.23- Dicarboxylate/Amino Acid:Cation (Na+ or H+) Symporter (DAACS) Family TC# 2.A.26- Branched Chain Amino Acid:Cation Symporter (LIVCS) Family TC# 2.A.42- Hydroxy/Aromatic Amino Acid Permease (HAAAP) Family TC# 2.A.78- Branched Chain Amino Acid Exporter (LIV-E) Family TC# 2.A.95- 6TMS Neutral Amino Acid Transporter (NAAT) Family TC# 2.A.118- Basic Amino Acid Antiporter (ArcD) Family TC# 2.A.120- Putative Amino Acid Permease (PAAP) Family Solute carrier family examples * (1) high affinity glutamate and neutral amino acid transporter * (3) heavy subunits of heteromeric amino acid transporters * (6) Bacterial Leucine Transp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterocytes
Enterocytes, or intestinal absorptive cells, are simple columnar epithelial cells which line the inner surface of the small and large intestines. A glycocalyx surface coat contains digestive enzymes. Microvilli on the apical surface increase its surface area. This facilitates transport of numerous small molecules into the enterocyte from the intestinal lumen. These include broken down proteins, fats, and sugars, as well as water, electrolytes, vitamins, and bile salts. Enterocytes also have an endocrine role, secreting hormones such as leptin. Function The major functions of enterocytes include: *Ion uptake, including sodium, calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc, and copper. This typically occurs through active transport. *Water uptake. This follows the osmotic gradient established by Na+/K+ ATPase on the basolateral surface. This can occur transcellularly or paracellularly. *Sugar uptake. Polysaccharides and disaccharidases in the glycocalyx break down large sugar molecules, which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metalloenzyme
Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large proportion of all proteins are part of this category. For instance, at least 1000 human proteins (out of ~20,000) contain zinc-binding protein domains although there may be up to 3000 human zinc metalloproteins. Abundance It is estimated that approximately half of all proteins contain a metal. In another estimate, about one quarter to one third of all proteins are proposed to require metals to carry out their functions. Thus, metalloproteins have many different functions in cells, such as storage and transport of proteins, enzymes and signal transduction proteins, or infectious diseases. The abundance of metal binding proteins may be inherent to the amino acids that proteins use, as even artificial proteins without evolutionary history will readily bind metals. Most metals in the human body are bound to proteins. For instance, the relatively high concentration of iron in the human body i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)