|
American College Of Radiology
The American College of Radiology (ACR), founded in 1923, is a professional medical society representing nearly 40,000 diagnostic radiologists, radiation oncologists, interventional radiologists, nuclear medicine physicians and medical physicists. The ACR has 54 chapters in the United States, Canada and the Council of Affiliated Regional Radiation Oncology Societies (CARROS). Medical imaging accreditation The ACR has accredited more than 39,000 medical imaging facilities in 10 imaging modalities since 1987, including: * Breast MRI * Breast Ultrasound * Computed Tomography * Mammography * Magnetic Resonance Imaging *Nuclear Medicine * Positron Emission Tomography *Radiation Oncology Practice * Stereotactic Breast Biopsy *Ultrasound ACR Appropriateness Criteria The ACR Appropriateness Criteria (ACR AC) are evidence-based guidelines that assist referring physicians and other providers in making the most appropriate imaging or treatment decision for a specific clinical condition. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
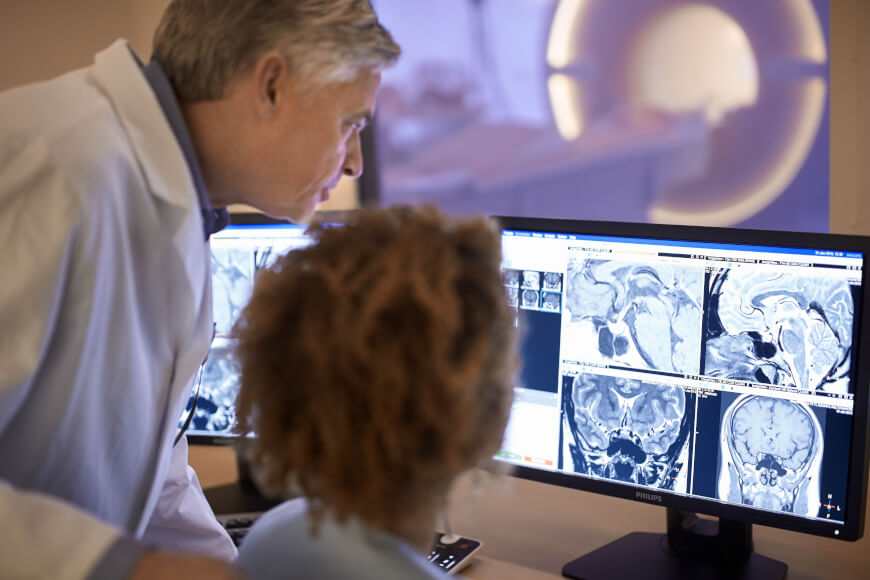
Radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation (such as ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging), as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves several different healthcare professions working as a team. The radiologist is a medical doctor who has completed the appropriate post-graduate training and interprets medical images, communicates these findings to other physicians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiological
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes: * ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma radiation (γ) * ''particle radiation'', such as alpha radiation (α), beta radiation (β), proton radiation and neutron radiation (particles of non-zero rest energy) * '' acoustic radiation'', such as ultrasound, sound, and seismic waves (dependent on a physical transmission medium) * ''gravitational radiation'', that takes the form of gravitational waves, or ripples in the curvature of spacetime Radiation is often categorized as either ''ionizing'' or ''non-ionizing'' depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 eV, which is enough to ionize atoms and molecules and break chemical bonds. This is an important distinction due to the large difference i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical And Health Organizations Based In Virginia
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiology Organizations
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation (such as ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging), as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves several different healthcare professions working as a team. The radiologist is a medical doctor who has completed the appropriate post-graduate training and interprets medical images, communicates these findings to other physicians by me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Associations Based In The United States
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Board Of Radiology
Established in 1934, the American Board of Radiology (ABR) is an independent, not-for-profit professional association with headquarters in Tucson, Arizona. It oversees the certification and ongoing professional development of physician specialists in diagnostic radiology, interventional radiology, and radiation oncology, as well as medical physicists in diagnostic, nuclear, and therapy medical physics. The ABR certifies its diplomates through a comprehensive process involving educational requirements, professional peer evaluation, and examination. See also *American Osteopathic Board of Radiology *American Board of Medical Specialties *American Board of Science in Nuclear Medicine The American Board of Science in Nuclear Medicine, founded in 1976, also known as the ABSNM is an organization in North America that offers certification to specialty areas of advanced nuclear medicine. The board offers certification in the followi ... References External links * Radiology orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiological Society Of North America
The Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) is a non-profit organization and an international society of radiologists, medical physicists and other medical imaging professionals representing 31 radiologic subspecialties from 145 countries around the world. Based in Oak Brook, Illinois, RSNA was established in 1915. RSNA's organizational mission is to promote excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society hosts an annual conference in Chicago and develops educational resources such as courses, workshops and webinars. RSNA also publishes five peer-reviewed radiology journals, offers quality improvement tools, sponsors research to advance quantitative imaging biomarkers, and conducts outreach to enhance radiology education and patient care in low-income and middle-income countries. RSNA Annual Meeting RSNA hosts the world's largest annual medical imaging conference, a five-day event starting the last ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Spring, Maryland
Silver Spring is a census-designated place (CDP) in southeastern Montgomery County, Maryland, United States, near Washington, D.C. Although officially unincorporated, in practice it is an edge city, with a population of 81,015 at the 2020 census, making it the fifth-most populous place in Maryland after Baltimore, Columbia, Germantown, and Waldorf. Downtown, next to the northern tip of Washington, D.C., is the oldest and most urbanized part of the community, surrounded by several inner suburban residential neighborhoods inside the Capital Beltway. Many mixed-use developments combining retail, residential, and office space have been built since 2004. Silver Spring takes its name from a mica-flecked spring discovered there in 1840 by Francis Preston Blair, who subsequently bought much of the surrounding land. Acorn Park, south of downtown, is believed to be the site of the original spring. Geography As an unincorporated CDP, Silver Spring's boundaries are not consistently de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reston, VA
Reston is a census-designated place in Fairfax County, Virginia and a principal city of the Washington metropolitan area. As of the 2020 U.S. Census, Reston's population was 63,226. Founded in 1964, Reston was influenced by the Garden City movement that emphasized planned, self-contained communities that intermingled green space, residential neighborhoods, and commercial development. The intent of Reston's founder, Robert E. Simon, was to build a town that would revolutionize post–World War II concepts of land use and residential/corporate development in suburban America. In 2018, Reston was ranked as the Best Place to Live in Virginia by ''Money'' magazine for its expanses of parks, lakes, golf courses, and bridle paths as well as the numerous shopping and dining opportunities in Reston Town Center. History In the early days of Colonial America, the land on which Reston sits was part of the Northern Neck Proprietary, a vast grant by King Charles II to Lord Thomas Fairfax tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ct Colonography
Virtual colonoscopy (VC, also called CT colonography or CT pneumocolon) is the use of CT scanning or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce two- and three-dimensional images of the colon (large intestine), from the lowest part, the rectum, to the lower end of the small intestine, and to display the images on an electronic display device. The procedure is used to screen for colon cancer and polyps, and may detect diverticulosis. A virtual colonoscopy can provide 3D reconstructed endoluminal views of the bowel. VC provides a secondary benefit of revealing diseases or abnormalities outside the colon. Procedure While preparations for VC vary, the patient will usually be asked to take laxatives or other oral agents at home the day before the procedure to clear stool from the colon. A suppository is also used to cleanse the rectum of any remaining fecal matter. The patient may also be given a solution designed to coat any residual faeces which may not have been cleared by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ónkos''), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass". Oncology is concerned with: * The diagnosis of any cancer in a person (pathology) * Therapy (e.g. surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other modalities) * Follow-up of cancer patients after successful treatment * Palliative care of patients with terminal malignancies * Ethical questions surrounding cancer care * Screening efforts: ** of populations, or ** of the relatives of patients (in types of cancer that are thought to have a hereditary basis, such as breast cancer) Diagnosis Medical histories remain an important screening tool: the character of the complaints and nonspecific symptoms (such as fatigue, weight loss, unexplained anemia, fever of unknown origin, paraneoplastic phenome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

