|
Anabaseine
Anabaseine (3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2,3′-bipyridine) is an alkaloid toxin produced by '' Nemertines'' and ''Aphaenogaster'' ants. It is structurally similar to nicotine and anabasine. Similarly, it has been shown to act as an agonist on most nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. Mechanism of action The iminium form of anabaseine binds to most nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. But, there is a higher binding affinity for receptors in the brain with a α7 subunit, as well as skeletal muscle receptors. Binding causes the depolarization of neurons, and induces the release of both dopamine and norepinephrine. Biological effects Anabaseine causes paralysis in crustaceans and insects, but not in vertebrates, presumably by acting as an agonist on peripheral neuromuscular nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Structure The anabaseine molecule consists of a non-aromatic te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
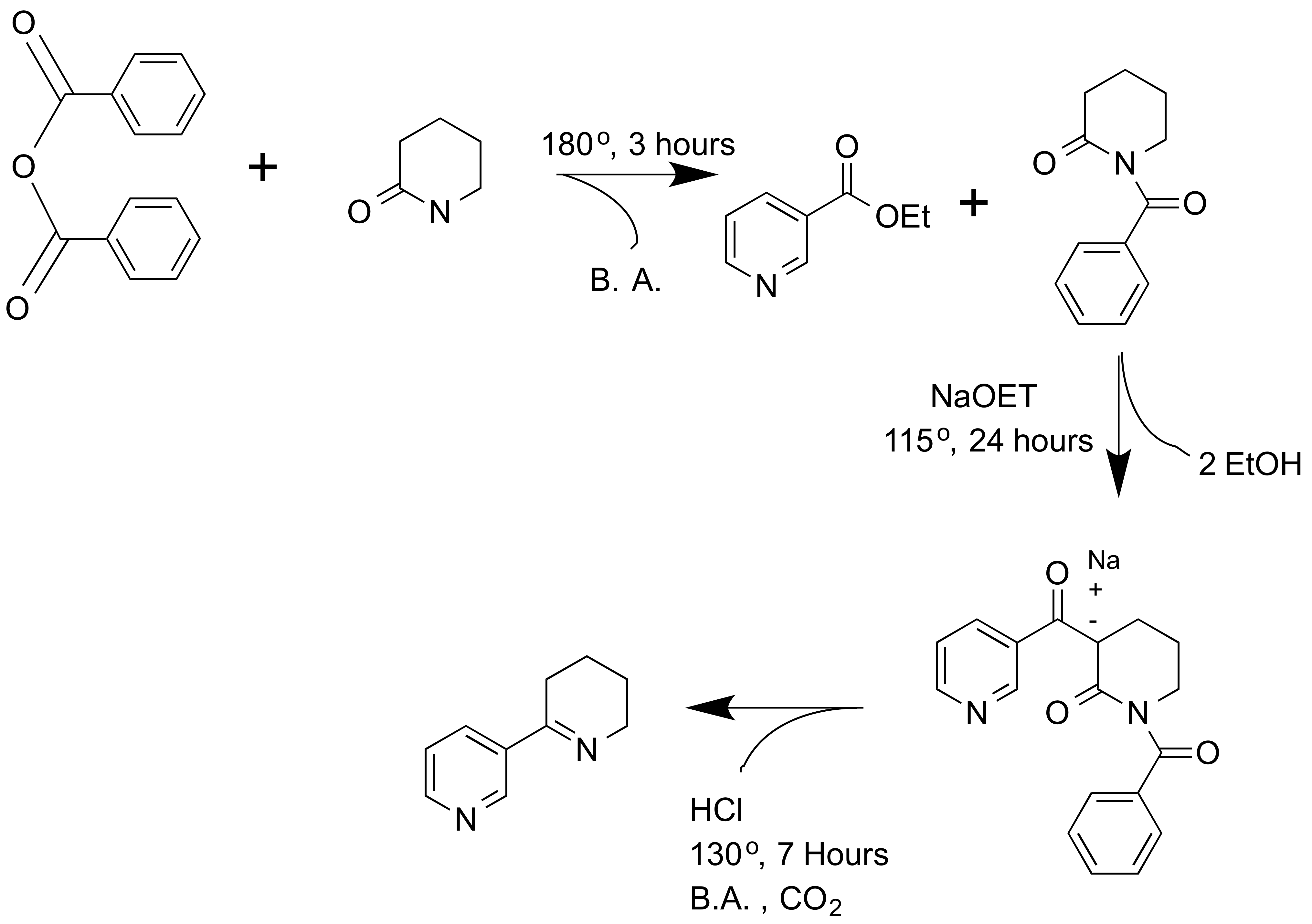
Anabaseine Synthesis
Anabaseine (3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2,3′-bipyridine) is an alkaloid toxin produced by '' Nemertines'' and ''Aphaenogaster'' ants. It is structurally similar to nicotine and anabasine. Similarly, it has been shown to act as an agonist on most nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. Mechanism of action The iminium form of anabaseine binds to most nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. But, there is a higher binding affinity for receptors in the brain with a α7 subunit, as well as skeletal muscle receptors. Binding causes the depolarization of neurons, and induces the release of both dopamine and norepinephrine. Biological effects Anabaseine causes paralysis in crustaceans and insects, but not in vertebrates, presumably by acting as an agonist on peripheral neuromuscular nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Structure The anabaseine molecule consists of a non-aromatic tetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GTS-21
GTS-21 (DMXBA) is a derivative of the natural product anabaseine that acts as a partial agonist at neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It binds to both the α4β2 and α7 subtypes, but activates only the α7 to any significant extent. Both GTS-21 itself and its demethylated active metabolite 4-OH-GTS-21 display nootropic and neuroprotective effects, and GTS-21 is being investigated for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, nicotine dependence, and, most significantly, for schizophrenia. Phase one of a clinical trial using DXMBA as a potential treatment was completed in January of 2005. 12 non-smoking subjects each received 3 daily treatments. The treatments consisted of 150mg of DMXBA, with another dose of 75mg administered 2 hours later, 75mg of DXMBA, with another dose of 37.5mg administered 2 hours later, and a placebo treatment. The order of the doses was randomized over the 3-day course of the treatments. A P50 auditory-evoked test measured a significant effect on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anabasine
Anabasine is a pyridine and piperidine alkaloid found in the Tree Tobacco (''Nicotiana glauca'') plant, a close relative of the common tobacco plant (''Nicotiana tabacum''). It is a structural isomer of, and chemically similar to, nicotine. Its principal (historical) industrial use is as an insecticide. Anabasine is present in trace amounts in tobacco smoke, and can be used as an indicator of a person's exposure to tobacco smoke. Pharmacology Anabasine is a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist. In high doses, it produces a depolarizing block of nerve transmission, which can cause symptoms similar to those of nicotine poisoning and, ultimately, death by asystole. In larger amounts it is thought to be teratogenic in swine. The intravenous LD50 of anabasine ranges from 11 mg/kg to 16 mg/kg in mice, depending on the enantiomer. Analogs B. Bhatti, et al. made some higher potency sterically strained bicyclic analogs of anabasine: *2-(Pyridin-3-yl)-1-azabicyclo .2. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , Medicinal plant, plants, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * jawed vertebrates, which include: ** cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays, and ratfish) ** bony vertebrates, which include: *** ray-fins (the majority of living bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described animal species; the rest are invertebrates, which lack vertebral columns. The vertebrates traditionally include the hagfish, which do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amide Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. In su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Closure
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where all the atoms are carbon (i.e., are carbocycles), none of the atoms are carbon (inorganic cyclic compounds), or where both carbon and non-carbon atoms are present (heterocyclic compounds). Depending on the ring size, the bond order of the individual links between ring atoms, and their arrangements within the rings, carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds may be aromatic or non-aromatic; in the latter case, they may vary from being fully saturated to having varying numbers of multiple bonds between the ring atoms. Because of the tremendous diversity allowed, in combination, by the valences of common atoms and their ability to form rings, the number of possible cyclic structures, even of small size (e.g., < 17 total atoms) numbers in the many b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decarboxylate
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carboxylation, the addition of CO2 to a compound. Enzymes that catalyze decarboxylations are called decarboxylases or, the more formal term, carboxy-lyases ( EC number 4.1.1). In organic chemistry The term "decarboxylation" usually means replacement of a carboxyl group () with a hydrogen atom: :RCO2H -> RH + CO2 Decarboxylation is one of the oldest known organic reactions. It is one of the processes assumed to accompany pyrolysis and destructive distillation. Metal salts, especially copper compounds, facilitate the reaction via the intermediacy of metal carboxylate complexes. Decarboxylation of aryl carboxylates can generate the equivalent of the corresponding aryl anion, which in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valerolactam
2-Piperidinone (2-piperidone or δ-valerolactam) is a chemical compound classified as a lactam A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid. The term is a portmanteau of the words ''lactone'' + ''amide''. Nomenclature Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size: * α-Lactam (3-atom rings) * β-Lacta .... It is used as an intermediate in the preparation of other chemicals. References {{heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzoic Anhydride
Benzoic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5CO)2O. It is acid anhydride of benzoic acid and the simplest symmetrical aromatic acid anhydride. It is a white solid. Preparation and reactions It is usually prepared by the dehydration reaction of benzoic acid, e.g. using acetic anhydride: :2 C6H5CO2H + (CH3CO)2O → (C6H5CO)2O + 2 CH3CO2H Alternatively, sodium benzoate can be treated with benzoyl chloride Benzoyl chloride, also known as benzenecarbonyl chloride, is an organochlorine compound with the formula . It is a colourless, fuming liquid with an irritating odour, and consists of a benzene ring () with an acyl chloride () substituent. It is .... It can be produced by dehydrating benzoic acid by heating. Benzoic anhydride provides a convenient way to prepare benzoic esters: :(C6H5CO)2O + ROH → C6H5CO2H + C6H5CO2R References {{Reflist Carboxylic anhydrides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structures Of Anabaseine At Physiological PH
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building structures, archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |