|
Anatomy Of A Rowing Stroke
In rowing, the stroke is the action of moving the oar through the water in order to propel the boat forward. The two fundamental reference points in the stroke are the ''catch'' where the oar blade is placed in the water, and the ''extraction'' (also known as the 'finish', 'release' or 'tapping down') where the oar blade is removed from the water. After the blade is placed in the water at the ''catch'', the rower applies pressure to the oar levering the boat forward which is called the ''drive'' phase of the stroke. Once the rower extracts the oar from the water, the ''recovery'' phase begins, setting up the rower's body for the next stroke.; when the oars are out of the water, and the preparation for the catch occurs Stages of a stroke Drive The drive is the phase from the catch to the extraction. *As soon as the oar blade is placed in the water at the catch, the rower begins to lever the boat past the blade by straightening the legs while the body remains leaned forward and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Of Man Rowing In A Professional Sport Rowing Boat At Regattastrecke Oberschleißheim, Germany
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems which, in turn, were replaced by flat panel displays of several types. Video systems vary in display resolution, aspect ratio, refresh rate, color capabilities and other qualities. Analog and digital variants exist and can be carried on a variety of media, including radio broadcast, magnetic tape, optical discs, computer files, and network streaming. History Analog video Video technology was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) television systems, but several new technologies for video display devices have since been invented. Video was originally exclusively a live technology. Charles Ginsburg led an Ampex research team developing one of the first practical video ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rowing
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically attached to the boat, and the rower drives the oar like a lever, exerting force in the ''same'' direction as the boat's travel; while paddles are completely hand-held and have no attachment to the boat, and are driven like a cantilever, exerting force ''opposite'' to the intended direction of the boat. In some strict terminologies, using oars for propulsion may be termed either "pulling" or "rowing", with different definitions for each. Where these strict terminologies are used, the definitions are reversed depending on the context. On saltwater a "pulling boat" has each person working one oar on one side, alternating port and starboard along the length of the boat; whilst "rowing" means each person operates two oars, one on each side of the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. A number of natural states of water exist. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor. Water co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watercraft Rowing
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically attached to the boat, and the rower drives the oar like a lever, exerting force in the ''same'' direction as the boat's travel; while paddles are completely hand-held and have no attachment to the boat, and are driven like a cantilever, exerting force ''opposite'' to the intended direction of the boat. In some strict terminologies, using oars for propulsion may be termed either "pulling" or "rowing", with different definitions for each. Where these strict terminologies are used, the definitions are reversed depending on the context. On saltwater a "pulling boat" has each person working one oar on one side, alternating port and starboard along the length of the boat; whilst "rowing" means each person operates two oars, one on each side of the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
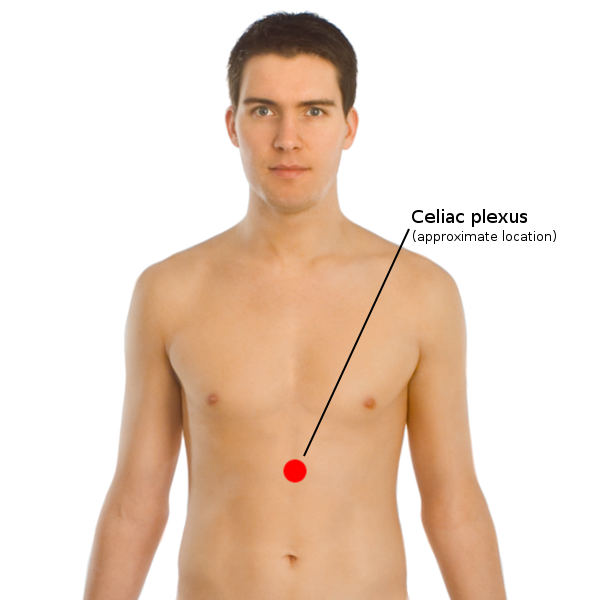
Solar Plexus
The celiac plexus, also known as the solar plexus because of its radiating nerve fibers, is a complex network of nerves located in the abdomen, near where the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, and renal arteries branch from the abdominal aorta. It is behind the stomach and the omental bursa, and in front of the crura of the diaphragm, on the level of the first lumbar vertebra. The plexus is formed in part by the greater and lesser splanchnic nerves of both sides, and fibers from the anterior and posterior vagal trunks. The celiac plexus proper consists of the celiac ganglia with a network of interconnecting fibers. The aorticorenal ganglia are often considered to be part of the celiac ganglia, and thus, part of the plexus. Structure The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses: Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus: Terminology The celiac plexus is often popularly referred to as the solar plexus. In the context of sparring or inj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
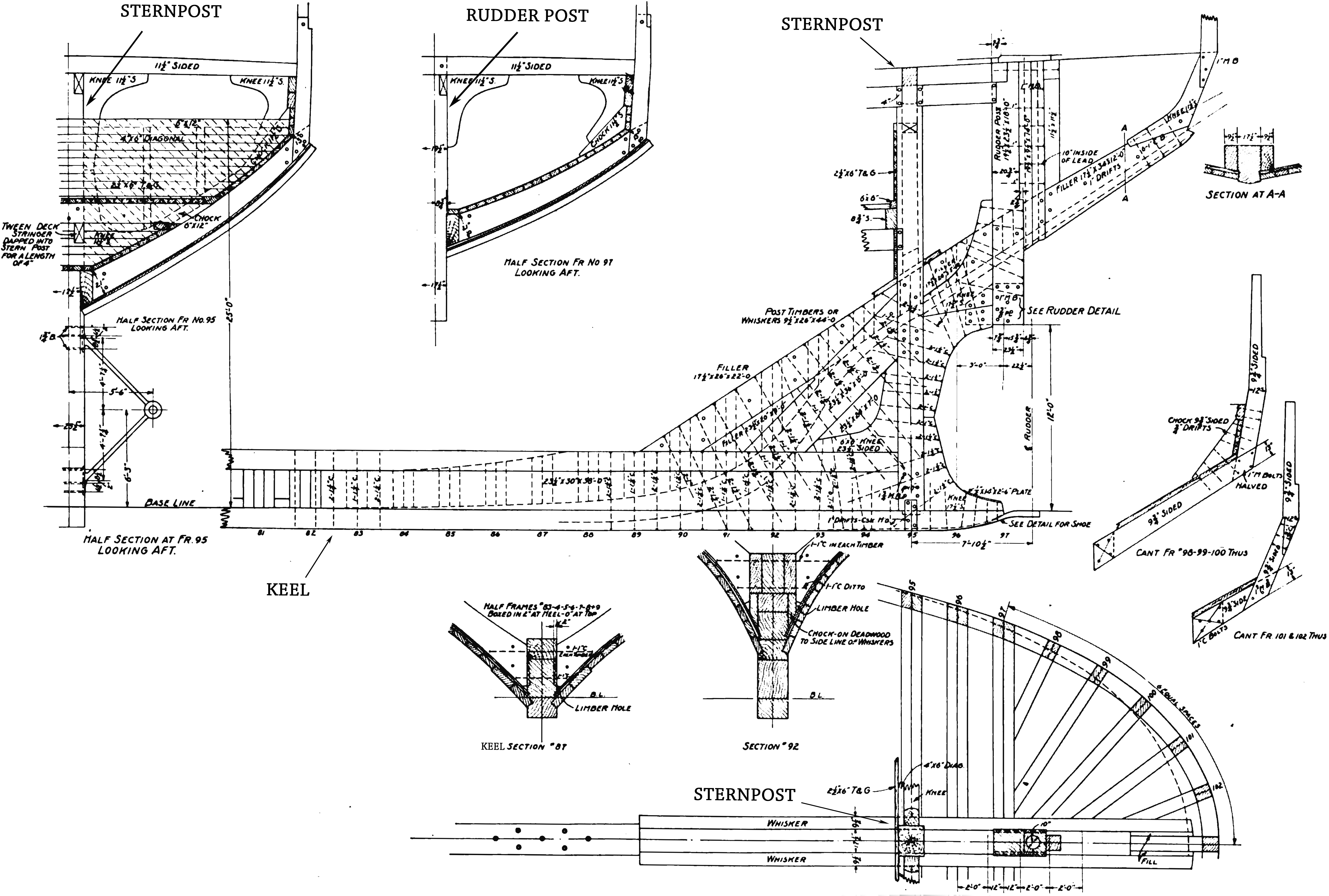
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweep Rowing
Sweep rowing is one of two disciplines of the sport of rowing. In sweep rowing each rower has one oar, usually held with both hands. As each rower has only one oar, the rowers have to be paired so that there is an oar on each side of the boat. In the United Kingdom, rowing generally refers to sweep rowing only. The term pulling was also used historically.W B Woodgate ''Boating'' Read Books, 2008 In the other rowing discipline, sculling, each rower holds two oars, one in each hand. Sweep or single oar rowing has a long history and was the means of propulsion for Greek triremes and Viking longboats. These boats were wide enough for the pairs of rowers to sit alongside each other. Boats can go faster, the narrower they are, because a smaller cross-sectional area reduces drag and wave drag and gives a sharper angle to the bow. The hulls can be kept narrower by attaching riggers to the gunwales, so that the oarlocks can be placed farther out to carry longer oars. A narrower hull mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)