|
András Kun
András Kun, O.F.M. (9 November 1911 – 19 September 1945 in Budapest, Hungary) was a Roman Catholic priest of the Franciscan Order. During the Holocaust in Hungary, Kun was also the commander of an Anti-Semitic death squad for the Arrow Cross Party. After the Second World War, Kun was prosecuted for war crimes by a Hungarian People's Tribunal after Hungary's occupation by Soviet armies. He was convicted and hanged. Life Early life and Church career András Kun was born 8 November 1911 in Nyírbátor, Kingdom of Hungary. He attended seminary in Rome. He then served as a priest in a Franciscan monastery. In 1943, Kun was, according to journalist Rezső Szirmai, expelled from the monastery and moved to Budapest. Although it is uncertain whether he ever had valid faculties, Kun sometimes gave sermons and offered Nuptial Masses at Sacred Heart of Jesus Roman Catholic Church in Városmajor. Participation in the Holocaust In early 1944, Kun enrolled in Hungary's Pro-Nazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Friars Minor
The Order of Friars Minor (also called the Franciscans, the Franciscan Order, or the Seraphic Order; postnominal abbreviation OFM) is a mendicant Catholic religious order, founded in 1209 by Francis of Assisi. The order adheres to the teachings and spiritual disciplines of the founder and of his main associates and followers, such as Clare of Assisi, Anthony of Padua, and Elizabeth of Hungary, among many others. The Order of Friars Minor is the largest of the contemporary First Orders within the Franciscan movement. Francis began preaching around 1207 and traveled to Rome to seek approval of his order from Pope Innocent III in 1209. The original Rule of Saint Francis approved by the pope disallowed ownership of property, requiring members of the order to beg for food while preaching. The austerity was meant to emulate the life and ministry of Jesus Christ. Franciscans traveled and preached in the streets, while boarding in church properties. The extreme poverty required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which may be a chapel, church, or temple, and may also serve as an oratory, or in the case of communities anything from a single building housing only one senior and two or three junior monks or nuns, to vast complexes and estates housing tens or hundreds. A monastery complex typically comprises a number of buildings which include a church, dormitory, cloister, refectory, library, balneary and infirmary, and outlying granges. Depending on the location, the monastic order and the occupation of its inhabitants, the complex may also include a wide range of buildings that facilitate self-sufficiency and service to the community. These may include a hospice, a school, and a range of agricultural and manufacturing buildings such as a barn, a fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armband
An armband is a piece of material worn around the arm. They may be worn for pure ornamentation, or to mark the wearer as belonging to group, or as insignia having a certain rank, status, office or role, or being in a particular state or condition. Sprung armbands, known as sleeve garters, have been used by men to keep overlong sleeves from dropping over the hands and thereby interfering with their use. Armbands may also refer to inflatable armbands used to assist flotation for swimmers or for use with sphygmomanometers, in which case they are generally referred to as cuffs. Variation Bronze Age armbands have been found made from bronze (sometimes gilded) and jet. Some were constructed so that it would have been impossible to remove them. When used as part of a military uniform it is called a brassard. Uniforms serving other purposes such as to identify members of clubs, societies or teams may also have armbands for certain ranks or functions. An armband might identify a group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Collar
A clerical collar, clergy collar, or, informally, dog collar, is an item of Christian clerical clothing. The clerical collar is almost always white and was originally made of cotton or linen but is now frequently made of plastic. There are various styles of clerical collar. The traditional full collar (the style informally described as a ''dog collar'') is a ring that closes at the back of the neck, presenting a seamless front. It is often attached with a ''collaret'' or ''collarino'' that covers the white collar almost completely, except for a small white rectangle at the base of the throat, and sometimes with the top edge of the collar exposed to mimic the collar of a cassock. Alternatively, it may simply be a detachable tab of white in the front of the clerical shirt. The clerical shirt is traditionally black (or another color appropriate to a person's ministry rank, such as purple for Anglican bishops), but today is available in a variety of colors depending on the wearer's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassock
The cassock or soutane is a Christian clerical clothing coat used by the clergy and male religious of the Oriental Orthodox Churches, Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church, in addition to some clergy in certain Protestant denominations such as Anglicans and Lutherans. "Ankle-length garment" is the literal meaning of the corresponding Latin term, . It is related to the habits traditionally worn by nuns, monks, and friars. The cassock derives historically from the tunic of classical antiquity that in ancient Rome was worn underneath the toga and the chiton that was worn beneath the himation in ancient Greece. In religious services, it has traditionally been worn underneath vestments, such as the alb. In the West, the cassock is little used today except for religious services, save for traditionalist and those other Catholic clergy and religious who continue to wear the cassock as their standard attire. However, in many countries it was the normal everyday wear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
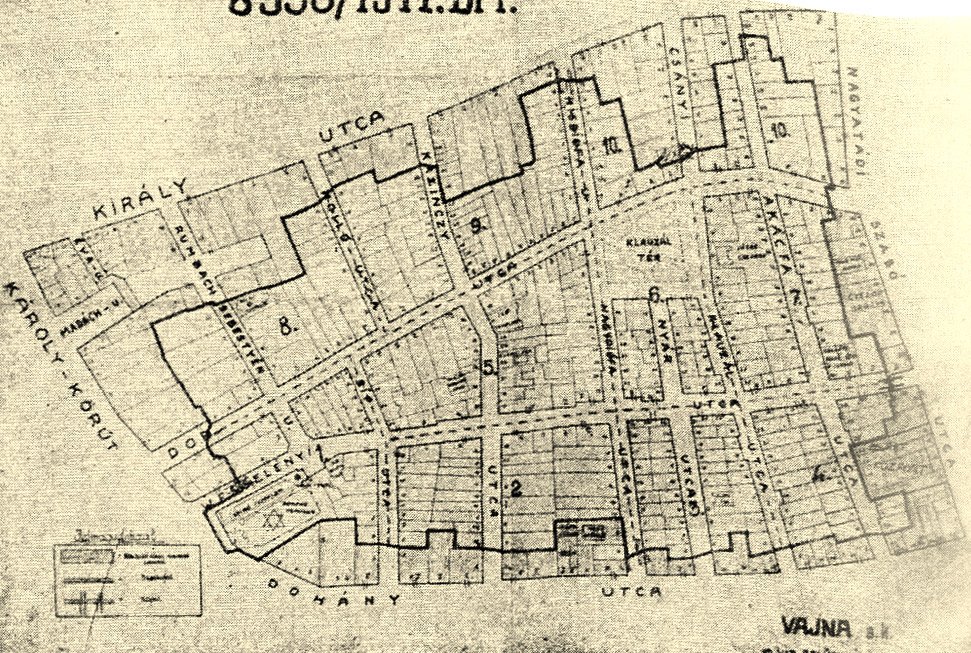
Budapest Ghetto
The Budapest Ghetto was a Nazi ghetto set up in Budapest, Hungary, where Jews were forced to relocate by a decree of the Government of National Unity led by the fascist Arrow cross party during the final stages of World War II. The ghetto existed from November 29, 1944 to January 17, 1945. History The area consisted of several blocks of the old Jewish quarter which included the two main synagogues of the city, the Neolog Dohány Street Synagogue and Orthodox Kazinczy Street Synagogue. The ghetto was created on November 29, 1944, by a decree of the Royal Hungarian Government. It was surrounded by a high fence reinforced with planks that was guarded so that contraband could not be sneaked in, and people could not get out. 70 000 Jews were moved into a 0.1 square mile (0,26 square kilometre) zone. The Nazi occupation of Budapest (Operation Margarethe) started on March 19, 1944. The ghetto was established in November 1944, and lasted for less than two months, until the liberation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Holocaust In Hungary
The Holocaust in Hungary was the dispossession, deportation, and systematic murder of more than half of the Hungarian Jews, primarily after the German occupation of Hungary in March 1944. At the time of the German invasion, Hungary had a Jewish population of 825,000, the largest remaining in Europe, further swollen by Jews escaping from elsewhere to the relative safety of that country. The Hungarian Prime Minister Miklós Kállay had been reluctant to deport them. Fearing Hungary was trying to pursue peace with the Allies, Adolf Hitler ordered the invasion. New restrictions against Jews were imposed soon after Germany occupied Hungary on 19 March 1944. The invading troops included a '' Sonderkommando'' led by SS officer Adolf Eichmann, who arrived in Budapest to supervise the deportation of the country's Jews to the Auschwitz concentration camp in occupied Poland. Between 15 May and 9 July 1944, over 434,000 Jews were deported on 147 trains, most of them to Auschwitz, where abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schutzstaffel
The ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS; also stylized as ''ᛋᛋ'' with Armanen runes; ; "Protection Squadron") was a major paramilitary organization under Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany, and later throughout German-occupied Europe during World War II. It began with a small guard unit known as the ''Saal-Schutz'' ("Hall Security") made up of party volunteers to provide security for party meetings in Munich. In 1925, Heinrich Himmler joined the unit, which had by then been reformed and given its final name. Under his direction (1929–1945) it grew from a small paramilitary formation during the Weimar Republic to one of the most powerful organizations in Nazi Germany. From the time of the Nazi Party's rise to power until the regime's collapse in 1945, the SS was the foremost agency of security, surveillance, and terror within Germany and German-occupied Europe. The two main constituent groups were the '' Allgemeine SS'' (General SS) and ''Waffen-SS'' (Armed SS). The ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English as the Bolshevists,. It signifies both Bolsheviks and adherents of Bolshevik policies. were a far-left, revolutionary Marxist faction founded by Vladimir Lenin that split with the Mensheviks from the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP), a revolutionary socialist political party formed in 1898, at its Second Party Congress in 1903. After forming their own party in 1912, the Bolsheviks took power during the October Revolution in the Russian Republic in November 1917, overthrowing the Provisional Government of Alexander Kerensky, and became the only ruling party in the subsequent Soviet Russia and later the Soviet Union. They considered themselves the leaders of the revolutionary proletariat of Russia. Their beli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Margarethe
Operation Margarethe (''Unternehmen Margarethe'') was the occupation of Hungary by German Nazi troops during World War II that was ordered by Adolf Hitler. Course of events Hungarian Prime Minister Miklós Kállay, who had been in office from 1942, had the knowledge and the approval of Hungarian Regent Miklós Horthy to seek secretly at negotiating a separate peace with the Allies in early 1944. Hitler wanted to prevent the Hungarians from turning against Germany. On 12 March 1944, German troops received orders by Hitler to capture critical Hungarian facilities. Hitler invited Horthy to the Palace of Klessheim, near of Salzburg, on 15 March. On the evening of 15 March 1944, when Admiral Horthy was watching a performance of the opera ''Petofi'', he received an urgent message from the German minister Dietrich von Jagow, who stated that Horthy had to see him immediately at the German legation. When Horthy arrived, Jagow gave him a letter from Hitler saying the ''Fuhrer'' wanted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Heart Of Jesus
The Most Sacred Heart of Jesus ( la, Cor Jesu Sacratissimum) is one of the most widely practised and well-known Catholic devotions, wherein the heart of Jesus is viewed as a symbol of "God's boundless and passionate love for mankind". This devotion to Christ is predominantly used in the Catholic Church, followed by high-church Anglicans, Lutherans and some Western Rite Orthodox. In the Latin Church, the liturgical Solemnity of the Most Sacred Heart of Jesus is celebrated the third Friday after Pentecost. The 12 promises of the Most Sacred Heart of Jesus are also extremely popular. The devotion is especially concerned with what the church deems to be the long-suffering love and compassion of the heart of Christ towards humanity. The popularization of this devotion in its modern form is derived from a Roman Catholic nun from France, Margaret Mary Alacoque, who said she learned the devotion from Jesus during a series of apparitions to her between 1673 and 1675, and later, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |