|
Ancalites
The Ancalites were a tribe of Iron Age Britain in the first century BCE. They are known only from a brief mention in the writings of Julius Caesar. They may have been one of the four tribes of Kent, represented in Caesar by references to the "four kings of that region" and in the archaeological record by distinct pottery assemblages. During Julius Caesar's second invasion of Britain in 54 BCE, following Caesar's military success and restoration of King Mandubracius to power over the Trinovantes, opposition to the Romans coalesced around the figure of Cassivellaunus which led to divided loyalties among the Britons, as Caesar records. Emissaries of five British tribes, including the Ancalites (the others being the Bibroci, the Segontiaci, the Cenimagni and the Cassi), arrived at the Roman camp to treat for peace, and agreed to reveal details of Cassivellaunus' stronghold. Caesar besieged him there and brought him to terms. When Caesar left Britain he took hostages from the Britons, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantiaci
The Cantiaci or Cantii were an Iron Age Celtic people living in Britain before the Roman conquest, and gave their name to a '' civitas'' of Roman Britain. They lived in the area now called Kent, in south-eastern England. Their capital was ''Durovernum Cantiacorum'', now Canterbury. They were bordered by the Regni to the west, and the Catuvellauni to the north. Julius Caesar landed in Cantium in 55 and 54 BCE, the first Roman expeditions to Britain. He recounts in his ''De Bello Gallico'' v. 14: Rulers Pre-Roman Iron Age Julius Caesar named five Celtic tribes inhabiting the land that would become the "heartland of the Catuvellauni": the Ancalites, the Bibroci, the Cassi, the Cenimagni, and the Segontiaci, each with their own "king" or chieftain. He found their way of life to be very similar to their cousins in Gaul with whom they were close – the invasion of Britain may have been triggered by the Britons' supply of arms to the Gauls, who were being subjug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
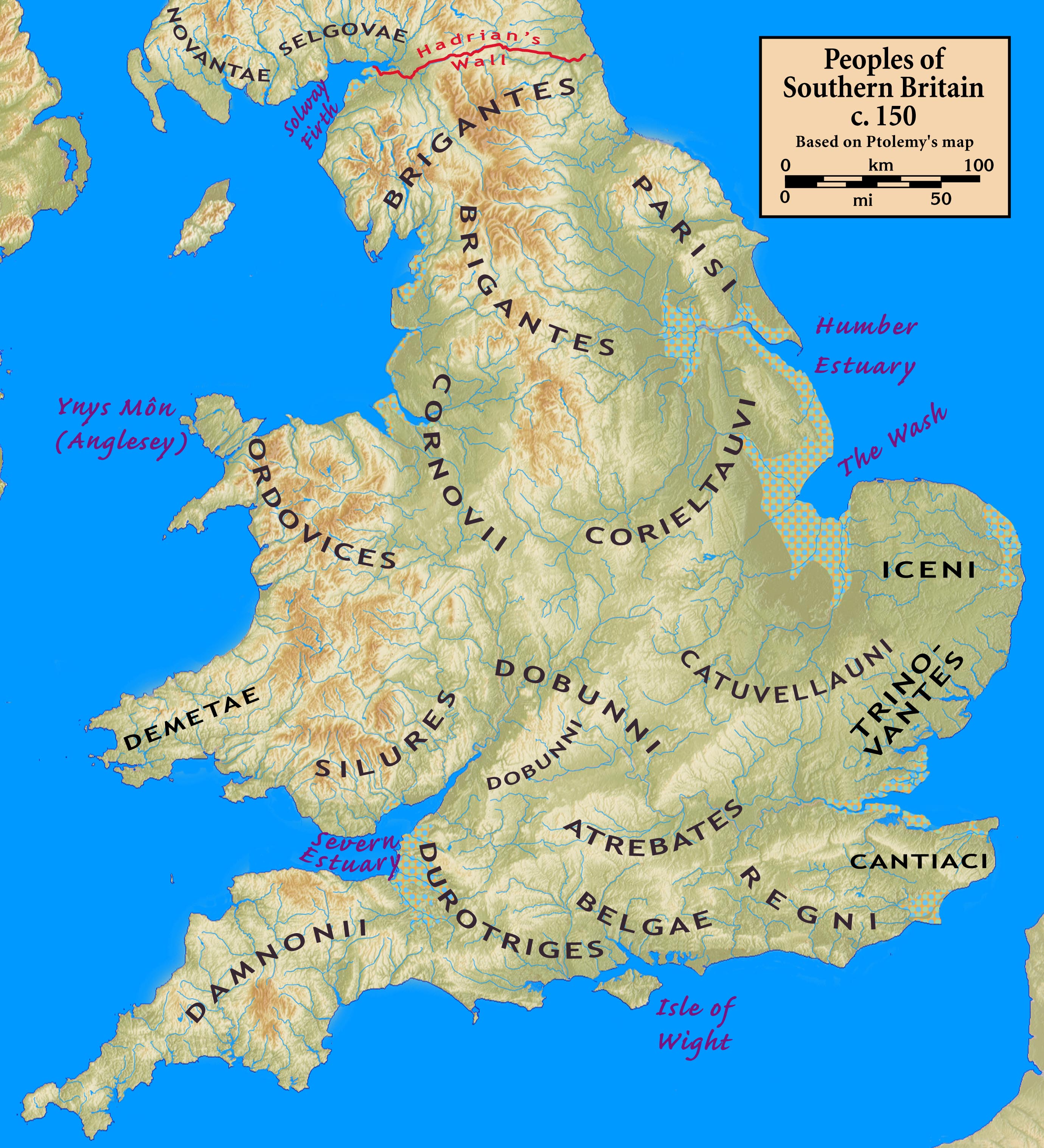
Iron Age Tribes In Britain
The names of the Celtic Iron Age tribes in Britain were recorded by Roman and Greek historians and geographers, especially Ptolemy. Information from the distribution of Celtic coins has also shed light on the extents of the territories of the various groups that occupied the island. Historiography The following ethnic names were recorded in the 2nd century CE at the earliest. Technically, the Iron Age had ended by this date, having transitioned into the Roman period. These tribes were not necessarily the same tribes that had been living in the same area during the Iron Age. Available evidence seems to indicate that the tribes of the Middle Iron Age tended to group together into larger tribal kingdoms during the Late Iron Age. The Belgae and Atrebates share their names with tribes in France and Belgium, which, together with Caesar's note that Diviciacus of the Suessiones had ruled territory in Britain, suggests that this part of the country might have been conquered and ruled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassivellaunus
Cassivellaunus was a historical British military leader who led the defence against Julius Caesar's second expedition to Britain in 54 BC. He led an alliance of tribes against Roman forces, but eventually surrendered after his location was revealed to Julius Caesar by defeated Britons. Cassivellaunus made an impact on the British consciousness. He appears in British legend as Cassibelanus, one of Geoffrey of Monmouth's kings of the Britons, and in the '' Mabinogion'', the ''Brut y Brenhinedd'' and the Welsh Triads as Caswallawn, son of Beli Mawr. Name The Common Brittonic personal name ''Cassiuellaunos'' stems from the word ''uellaunos'' ('chief, commandant'). The meaning of the prefix ''cassi-'' has been debated, but it possibly signifies 'tin, bronze'. Cassivellaunus may thus been translated as 'Chief-of-Tin', that is to say 'the inflexible'. The personal name ''Ver-cassivellaunus'' ('True-Chief-of-Tin') is related. History Cassivellaunus appears in Julius Caesar's ''Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibroci
The Bibroci were a tribe of Iron Age Britain in the first century BCE. They are known only from a brief mention in the writings of Julius Caesar. They may have been one of the four tribes of Kent, represented in Caesar by references to the "four kings of that region" and in the archaeological record by distinct pottery assemblages. Etymology The name ''Bibroci'' stems from Gaulish ''*bibros'' ('beaver'), ultimately from a Proto-Indo-European root ''*bhe-bhros.'' History During Julius Caesar's second invasion of Britain in 54 BCE, following Caesar's military success and restoration of King Mandubracius to power over the Trinovantes, opposition to the Romans coalesced around the figure of Cassivellaunus which led to divided loyalties among the Britons, as Caesar records. Emissaries of five British tribes, including the Bibroci (the others being the Ancalites, the Segontiaci, the Cenimagni and the Cassi), arrived at the Roman camp to treat for peace, and agreed to reveal details o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segontiaci
The Segontiaci were a tribe of Iron Age Britain in the first century BCE. They are known only from a brief mention in the writings of Julius Caesar. They may have been one of the four tribes of Kent, represented in Caesar by references to the "four kings of that region" and in the archaeological record by distinct pottery assemblages. During Julius Caesar's second invasion of Britain in 54 BCE, following Caesar's military success and restoration of King Mandubracius to power over the Trinovantes, opposition to the Romans coalesced around the figure of Cassivellaunus which led to divided loyalties among the Britons, as Caesar records. Emissaries of five British tribes, including the Segontiaci (the others being the Ancalites, the Bibroci, the Cenimagni and the Cassi), arrived at the Roman camp to treat for peace, and agreed to reveal details of Cassivellaunus' stronghold. Caesar besieged him there and brought him to terms. When Caesar left Britain he took hostages from the Britons, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenimagni
The Cenimagni were a tribe of Iron Age Britain in the first century BCE. They are known only from a brief mention in the writings of Julius Caesar. It has been suggested that the name is a variant of ''Iceni'' with the Latin adjective ''magni'', meaning "great". Others have suggested that they may have been one of the four tribes of Kent, represented in Caesar by references to the "four kings of that region" and in the archaeological record by distinct pottery assemblages. During Julius Caesar's second invasion of Britain in 54 BCE, following Caesar's military success and restoration of King Mandubracius to power over the Trinovantes, opposition to the Romans coalesced around the figure of Cassivellaunus which led to divided loyalties among the Britons, as Caesar records. Emissaries of five British tribes, including the Cenimagni (the others being the Ancalites, the Segontiaci, the Bibroci and the Cassi), arrived at the Roman camp to treat for peace, and agreed to reveal details of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Iron Age
The British Iron Age is a conventional name used in the archaeology of Great Britain, referring to the prehistoric and protohistoric phases of the Iron Age culture of the main island and the smaller islands, typically excluding prehistoric Ireland, which had an independent Iron Age culture of its own. The parallel phase of Irish archaeology is termed the Irish Iron Age. The Iron Age is not an archaeological horizon of common artefacts but is rather a locally-diverse cultural phase. The British Iron Age followed the British Bronze Age and lasted in theory from the first significant use of iron for tools and weapons in Britain to the Romanisation of the southern half of the island. The Romanised culture is termed Roman Britain and is considered to supplant the British Iron Age. The tribes living in Britain during this time are often popularly considered to be part of a broadly-Celtic culture, but in recent years, that has been disputed. At a minimum, "Celtic" is a linguistic ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henley-on-Thames
Henley-on-Thames ( ) is a town and civil parish on the River Thames in Oxfordshire, England, northeast of Reading, west of Maidenhead, southeast of Oxford and west of London (by road), near the tripoint of Oxfordshire, Berkshire and Buckinghamshire. The population at the 2011 Census was 11,619. History Henley does not appear in Domesday Book of 1086; often it is mistaken for ''Henlei'' in the book which is in Surrey. There is archaeological evidence of people residing in Henley since the second century as part of the Romano-British period. The first record of Henley as a substantial settlement is from 1179, when it is recorded that King Henry II "had bought land for the making of buildings". King John granted the manor of Benson and the town and manor of Henley to Robert Harcourt in 1199. A church at Henley is first mentioned in 1204. In 1205 the town received a tax for street paving, and in 1234 the bridge is first mentioned. In 1278 Henley is described as a hamlet of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point they diverged into the Welsh, Cornish and Bretons (among others). They spoke the Common Brittonic language, the ancestor of the modern Brittonic languages. The earliest written evidence for the Britons is from Greco-Roman writers and dates to the Iron Age.Koch, pp. 291–292. Celtic Britain was made up of many tribes and kingdoms, associated with various hillforts. The Britons followed an Ancient Celtic religion overseen by druids. Some of the southern tribes had strong links with mainland Europe, especially Gaul and Belgica, and minted their own coins. The Roman Empire conquered most of Britain in the 1st century, creating the province of Britannia. The Romans invaded northern Britain, but the Britons and Caledonians in the north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the adven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire to the north, Oxfordshire to the northeast and Berkshire to the east. The county town was originally Wilton, after which the county is named, but Wiltshire Council is now based in the county town of Trowbridge. Within the county's boundary are two unitary authority areas, Wiltshire and Swindon, governed respectively by Wiltshire Council and Swindon Borough Council. Wiltshire is characterised by its high downland and wide valleys. Salisbury Plain is noted for being the location of the Stonehenge and Avebury stone circles (which together are a UNESCO Cultural and World Heritage site) and other ancient landmarks, and as a training area for the British Army. The city of Salisbury is notable for its medieval cathedral. Swindon is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxfordshire
Oxfordshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the north west of South East England. It is a mainly rural county, with its largest settlement being the city of Oxford. The county is a centre of research and development, primarily due to the work of the University of Oxford and several notable science parks. These include the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus and Milton Park, both situated around the towns of Didcot and Abingdon-on-Thames. It is a landlocked county, bordered by six counties: Berkshire to the south, Buckinghamshire to the east, Wiltshire to the south west, Gloucestershire to the west, Warwickshire to the north west, and Northamptonshire to the north east. Oxfordshire is locally governed by Oxfordshire County Council, together with local councils of its five non-metropolitan districts: City of Oxford, Cherwell, South Oxfordshire, Vale of White Horse, and West Oxfordshire. Present-day Oxfordshire spanning the area south of the Thames was h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)