|
Americhelydia
Americhelydia is a clade of turtles that consists of sea turtles, snapping turtles, the Central American river turtle and mud turtles, supported by several lines of molecular work. Prior to these studies some morphological and developmental work have considered sea turtles to be basal members of Cryptodira The Cryptodira ('' el, hidden neck'') are a suborder of Testudines that includes most living tortoises and turtles. Cryptodira differ from Pleurodira (side-necked turtles) in that they lower their necks and pull the heads straight back into the ... and kinosternids related to the trionychians in the clade Trionychoidea. Americhelydia and Testudinoidea, both clades within Durocryptodira (hardshell turtles), split a part during the early Creataceous. References Cryptodira {{paleo-turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
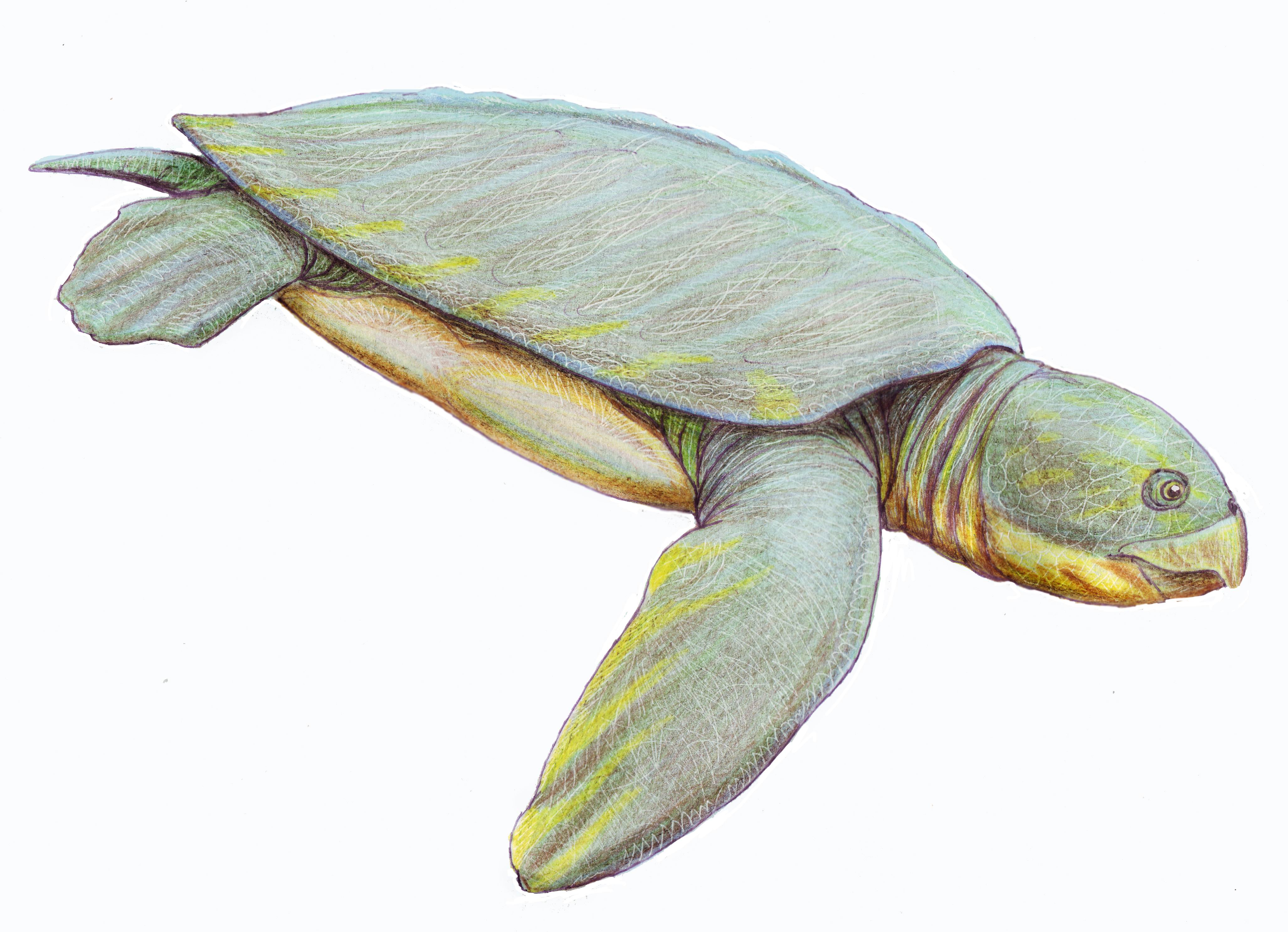
Sea Turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, Kemp's ridley, and olive ridley sea turtles. All six of the sea turtle species present in US waters (all of those listed above except the flatback) are listed as endangered and/or threatened under the Endangered Species Act. The seventh sea turtle species is the flatback, which exists in the waters of Australia, Papua New Guinea and Indonesia. Sea turtles can be separated into the categories of hard-shelled (cheloniid) and leathery-shelled ( dermochelyid).Wyneken, J. 2001. The Anatomy of Sea Turtles. U.S Department of Commerce NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-470, 1-172 pp. There is only one dermochelyid species which is the leatherback sea turtle. Description For each of the seven types of sea turtles, females and males are the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptodira
The Cryptodira ('' el, hidden neck'') are a suborder of Testudines that includes most living tortoises and turtles. Cryptodira differ from Pleurodira (side-necked turtles) in that they lower their necks and pull the heads straight back into the shells, instead of folding their necks sideways along the body under the shells' marginals. They include among their species freshwater turtles, snapping turtles, tortoises, softshell turtles, and sea turtles. Neck retraction The Cryptodira are characterized by retraction of the head in the vertical plane, which permits for primarily vertical movements and restricted lateral movements outside of the shell. These motions are largely due to the morphology and arrangement of cervical vertebrae. In all recent turtles, the cervical column consists of nine joints and eight vertebrae. Compared to the narrow vertebrae and the closely positioned zygapophyses of the pleurodires, the cryptodires’ vertebrae take on the opposite shape. Their ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, Kemp's ridley, and olive ridley sea turtles. All six of the sea turtle species present in US waters (all of those listed above except the flatback) are listed as endangered and/or threatened under the Endangered Species Act. The seventh sea turtle species is the flatback, which exists in the waters of Australia, Papua New Guinea and Indonesia. Sea turtles can be separated into the categories of hard-shelled (cheloniid) and leathery-shelled ( dermochelyid).Wyneken, J. 2001. The Anatomy of Sea Turtles. U.S Department of Commerce NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-470, 1-172 pp. There is only one dermochelyid species which is the leatherback sea turtle. Description For each of the seven types of sea turtles, females and males are the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time from 163.5 ± 1.0 to 145.0 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic strata.Owen 1987. In European lithostratigraphy, the name "Malm" indicates rocks of Late Jurassic age. In the past, ''Malm'' was also used to indicate the unit of geological time, but this usage is now discouraged to make a clear distinction between lithostratigraphic and geochronologic/chronostratigraphic units. Subdivisions The Late Jurassic is divided into three ages, which correspond with the three (faunal) stages of Upper Jurassic rock: Paleogeography During the Late Jurassic Epoch, Pangaea broke up into two supercontinents, Laurasia to the north, and Gondwana to the south. The result of this break-up was the spawning of the Atlantic Ocean. However, at this time, the Atlantic Ocean was relatively narrow. Life forms of the epoch This epoch is well known for many famous types of dinosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxochelys
''Toxochelys'' () is an extinct genus of marine turtle from the Late Cretaceous period. It is the most commonly found fossilized turtle species in the Smoky Hill Chalk, in western Kansas. Description ''Toxochelys'' was about 2 m (6 ft) in length. Two species in the genus are recognized, ''Toxochelys latiremis'' and ''Toxochelys moorevillensis''. Phylogenetic analysis shows that ''Toxochelys'' belong to an extinct lineage of turtles transitional between modern sea turtles Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, ... and other turtles. ''Toxochelys bauri'' Williston, 1905, based on the skeleton YPM 1786, is a synonym of '' Ctenochelys stenoporus''.R. Zangerl. 1953. The vertebrate fauna of the Selma Formation of Alabama. Part IV. The turtles of the family Toxochelyid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trionychia
Trionychia is a superfamily of turtles which encompasses the species that are commonly referred to as softshelled turtles as well as some others. The group contains two families, Carettochelyidae, which has only one living species, the pig-nosed turtle (''Carettochelys insculpta'') native to New Guinea and Northern Australia, and Trionychidae, the softshelled turtles, containing numerous species native to Asia, North America and Africa. These families likely diverged during the late Jurassic. The oldest known stem-trionychian is '' Sinaspideretes'' from the Late Jurassic of China. Systematics Except for those not assigned to a family, only living genera are listed here. *Family Carettochelyidae ** Subfamily Carettochelyinae *** Genus '' Carettochelys'' *Pan-Trionychidae ** Family PlastomenidaeOne or more basal lineages formerly believed to be a distinct family (fossil) ** Family Trionychidae ***Subfamily Cyclanorbinae **** Genus '' Cyclanorbis'' **** Genus '' Cycloderma' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central American River Turtle
The hickatee (''Dermatemys mawii'') or in Spanish ''tortuga blanca'' ('white turtle'), also called the Central American river turtle, is the only living species in the family Dermatemydidae. The species is found in the Atlantic drainages of Central America, specifically Belize, Guatemala, southern Mexico and probably Honduras. It is a relatively large-bodied species, with records of straight carapace length and weights of ; although most individuals are smaller. This is a herbivorous and almost completely aquatic turtle that does not even surface to bask. Bizarrely for reptiles, the eggs can remain viable even after being underwater for weeks -in the recent past, some scientists mistakenly claimed it nests underwater, likely due to visiting Central America during a frequent flood, when nests are often submerged. In the culture of the Ancient Mayan civilisation this species and turtles in general had numerous uses such as being used in warfare, as musical instruments and as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snapping Turtle
The Chelydridae is a family of turtles that has seven extinct and two extant genera. The extant genera are the snapping turtles, ''Chelydra'' and '' Macrochelys''. Both are endemic to the Western Hemisphere. The extinct genera are '' Acherontemys'', '' Chelydrops'', '' Chelydropsis'', ''Emarginachelys'', '' Macrocephalochelys'', '' Planiplastron'', and '' Protochelydra''. Fossil history The Chelydridae have a long fossil history, with extinct species reported from North America as well as all over Asia and Europe, far outside their present range. The earliest described chelydrid is '' Emarginachelys cretacea'', known from well-preserved fossils from the Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous of Montana. Another well-preserved fossil chelydrid is the Late Paleocene ''Protochelydra zangerli'' from North Dakota. The carapace of ''P. zangerli'' is higher-domed than that of the recent ''Chelydra'', a trait conjectured to be associated with the coexistence of large, turtle-eatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenochelys
''Ctenochelys'' is an extinct genus of marine turtle (Cryptodira, Pancheloniidae), which existed during the Cretaceous period, and lived in the shallow waters of the Western Interior Seaway. Its fossils have been found in the Ripley Formation and Mooreville Chalk of central Alabama, United States. It was first named by C.H. Sternberg in 1904, and contains two species, ''C. stenoporus'' and ''C. acris''. Species *''Ctenochelys stenoporus'' is the type species. It was originally thought to be a species of ''Toxochelys''; ''T. bauri'', until Sternberg declared it a separate genus. The two genera are similar in carapaces. *''Ctenochelys acris'' was first named by Zangerl in 1953 and is now thought to be one of the earliest ancestors of modern cheloniid Cheloniidae is a family of typically large marine turtles that are characterised by their common traits such as, having a flat streamlined wide and rounded shell and almost paddle-like flippers for their forelimbs. They are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchelonioidea
Panchelonioidea is a clade of marine turtles that includes the sea turtle Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhe ...s and related taxa. Phylogeny Evers et al. (2019): References Cryptodira {{Turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kerguelen P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinosternidae
The Kinosternidae are a family of mostly small turtles that includes the mud turtles and musk turtles. The family contains 25 species within four genera, but taxonomic reclassification is an ongoing process, so many sources vary on the exact numbers of species and subspecies. They inhabit slow-moving bodies of water, often with soft, muddy bottoms and abundant vegetation. Description Most kinosternids are small turtles, in carapace length. The highly domed carapace has a distinct keel down its center. The genus '' Staurotypus'' gets much larger, to . Females are generally larger than males, but males have much longer tails. Kinosternids can be black, brown, green, or yellowish in color. Most species do not have shell markings, but some species have radiating black markings on each carapace scute. Some species have distinctive yellow striping along the sides of the head and neck. The musk turtles are so named because they are capable of releasing a foul-smelling musk from gland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |