|
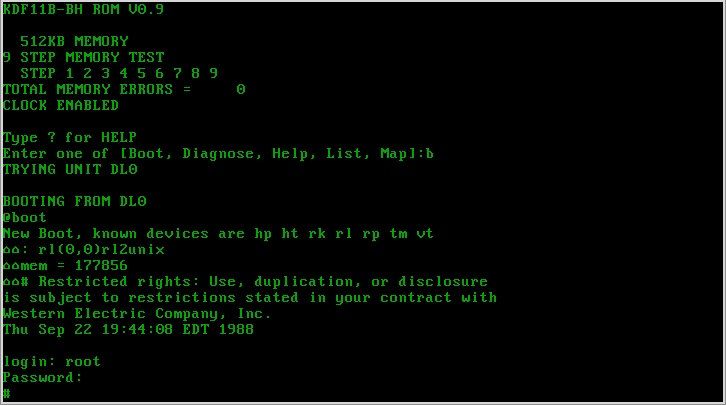
Amdahl UTS
UTS is a discontinued implementation of the UNIX operating system for IBM mainframe (and compatible) computers. Amdahl created the first versions of UTS, and released it in May 1981, with UTS Global acquiring rights to the product in 2002. UTS Global has since gone out of business. System requirements UTS Release 4.5 supports the following S/390 model processors and their successors: * Amdahl 5990, 5995A, 5995M series of ECL processors * Amdahl Millennium Global Server series of CMOS processors * Fujitsu Global Server * IBM ES/9000/9021 series of ECL processors * IBM G4, G5 & G6 Servers (the 9672 R and X series of CMOS processors) History The UTS project had its origins in work started at Princeton University in 1975 to port UNIX to the IBM VM/370 system. Team members there were Tom Lyon, Joseph Skudlarek, Peter Eichenberger, and Eric Schmidt. Tom Lyon joined Amdahl in 1978, and by 1979 there was a full Version 6 Unix system on the Amdahl 470 being used internally for des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amdahl Corporation
Amdahl Corporation was an information technology company which specialized in IBM mainframe-compatible computer products, some of which were regarded as supercomputers competing with those from Cray Research. Founded in 1970 by Gene Amdahl, a former IBM computer engineer best known as chief architect of System/360, it was a wholly owned subsidiary of Fujitsu since 1997. The company was located in Sunnyvale, California. From its first machine in 1975, Amdahl's business was to provide mainframe computers that were plug-compatible with contemporary IBM mainframes, but offering higher reliability, running somewhat faster, and costing somewhat less. They often had additional practical advantages as well, in terms of size, power requirements, of being air-cooled instead of requiring a chilled water supply. This offered a price/performance ratio superior to the IBM lineup, and made Amdahl one of the few real competitors to "Big Blue" in the very high-margin computer market segment. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Schmidt
Eric Emerson Schmidt (born April 27, 1955) is an American businessman and software engineer known for being the CEO of Google from 2001 to 2011, executive chairman of Google from 2011 to 2015, executive chairman of Alphabet Inc. from 2015 to 2017, and Technical Advisor at Alphabet from 2017 to 2020. As an intern at Bell Labs, Schmidt in 1975 was co-author of Lex, a software program to generate lexical analysers for the Unix computer operating system. From 1997 to 2001, he was chief executive officer (CEO) of Novell. He has served on various other boards in academia and industry, including the Boards of Trustees for Carnegie Mellon University, Apple, Princeton University, and Mayo Clinic. In 2008, during his tenure as Google chairman, Schmidt campaigned for Barack Obama, and subsequently became a member of Obama's President's Council of Advisors on Science and Technology, with Eric Lander. Lander later became Joe Biden's science advisor. In the meantime, Schmidt had left Googl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OS/390
OS/390 is an IBM operating system for the System/390 IBM mainframe computers. Overview OS/390 was introduced in late 1995 in an effort to simplify the packaging and ordering for the key, entitled elements needed to complete a fully functional MVS operating system package. These elements included, but were not limited to: *Data Facility Storage Management Subsystem Data Facility Product (DFP)Provides access methods to enable I/O to, e.g., DASD subsystems, printers, Tape; provides utilities and program management * Job Entry Subsystem (JES)Provides the ability to submit batch work and manage print * IBM Communications ServerProvides VTAM and TCP/IP communications protocols An additional benefit of the OS/390 packaging concept was to improve reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS) for the operating system, as the number of different combinations of elements that a customer could order and run was drastically reduced. This reduced the overall time required for custome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIX System Services
z/OS UNIX System Services (z/OS UNIX, or informally USS) is a base element of z/OS. z/OS UNIX is a certified UNIX operating system implementation (XPG4 UNIX 95) optimized for mainframe architecture. It is the first UNIX 95 to not be derived from the AT&T source code. Through integration with the rest of z/OS, additional Time Sharing Option (TSO) commands are available alongside the usual UNIX services, making it possible to process UNIX files using ISPF. Extensions in JCL make it possible to use these files in batch processing. Overview UNIX System Services allows UNIX applications from other platforms to run on IBM System z mainframes running z/OS. In many cases only a recompile is necessary, although additional effort may be advisable for z/OS integration (such as SMP/E installation support). While z/OS UNIX supports ASCII and Unicode, and there's no technical requirement to modify ASCII and Unicode UNIX applications, many z/OS users often prefer EBCDIC support in their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenSolaris For System Z
OpenSolaris for System z is a discontinuedGavin Clarke, 29 March 2010Sun's IBM-mainframe flower wilts under Oracle's hard gaze ''The Register'' port of the OpenSolaris operating system to the IBM System z line of mainframe computers. History OpenSolaris is based on Solaris (operating system), Solaris, which was originally released by Sun Microsystems in 1991. Sun released the bulk of the Solaris system source code in OpenSolaris on 14 June 2005, which made it possible for developers to create other OpenSolaris distributions. Sine Nomine Associates began a project to bring OpenSolaris to the IBM mainframe in July, 2006. The project was named ''Sirius'' (in analogy to the Polaris project to port OpenSolaris to PowerPC). In April, 2007, Sine Nomine presented an initial progress report at IBM's System z Technical Expo conference. At the Gartner Data Center Conference in Las Vegas, Nevada in late 2007, Sine Nomine demonstrated OpenSolaris running on IBM System z under z/VM. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux On IBM Z
Linux on IBM Z or Linux on zSystems is the collective term for the Linux operating system compiled to run on IBM mainframes, especially IBM Z / IBM zSystems and IBM LinuxONE servers. Similar terms which imply the same meaning are ''Linux/390'', ''Linux/390x,'' etc. The three Linux distributions certified for usage on the IBM Z hardware platform are Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, and Ubuntu. History Linux on IBM Z originated as two separate efforts to port Linux to IBM's System/390 servers. The first effort, the "Bigfoot" project, developed by Linas Vepstas in late 1998 through early 1999, was an independent distribution and has since been abandoned. IBM published a collection of patches and additions to the Linux 2.2.13 kernel on December 18, 1999, to start today's mainline Linux on IBM Z. Formal product announcements quickly followed in 2000, including the Integrated Facility for Linux (IFL) engines. Think Blue Linux was an early mainframe distribution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervisor
A hypervisor (also known as a virtual machine monitor, VMM, or virtualizer) is a type of computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a ''host machine'', and each virtual machine is called a ''guest machine''. The hypervisor presents the guest operating systems with a virtual operating platform and manages the execution of the guest operating systems. Unlike an emulator, the guest executes most instructions on the native hardware. Multiple instances of a variety of operating systems may share the virtualized hardware resources: for example, Linux, Windows, and macOS instances can all run on a single physical x86 machine. This contrasts with operating-system–level virtualization, where all instances (usually called ''containers'') must share a single kernel, though the guest operating systems can differ in user space, such as different Linux distributions with the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VM (operating System)
VM (often: VM/CMS) is a family of IBM virtual machine operating systems used on IBM mainframes System/370, System/390, zSeries, System z and compatible systems, including the Hercules emulator for personal computers. The following versions are known: ;Virtual Machine Facility/370 :VM/370, released in 1972, is a System/370 reimplementation of earlier CP/CMS operating system. ;VM/370 Basic System Extensions Program Product :VM/BSE (BSEPP) is an enhancement to VM/370 that adds support for more devices (such as 3370-type fixed-block-architecture DASD drives), improvements to the CMS environment (such as an improved editor), and some stability enhancements to CP. ;VM/370 System Extensions Program Product :VM/SE (SEPP) is an enhancement to VM/370 that includes the facilities of VM/BSE, as well as a few additional fixes and features. ;Virtual Machine/System Product :VM/SP, a milestone version, replaces VM/370, VM/BSE and VM/SE. Release 1 added EXEC2 and XEDIT System Product Edit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IX/370
AIX (Advanced Interactive eXecutive, pronounced , "ay-eye-ex") is a series of Proprietary software, proprietary Unix operating systems developed and sold by IBM for several of its computer platforms. Background Originally released for the IBM RT PC RISC workstation in 1986, AIX has supported a wide variety of hardware platforms, including the IBM RS/6000 series and later IBM Power microprocessors, Power and PowerPC-based systems, IBM System i, System/370 mainframes, IBM Personal System/2, PS/2 personal computers, and the Apple Network Server. It is currently supported on IBM Power Systems alongside IBM i and Linux. AIX is based on UNIX System V with 4.3BSD-compatible extensions. It is certified to the UNIX 03 and UNIX V7 marks of the Single UNIX Specification, beginning with AIX versions 5.3 and 7.2 TL5 respectively. Older versions were previously certified to the UNIX 95 and UNIX 98 marks. AIX was the first operating system to have a journaling file system, and IBM has c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Version 7 Unix
Seventh Edition Unix, also called Version 7 Unix, Version 7 or just V7, was an important early release of the Unix operating system. V7, released in 1979, was the last Bell Laboratories release to see widespread distribution before the commercialization of Unix by AT&T Corporation in the early 1980s. V7 was originally developed for Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-11 minicomputers and was later ported to other platforms. Overview Unix versions from Bell Labs were designated by the edition of the user's manual with which they were accompanied. Released in 1979, the Seventh Edition was preceded by Sixth Edition, which was the first version licensed to commercial users. Development of the Research Unix line continued with the Eighth Edition, which incorporated development from 4.1BSD, through the Tenth Edition, after which the Bell Labs researchers concentrated on developing Plan 9. V7 was the first readily portable version of Unix. As this was the era of minicomputers, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Version 6 Unix
Sixth Edition Unix, also called Version 6 Unix or just V6, was the first version of the Unix operating system to see wide release outside Bell Labs. It was released in May 1975 and, like its direct predecessor, targeted the DEC PDP-11 family of minicomputers. It was superseded by Version 7 Unix in 1978/1979, although V6 systems remained in regular operation until at least 1985. AT&T Corporation licensed Version 5 Unix to educational institutions only, but licensed Version 6 also to commercial users for $20,000, and it remained the most widely used version into the 1980s. An enhanced V6 was the basis of the first ever commercially sold Unix version, INTERACTIVE's IS/1. Bell's own PWB/UNIX 1.0 was also based on V6, where earlier (unreleased) versions were based on V4 and V5. Whitesmiths produced and marketed a (binary-compatible) V6 clone under the name Idris. Source code V6 Unix was released as a distribution including the full source code. Since source code was available a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |