|
American Osteopathic Board Of Radiology
The American Osteopathic Board of Radiology (AOBR) is an organization that provides board certification to qualified Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) who specialize in the use of imaging in the diagnosis and treatment of disease (radiologists). The board is one 18 medical specialty certifying boards of the American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists approved by the American Osteopathic Association (AOA), and was established in 1939. The American Osteopathic Board of Radiology and the American Board of Radiology are the two certifying boards for radiologists in the United States. As of December 2011, 732 osteopathic radiologists held active certification with the AOBR. Radiologists board certified by the AOBR are eligible for membership in the American College of Radiology. Board certification Initial certification is available to osteopathic radiologists who have successfully completed an AOA-approved residency in diagnostic radiology or radiation onc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milan, Missouri
Milan ( ) is a city in Sullivan County, Missouri, United States. The population was 1,819 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Sullivan County. Geography Milan is located at the intersection of Missouri routes 5 and 6. Locust Creek flows past the west side of the city and the Locust Creek Conservation Area is three miles to the southwest. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which is land and is water. History Milan was laid out in 1845, and most likely named after Milan, in Italy. A post office called Milan has been in operation since 1847. Camp Ground Church and Cemetery, Milan Railroad Depot, and Quincy, Omaha and Kansas City Railroad Office Building are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Demographics 2010 census As of the census of 2010, there were 1,960 people, 746 households, and 462 families living in the city. The population density was . There were 845 housing units at an average density ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic Radiology
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging. Measurement and recording techniques that are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others, represent other technologies that produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph versus time or maps that contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
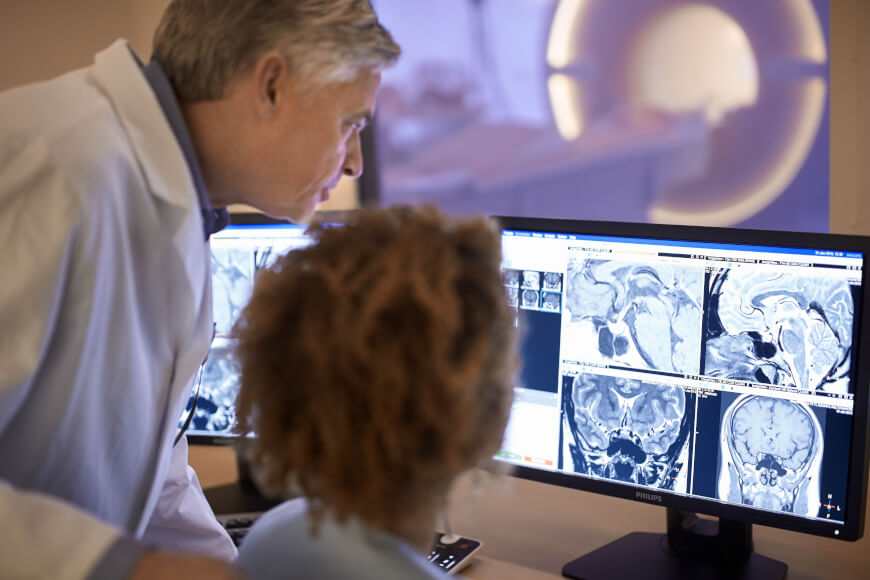
Radiology Organizations
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation (such as ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging), as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves several different healthcare professions working as a team. The radiologist is a medical doctor who has completed the appropriate post-graduate training and interprets medical images, communicates these findings to other physicians by me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizations Established In 1939
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose. The word is derived from the Greek word ''organon'', which means tool or instrument, musical instrument, and organ. Types There are a variety of legal types of organizations, including corporations, governments, non-governmental organizations, political organizations, international organizations, armed forces, charities, not-for-profit corporations, partnerships, cooperatives, and educational institutions, etc. A hybrid organization is a body that operates in both the public sector and the private sector simultaneously, fulfilling public duties and developing commercial market activities. A voluntary association is an organization consisting of volunteers. Such organizations may be able to operate without legal formalities, depending on jurisdiction, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteopathic Medical Associations In The United States
Osteopathy () is a type of alternative medicine that emphasizes physical manipulation of the body's muscle tissue and bones. Practitioners of osteopathy are referred to as osteopaths. Osteopathic manipulation is the core set of techniques in osteopathy. Parts of osteopathy, such as craniosacral therapy, have no therapeutic value and have been labeled as pseudoscience and quackery. The techniques are based on an ideology created by Andrew Taylor Still (1828–1917) which posits the existence of a " myofascial continuity"—a tissue layer that "links every part of the body with every other part". Osteopaths attempt to diagnose and treat what was originally called "the osteopathic lesion", but which is now named "somatic dysfunction", by manipulating a person's bones and muscles. Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment (OMT) techniques are most commonly used to treat back pain and other musculoskeletal issues. Osteopathic manipulation is still included in the curricula of osteopathic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Osteopathic College Of Radiology
The American Osteopathic College of Radiology (AOCR), founded in 1941, is a non-profit professional medical association in the United States representing Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) that specialize in radiology. The AOCR is accredited by the American Osteopathic Association (AOA) and the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to oversee continuing medical education activities for osteopathic radiologists. The AOCR is one of two professional organizations representing American radiologists, the other organization is the American College of Radiology. The college publishes ''The Journal of the American Osteopathic College of Radiology'' (''JAOCR''). Certified fellows of the American Osteopathic College of Radiology are eligible to become senior members of the American Society of Neuroradiology in addition to their certified peers from the American Board of Radiology and the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada. Additionally, osteopathic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement (e.g., stents), and angioplasty of narrowed structures. The main benefits of interventional radiology techniques are that they can reach the deep structures of the body through a body orifice or tiny incision using small needles and wires. That decreases risks, pain, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Radiology
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performed by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy. The word itself comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek words ἀγγεῖον ''angeion'' 'vessel' and γράφειν ''graphein'' 'to write, record'. The film or image of the blood vessels is called an ''angiograph'', or more commonly an ''angiogram''. Though the word can describe both an arteriogram and a venogram, in everyday usage the terms angiogram and arteriogram are often used synonymously, whereas the term venogram is used more precisely. The term angiography has been applied to radionuclide angiography and newer vascular imaging techniques such as Carbon Dioxide Angiography, CO2 angiography, Computed tomo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediatric Radiology
Paediatric radiology (or pediatric radiology) is a subspecialty of radiology involving the imaging of fetuses, infants, children, adolescents and young adults. Many paediatric radiologists practice at children's hospitals. Although some diseases seen in paediatrics are the same as that in adults, there are many conditions which are seen only in infants. The specialty has to take in account the dynamics of a growing body, from pre-term infants to large adolescents, where the organs follow growth patterns and phases. These require specialised imaging and treatment which is carried out in a Children's hospital, which has all the facilities necessary to treat children and their specific pathologies. Environment To successfully diagnose a paediatric condition, high-quality images are needed to give a diagnosis. To achieve this requires creating an environment where a child is comfortable. This is one of the most essential elements to paediatric radiology. For imaging departments which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroradiology
Neuroradiology is a subspecialty of radiology focusing on the diagnosis and characterization of abnormalities of the central and peripheral nervous system, spine, and head and neck using neuroimaging techniques. Medical issues utilizing neuroradiology include arteriovenous malformations, tumors, aneurysms, and strokes. Professional organizations The major professional association in the United States representing neuroradiologists is the American Society of Neuroradiology (ASNR). The ASNR publishes the ''American Journal of Neuroradiology'' (AJNR). The ASNR annual meeting rotates through different cities, and usually takes place between late April and early June. The specialty neuroradiology societies that are associated with the ASNR include the American Society of Pediatric Neuroradiology (ASPNR), the American Society of Spine Radiology (ASSR), the American Society of Head and Neck Radiology (ASHNR), and the American Society of Functional Neuroradiology (ASFNR). These societ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Oncology
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizing radiation works by damaging the DNA of cancerous tissue l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Residency
Residency or postgraduate training is specifically a stage of graduate medical education. It refers to a qualified physician (one who holds the degree of MD, DO, MBBS, MBChB), veterinarian ( DVM or VMD) , dentist ( DDS or DMD) or podiatrist ( DPM) who practices medicine, veterinary medicine , dentistry, or podiatry, respectively, usually in a hospital or clinic, under the direct or indirect supervision of a senior medical clinician registered in that specialty such as an attending physician or consultant. In many jurisdictions, successful completion of such training is a requirement in order to obtain an unrestricted license to practice medicine, and in particular a license to practice a chosen specialty. In the meantime they practice "on" the license of their supervising physician. An individual engaged in such training may be referred to as a resident, registrar or trainee depending on the jurisdiction. Residency training may be followed by fellowship or sub-specialty traini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |