|
Amqu
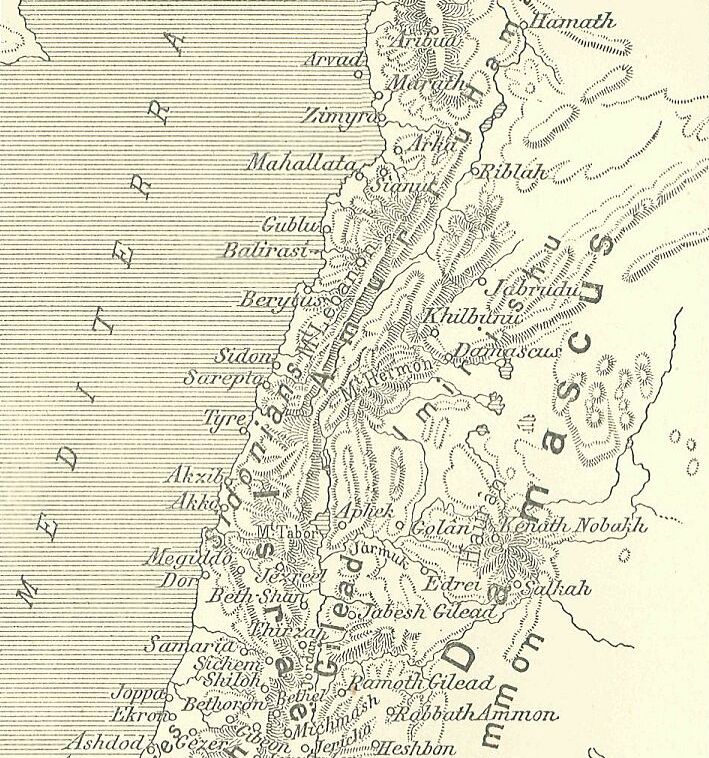
The Amqu (also Amka, Amki, Amq) is a region (now in eastern Lebanon), equivalent to the Beqaa Valley region, named in the 1350–1335 BC Amarna letters corpus. In the Amarna letters, two other associated regions appear to be east(?) and north(?), and are often mentioned in association with ''Amqu'', namely Nuhašše, and Niya-Niye (or Nii). A third hypothetical region, either adjacent or within the region of Amqu, is Subaru, as according to the letter corpus possessions or people were sold: "at the land of Subaru". The affairs in the region are often associated with Hatti, or the King of Hatti-(to the north), or with Etakkama of Qidšu/Qinsa-(also Kissa)-(i.e. Kadesh). Abdi-Riša letter-(his only letter) (The scribe wrote four identical letters-(for four city-state leaders), so who the 'author' is has to be speculative.) EA 363, title: "A joint report on Amqu (4)" El Amarna letter 363, ( EA for 'el Amarna'), "Report no 4" of 4. :"Say to the king-(i.e. Pharaoh), my lord, my god ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdi-Riša
Abdi-Riša was a ruler-'mayor' of Enišasi, during the period of the Amarna letters correspondence (1350–1335 BC). Another mayor of Enišasi, Šatiya, is found in the Amarna letters corpus. The name "Abdi-Riša" means ''"servant-Riša"''. Abdi-Riša is only referenced in his own letter EA 363, a letter to pharaoh, ( EA for 'el Amarna'). Letter no. 363 is a unique letter, being part of a letter–series, (by the same scribe): :EA 174-(1), ''"Report on Amqu (1)"'' :EA 175-(2), ''"Report on Amqu (2)"'' :EA 176-(3), ''"Report on Amqu (3)"'' :EA 363-(4), ''"Report on Amqu (4)"'' the Amqu being the ''"Beqaa Valley area"'' of Lebanon. As letter EA 363 was discovered later, (in a separate in-situ deposit), than the original letters of the Amarna letters correspondence, it is undamaged. Abdi-Riša letter EA 363, title: "A joint report on Amqu (4)" :Say to the king-(i.e. Pharaoh), my lord, my god, my Sun: Message of ''Abdi-Riša'', your servant, the ruler of E(ni)šasi. I fall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etakkama
Etakkama, as a common name, but also, Aitukama, Atak(k)ama, Etak(k)ama, and Itak(k)ama is the name for the 'mayor' (king) of Qidšu, (Kadesh) of the 1350–1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. (Qidšu is also referenced as: Qinšu, also Kissa). Etakkama is referenced in 11 of the 382 EA letters, ( EA for 'el Amarna'), and especially, a ''series of 4'' identical letters concerning: Amqu, the region of the Beqaa in Lebanon. Those 4 letters concern the intrigues of city/city-state takeovers, along with troops from Hatti, and the claim of: ''Etakkama's troops from 'Kinsa' ''-(Qidšu-''Kissa'')-Kadesh) and are titled: ''"A joint report on Amqu (1-4)"''. Etakkama was the author of one letter, EA 189. Letter no. 189, title: ''"Etakkama of Qadesh"'' :To the king, my lord: Message of ''Etakkama'', your servant. I fall at the feet of my lord, my Sun, 7 times plus 7. My lord, I am your servant, but the wicked Biryawaza has gone on defaming me in your sight, my lord, and when he was defa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niya (kingdom)
Niya, Niye, and also Niy of Thutmose I's Ancient Egypt, also Nii of the Amarna letters, and Nihe, etc. was a kingdom in Syria, or northern Syria. In the Amarna letters correspondence of 1350- 1335 BC, ''Nii'' is only referenced in two letters, but each is of some importance. The city of Tunip in the northern Levant had been trying to communicate to the Egyptian pharaoh for two decades, and finally resorted to another letter, EA 59: entitled: ''"From the citizens of Tunip"'', ( EA for 'el Amarna'). The city-state of Arqa also sent a letter to pharaoh, requesting aid (EA 100). The other letter referencing ''Nii'' concerns the individual Etakkama, his collusion with the Hittites, and the takeover of territory, 'city-states', and peoples in the northern and western Levant. Amarna letters ''"Nii"'', 2--letters EA 59, title: "From the citizens of Tunip" :"To the king of Egypt, our lord: Message of "the citizens of Tunip", your servant. For you may all go well. And we fall at the fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enišasi
Enišasi, was a city, or city-state located in the Beqaa Valley-(called ''Amqu'', or ''Amka'') of Lebanon, during the 1350- 1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. Of the 382–Amarna letters, Enišasi is only referenced in two letters. Enišasi was located near ''Hašabu'', (Tell Hašbe), and ''Hasi'', (Tell Hizzin?), southwest of Baalbek. Two 'mayors', or rulers of Enišasi were Šatiya and Abdi-Riša, who each authored a letter to the Egyptian pharaoh, EA 187- (title: ''A daughter sent to the Pharaoh''), and EA 363- (title: ''A joint report on Amqu–(4)''). ( EA is for 'el Amarna'.) See also *Abdi-Riša, mayor * Šatiya, mayor *Amarna letters *Amarna letters–localities and their rulers References *Moran, William L. William Lambert Moran (August 11, 1921 – December 19, 2000) was an American Assyriologist. He was born in Chicago, United States. In 1939, Moran joined the Jesuit order. He then attended Loyola University in Chicago, where he received hi ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beqaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important farming region. Industry also flourishes in Beqaa, especially that related to agriculture. The Beqaa is located about east of Beirut. The valley is situated between Mount Lebanon to the west and the Anti-Lebanon Mountains to the east. It forms the northeasternmost extension of the Great Rift Valley, which stretches from Syria to the Red Sea. Beqaa Valley is long and wide on average. It has a Mediterranean climate of wet, often snowy winters and dry, warm summers. The region receives limited rainfall, particularly in the north, because Mount Lebanon creates a rain shadow that blocks precipitation coming from the sea. The northern section has an average annual rainfall of , compared to in the central valley. Nevertheless, two rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue Line (Lebanon), the south, while Cyprus lies to its west across the Mediterranean Sea; its location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabs, Arabian hinterland has contributed to History of Lebanon, its rich history and shaped Culture of Lebanon, a cultural identity of demographics of Lebanon#Religious groups, religious diversity. It is part of the Levant region of the Middle East. Lebanon is home to roughly six million people and covers an area of , making it the List of countries and dependencies by area, second smallest country in continental Asia. The official language of the state is Arabic, while French language, French is also formally recognized; the Lebanese Arabic, Lebanese dialect of Arabic is used alongside Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna
Amarna (; ar, العمارنة, al-ʿamārnah) is an extensive Egyptian archaeological site containing the remains of what was the capital city of the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, and abandoned shortly after his death in 1332 BC. The name that the ancient Egyptians used for the city is transliterated in English as Akhetaten or Akhetaton, meaning " the horizon of the Aten".David (1998), p. 125 The site is on the east bank of the Nile River, in what today is the Egyptian province of Minya. It is about south of the city of al-Minya, south of the Egyptian capital, Cairo, and north of Luxor (site of the previous capital, Thebes). The city of Deir Mawas lies directly to its west. On the east side of Amarna there are several modern villages, the chief of which are l-Till in the north and el-Hagg Qandil in the south. Activity in the region flourished from the Amarna Period until the later Roman e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letters Locations
Amarna (; ar, العمارنة, al-ʿamārnah) is an extensive Egyptian archaeological site containing the remains of what was the capital city of the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, and abandoned shortly after his death in 1332 BC. The name that the ancient Egyptians used for the city is transliterated in English as Akhetaten or Akhetaton, meaning " the horizon of the Aten".David (1998), p. 125 The site is on the east bank of the Nile River, in what today is the Egyptian province of Minya. It is about south of the city of al-Minya, south of the Egyptian capital, Cairo, and north of Luxor (site of the previous capital, Thebes). The city of Deir Mawas lies directly to its west. On the east side of Amarna there are several modern villages, the chief of which are l-Till in the north and el-Hagg Qandil in the south. Activity in the region flourished from the Amarna Period until the later Roman era ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William L
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aammiq Wetland
The Aammiq Wetland (the name is also sometimes transliterated as "Ammiq"or "Aamiq") is the largest remaining freshwater wetland in Lebanon, a remnant of much more extensive marshes and lakes that once existed in the Bekaa Valley. It has been designated an Important Bird Area in the Middle East (BirdLife International, 1994), is included in the Directory of Wetlands in the Middle East (IUCN, 1995), was declared Ramsar Convention site number 978 in 1999, and most recently (2005) was designated, with Al Shouf Cedar Nature Reserve, a “Biosphere reserve” by UNESCO. Description The swamp lies on one of the most important bird migration routes in the world, and over 250 species of birds have been recorded in the area, including the globally vulnerable greater spotted eagle (''Aquila clanga''), eastern imperial eagle (''Aquila heliaca''), and lesser kestrel (''Falco naumanni''). Records of globally near-threatened bird species at the wetland include great snipe (''Gallinago media' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pítati
The Pitati ( Egyptian: , Cuneiform: ) were a contingent of archers of ancient Egypt that were often requested and dispatched to support Egyptian vassals in Canaan. They are recorded in the correspondence of the 1350 BC Amarna letters, and were often requested to defend against the Habiru, also rogue vassal-kings and foreign troops of neighboring kingdoms (for example, Hatti), who were on the attack. The vassal cities and "city-states" were constantly requesting the services (protection) of the Pharaoh's armies, by means of this "archer-army" force, basically garrison forces. A request for lodging, and preparations of food, drink, straw, and other supplies required,Moran, William L., 1992. ''The Amarna Letters,'' p. 352-353. ''EA 325'': Title: (from, Man of the City: Yidya): ''Preparations completed, (2)'', "...indeed prepared absolutely everything—food, strong drink, oxen, 'sheep and goats', grain, straw, absolutely everything that the king, my lord, commanded." is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostration Formula
In the 1350 BC correspondence of 382–letters, called the Amarna letters, the prostration formula is usually the opening subservient remarks to the addressee, the Egyptian pharaoh. The formula is based on prostration, namely reverence and submissiveness. Often the letters are from vassal rulers or vassal city-states, especially in Canaan but also in other localities. The formula is often repetitive, or multi-part, with parts seeming to repeat and can go forward in a typical standard format. However, the prostration formula may also be duplicated in a similar format at the end of a letter, or a foreshortened part of the formula may be entered, for effect, in the middle of a letter. Some example letters with the ''Prostration formula'' The letters EA 242 and 246 are from Biridiya of Magidda-(Megiddo), (EA for 'el Amarna'). Biridiya letter 242, no. 1 of 7: title: ''"Request granted"'' :Say to the king-(i.e. pharaoh), my lord and my Sun: Message-(' um– ma') of Biridiy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |