|
Amergin Glúingel
Amergin ''Glúingel'' ("white knees") (also spelled Amhairghin Glúngheal) or ''Glúnmar'' ("big knee") is a bard, druid and judge for the Milesians in the Irish Mythological Cycle. He was appointed Chief Ollam of Ireland by his two brothers the kings of Ireland. A number of poems attributed to Amergin are part of the Milesian mythology. One of the seven sons of Míl Espáine, he took part in the Milesian conquest of Ireland from the Tuatha Dé Danann, in revenge for their great-uncle Íth, who had been treacherously killed by the three kings of the Tuatha Dé Danann, Mac Cuill, Mac Cecht and Mac Gréine. They landed at the estuary of Inber Scéne, named after Amergin's wife Scéne, who had died at sea. The three queens of the Tuatha Dé Danann, (Banba, Ériu and Fódla), gave, in turn, permission for Amergin and his people to settle in Ireland. Each of the sisters required Amergin to name the island after each of them, which he did: Ériu is the origin of the modern name Éire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bard
In Celtic cultures, a bard is a professional story teller, verse-maker, music composer, oral historian and genealogist, employed by a patron (such as a monarch or chieftain) to commemorate one or more of the patron's ancestors and to praise the patron's own activities. With the decline of a living bardic tradition in the modern period, the term has loosened to mean a generic minstrel or author (especially a famous one). For example, William Shakespeare and Rabindranath Tagore are respectively known as "the Bard of Avon" (often simply "the Bard") and "the Bard of Bengal". Oxford Dictionary of English, s.v. ''bard'', n.1. In 16th-century Scotland, it turned into a derogatory term for an itinerant musician; nonetheless it was later romanticised by Sir Walter Scott (1771–1832). Etymology The English term ''bard'' is a loan word from the Celtic languages: Gaulish: ''bardo-'' ('bard, poet'), mga, bard and ('bard, poet'), wlm, bardd ('singer, poet'), Middle Breton: ''barz'' ('m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Érimón
Érimón, (modern spelling: Éiremhón), commonly Anglicised as Heremon, son of Míl Espáine (and great-grandson of Breoghan, king of Celtic Galicia), according to medieval Irish legends and historical traditions, was one of the chieftains who took part in the Milesian invasion of Ireland, which conquered the island from the Tuatha Dé Danann, and one of the first Milesian High Kings. Background Before coming to Ireland, he and his older brother Éber Donn were joint rulers of Spain. His great-uncle Íth made a peaceful expedition to Ireland, which he had seen from the top of a tower built by his father Breogan, but was killed by the three kings of the Tuatha Dé Danann, Mac Cuill, Mac Cecht and Mac Gréine, and in revenge the Milesians invaded in force, with Érimón and Éber Donn in command. They defeated the Tuatha Dé Danann in the Battle of Tailtiu. Éber Donn had been killed, and the High Kingship was divided between Érimón in the north and his younger brother Éber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Irish Literature
Early Irish literature is one of the oldest vernacular literatures in Western Europe, though inscriptions utilising Irish and Latin are found on Ogham stones dating from the 4th century, indicating simultaneous usage of both languages by this period of late antiquity. According to Professor Elva Johnston, "the Irish were apparently the first western European people to develop a full-scale vernacular written literature expressed in a range of literary genres". A significant number of loan words in Irish from other Indo-European languages, including, but not limited to Latin and Greek, are evidenced in Sanas Cormaic, which dates from the 9th century. Two of the earliest examples of literature from an Irish perspective are Saint Patrick's ''Confessio'' and ''Letter to Coroticus'', written in Latin some time in the 5th century, and preserved in the ''Book of Armagh''. The earliest Irish authors It is unclear when literacy first came to Ireland. The earliest Irish writings are inscr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugh
Lugh or Lug (; ga, label=Modern Irish, Lú ) is a figure in Irish mythology. A member of the Tuatha Dé Danann, a group of supernatural beings, Lugh is portrayed as a warrior, a king, a master craftsman and a savior.Olmsted, Garrett. ''The Gods of the Celts and the Indo-Europeans''. University of Innsbruck, 1994. p.117 He is associated with skill and mastery in multiple disciplines, including the arts.Monaghan, Patricia. ''The Encyclopedia of Celtic Mythology and Folklore''. Infobase Publishing, 2004. pp.296-297 Lugh also has associations with oaths, truth and the law, and therefore with rightful kingship.Koch, John T. ''Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia''. ABC-CLIO, 2006. p.1200 Lugh is linked with the harvest festival of Lughnasadh, which bears his name. His most common epithets are ''Lámfada'' ("long hand" or "long arm", possibly for his skill with a spear or his ability as a ruler) and ''Samildánach'' ("equally skilled in many arts"). In mythology, Lugh is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Taliesin
The Book of Taliesin ( cy, Llyfr Taliesin) is one of the most famous of Middle Welsh manuscripts, dating from the first half of the 14th century though many of the fifty-six poems it preserves are taken to originate in the 10th century or before. The volume contains some of the oldest poems in Welsh, possibly but not certainly dating back to the sixth century and to a real poet called Taliesin (though these, if genuine, would have been composed in the Cumbric dialect of Brittonic-speaking early medieval north Britain, being adapted to the Welsh dialect of Brittonic in the course of their transmission in Wales). Date and provenance of the manuscript The manuscript, known as Peniarth MS 2 and kept at the National Library of Wales, is incomplete, having lost a number of its original leaves including the first. It was named ''Llyfr Taliessin'' in the seventeenth century by Edward Lhuyd and hence is known in English as "The Book of Taliesin". The palaeographer John Gwenogvryn Eva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taliesin
Taliesin ( , ; 6th century AD) was an early Brittonic poet of Sub-Roman Britain whose work has possibly survived in a Middle Welsh manuscript, the '' Book of Taliesin''. Taliesin was a renowned bard who is believed to have sung at the courts of at least three kings. In 1960, Ifor Williams identified eleven of the medieval poems ascribed to Taliesin as possibly originating as early as the sixth century, and so possibly being composed by a historical Taliesin. The bulk of this work praises King Urien of Rheged and his son Owain mab Urien, although several of the poems indicate that Taliesin also served as court bard to King Brochfael Ysgithrog of Powys and his successor Cynan Garwyn, either before or during his time at Urien's court. Some of the events to which the poems refer, such as the Battle of Arfderydd (c. 573), are referred to in other sources. John T. Koch argues that the description of Easter in the praise poem ''Yspeil Taliesin'' ('The Spoils of Taliesin') indicates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welsh Mythology
Welsh mythology (Welsh: ''Mytholeg Cymru'') consists of both folk traditions developed in Wales, and traditions developed by the Celtic Britons elsewhere before the end of the first millennium. As in most of the predominantly oral societies Celtic mythology and history were recorded orally by specialists such as druids ( cy, derwyddon). This oral record has been lost or altered as a result of outside contact and invasion over the years. Much of this altered mythology and history is preserved in medieval Welsh manuscripts, which include the Red Book of Hergest, the White Book of Rhydderch, the Book of Aneirin and the Book of Taliesin. Other works connected to Welsh mythology include the ninth-century Latin historical compilation ''Historia Brittonum'' ("History of the Britons") and Geoffrey of Monmouth's twelfth-century Latin chronicle ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' ("History of the Kings of Britain"), as well as later folklore, such as the materials collected in ''The Welsh Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Welsh Poetry
Medieval Welsh literature is the literature written in the Welsh language during the Middle Ages. This includes material starting from the 5th century AD, when Welsh was in the process of becoming distinct from Common Brittonic, and continuing to the works of the 16th century. The Welsh language became distinct from other dialects of Old British sometime between AD 400 and 700; the earliest surviving literature in Welsh is poetry dating from this period. The poetic tradition represented in the work of ''Y Cynfeirdd'' ("The Early Poets"), as they are known, then survives for over a thousand years to the work of the ''Poets of the Nobility'' in the 16th century. The core tradition was praise poetry; and the poet Taliesin was regarded as the first in the line. The other aspect of the tradition was the professionalism of the poets and their reliance on patronage from kings, princes and nobles for their living. The fall of the Kingdom of Gwynedd and the loss of Welsh independence in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millmount Fort
Millmount is a large fortified complex situated on a great mound on the South bank of the River Boyne located in Drogheda, County Louth, Ireland. The fort has played a crucial part in Drogheda's history and has been a dominant feature from Norman settlement, to Cromwell's invasion to the more recent Civil War in 1922, in which the famous Martello tower was shelled and all but destroyed. Today the complex houses the Millmount Museum which houses a wide variety of artifacts of local and national importance. The complex is Drogheda's most dominant feature, clearly visible from all parts of the town. The Martello tower is affectionately known as "The Cup and Saucer" by locals. The whole fort is a national monument and has been designated as Drogheda's Cultural Quarter. History It has been fortified in historical times since the early 12th Century CE when the invading Normans built a mote and bailey on what was probably originally a neolithic passage grave similar to Newgrange. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
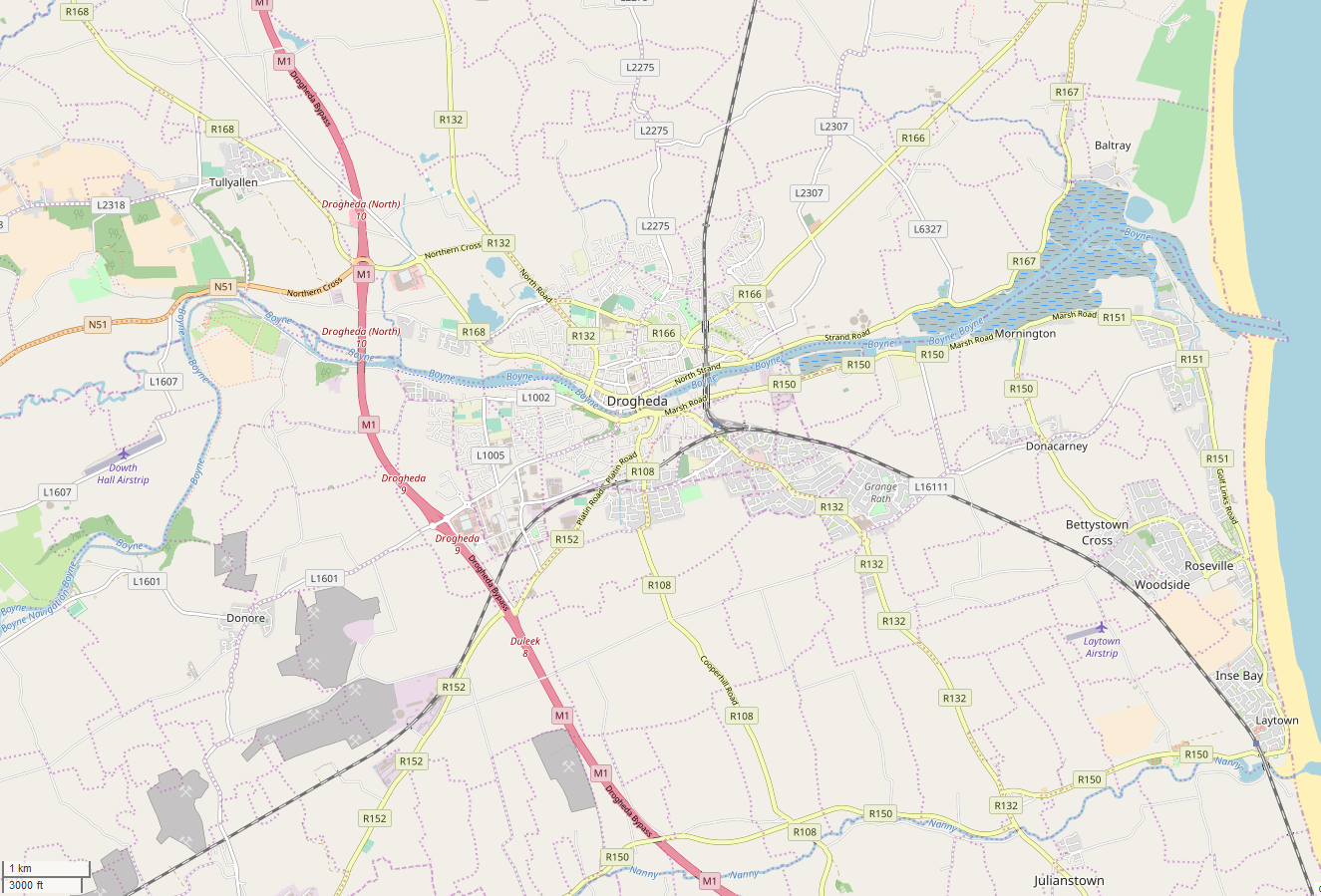
Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth but with the south fringes of the town in County Meath, north of Dublin. Drogheda has a population of approximately 41,000 inhabitants (2016), making it the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, eleventh largest settlement by population in all of Ireland, and the largest town in the Republic of Ireland by both population and area. It is the last bridging point on the River Boyne before it enters the Irish Sea. The UNESCO World Heritage Site of Newgrange is located west of the town. Drogheda was founded as two separately administered towns in two different territories: Drogheda-in-Kingdom of Meath, Meath (i.e. the Lordship of Meath, Lordship and Liberty of Meath, from which a charter was granted in 1194) and Drogheda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of The Four Masters
The ''Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland'' ( ga, Annála Ríoghachta Éireann) or the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' (''Annála na gCeithre Máistrí'') are chronicles of medieval Irish history. The entries span from the Deluge, dated as 2,242 years after creation to AD 1616. Publication delay Due to the criticisms by 17th century Irish historian Tuileagna Ó Maol Chonaire, the text was not published in the lifetimes of any of the participants. Text The annals are mainly a compilation of earlier annals, although there is some original work. They were compiled between 1632 and 1636, allegedly in a cottage beside the ruins of Donegal Abbey, just outside Donegal Town. At this time, however, the Franciscans had a house of refuge by the River Drowes in County Leitrim, just outside Ballyshannon, and it was here, according to others, that the ''Annals'' were compiled. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Keating
Geoffrey Keating ( ga, Seathrún Céitinn; c. 1569 – c. 1644) was a 17th-century historian. He was born in County Tipperary, Ireland, and is buried in Tubrid Graveyard in the parish of Ballylooby-Duhill. He became an Irish Catholic priest and a poet. Biography It was generally believed until recently that Keating had been born in Burgess, County Tipperary; indeed, a monument to Keating was raised beside the bridge at Burgess, in 1990; but Diarmuid Ó Murchadha writes, In November 1603, he was one of forty students who sailed for Bordeaux under the charge of the Rev. Diarmaid MacCarthy to begin their studies at the Irish College which had just been founded in that city by Cardinal François de Sourdis, Archbishop of Bordeaux. On his arrival in France he wrote ''Farewell to Ireland'', and upon hearing of the Flight of the Earls wrote ''Lament on the Sad State of Ireland''. After obtaining the degree of Doctor of Divinity at the University of Bordeaux he returned about 1610 to I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |