|
Ambrysus (Phocis)
Ambrysus or Ambrysos ( grc, Ἄμβρυσος) or Ambrosus or Ambrosos (Ἄμβρωσσος) or Amphrysus or Amphrysos (Ἄμφρυσος) was a town of ancient Phocis, situated 60 stadia from Stiris, northeast of Anticyra, at the southern foot of Mount Cirphis (not at the foot of Parnassus, as Pausanias states), and in a fertile valley, producing abundance of wine and the coccus, or kermes berry, used to dye scarlet. It was located in the southern part of Phocis, bordering on the territory of Parapotamii. It was destroyed by order of the Amphictyons, but was rebuilt and fortified by the Thebans with a double wall, in their war against Philip II of Macedon, who had during the Third Sacred War taken Ambrysus among other cities in Phocis (346 BCE). In , it was attacked by the Aetolians, like the city of Daulis. Its fortifications were considered by Pausanias the strongest in Greece, next to those of Messene. It was taken by the Romans in the Second Macedonian War, 198 BCE. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Phocis
Phocis was an ancient region in the central part of Ancient Greece, which included Delphi. A modern administrative unit, also called Phocis, is named after the ancient region, although the modern region is substantially larger than the ancient one. Geopolitically, Phocis was the country of the Phocians, who spoke their own version of Doric Greek, one of the three main dialects of ancient Greek. They were one of several small mountain states of Central Greece, whose dialects are classified as Northwest Doric. It was from their region that the Dorians crossed the Gulf of Corinth at the beginning of the Greek Iron Age to burn Pylos and other southern Greek strongholds and seize control of the Peloponnesus. The dialects of the two groups of Dorians north and south of the Gulf then began to diverge. One of the states around Phocis was still called Doris in classical times. As there is considerable evidence that the invasion began about 1000 BC, the ancestors of the classical Phocia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip II Of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ancient kingdom, and the father of Alexander the Great. The rise of Macedon—its conquest and political consolidation of most of Classical Greece during his reign—was achieved by his reformation of the army (the establishment of the Macedonian phalanx that proved critical in securing victories on the battlefield), his extensive use of siege engines, and his utilization of effective diplomacy and marriage alliances. After defeating the Greek city-states of Athens and Thebes at the Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, Philip II led the effort to establish a federation of Greek states known as the League of Corinth, with him as the elected hegemon and commander-in-chief of Greece for a planned invasion of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distomo
:"Distomo" ''may also refer to a work by Federico García Lorca'' Distomo ( el, Δίστομο) is a town in western Boeotia, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Distomo-Arachova-Antikyra, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 131.270 km2, the community 80.498 km2. Population 3,881 (2011). Distomo is situated in the western foothills of Mount Helicon, at about 450 m elevation. It is 5 km north of the Gulf of Corinth coast, 9 km southeast of Arachova, 12 km east of Desfina, 16 km southeast of Delphi, 18 km west of Livadeia and 105 km northwest of Athens. The Greek National Road 48 (Naupactus - Arachova - Livadeia) passes north of the town. Distomo is known as the site of the Distomo massacre that was perpetrated by the German army against the local inhabitants during the Second World War. One of the most important monuments of Byzantine architecture and a UNES ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agora
The agora (; grc, ἀγορά, romanized: ', meaning "market" in Modern Greek) was a central public space in ancient Greek city-states. It is the best representation of a city-state's response to accommodate the social and political order of the polis. The literal meaning of the word "agora" is "gathering place" or "assembly". The agora was the center of the athletic, artistic, business, social, spiritual and political life in the city. The Ancient Agora of Athens is the best-known example. Origins Early in Greek history (13th–4th centuries BC), free-born citizens would gather in the agora for military duty or to hear statements of the ruling king or council. Later, the agora also served as a marketplace, where merchants kept stalls or shops to sell their goods amid colonnades. This attracted artisans who built workshops nearby. From these twin functions of the agora as a political and a commercial spot came the two Greek verbs , ''agorázō'', "I shop", and , ''agoreúō'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Macedonian War
The Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. During their intervention, although the Romans declared the "freedom of the Greeks" against the rule from the Macedonian kingdom, the war marked a significant stage in increasing Roman intervention in the affairs of the eastern Mediterranean, which would eventually lead to Rome's conquest of the entire region. Background In 204 BC King Ptolemy IV Philopator of Egypt died, leaving the throne to his six-year-old son Ptolemy V. Philip V of Macedon and Antiochus the Great of the Seleucid Empire decided to exploit the weakness of the young king by taking Ptolemaic territory for themselves and they signed a secret pact defining spheres of interest, opening the Fifth Syrian War. Philip first turned his attention to the independent Greek ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Greece
Greece in the Roman era describes the Roman conquest of Greece, as well as the period of Greek history when Greece was dominated first by the Roman Republic and then by the Roman Empire. The Roman era of Greek history began with the Corinthian defeat in the Battle of Corinth in 146 BC. However, before the Achaean War, the Roman Republic had been steadily gaining control of mainland Greece by defeating the Kingdom of Macedon in a series of conflicts known as the Macedonian Wars. The Fourth Macedonian War ended at the Battle of Pydna in 148 BC with the defeat of the Macedonian royal pretender Andriscus. The definitive Roman occupation of the Greek world was established after the Battle of Actium (31 BC), in which Augustus defeated Cleopatra VII, the Greek Ptolemaic queen of Egypt, and the Roman general Mark Antony, and afterwards conquered Alexandria (30 BC), the last great city of Hellenistic Egypt. The Roman era of Greek history continued with Emperor Constantine the Great's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messene
Messene (Greek: Μεσσήνη 𐀕𐀼𐀙 ''Messini''), officially Ancient Messene, is a local community within the regional unit (''perifereiaki enotita'') of Messenia in the region (''perifereia'') of Peloponnese. It is best known for the ruins of the large classical city-state of Ancient Messene. The site was founded in the Bronze Age as Ithome, an ancient city originally of Achaean Greeks which eventually came under the hegemony of the military state of Sparta with which it had a long struggle. During the latter period many inhabitants went into exile, and eventually it was destroyed by the Spartans and abandoned for some time. After the defeat of the Spartans at the Battle of Leuctra (371 BC), the Thebans invaded the Peloponnese and Epaminondas built the new city of Messene on the site in 369 BC over the ruins of Ithome and invited the return of the previous inhabitants and their descendants. The substantial ruins are a major historical attraction. Much has been archa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daulis
Daulis ( grc, Δαυλίς), at a later time Daulia (Δαυλία), and also Daulium or Daulion (Δαύλιον), was a town of ancient Phocis, near the frontiers of Boeotia, and on the road from Orchomenus and Chaeroneia to Delphi. Overview It is said to have derived its name from the woody character of the district, since δαυλός was used by the inhabitants instead of δαλός, while others sought for the origin of the name in the mythical nymph Daulis, a daughter of Cephissus. Daulis is mentioned by Homer as a Phocian town along with Crissa and Panopeus in the Catalogue of Ships in the ''Iliad''. It is celebrated in mythology as the residence of the Thracian king, Tereus, who married Procne, the daughter of Pandion, king of ancient Athens, and as the scene of those horrible deeds in consequence of which Procne was changed into a swallow, and her sister Philomela into a nightingale. Hence the latter was called by the poets the Daulian bird. The woody district round th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
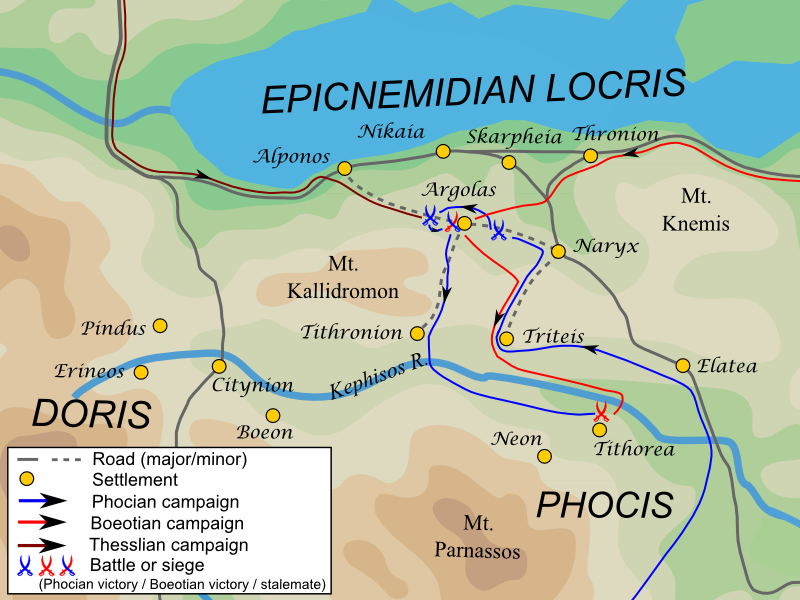
Third Sacred War
The Third Sacred War (356–346 BC) was fought between the forces of the Delphic Amphictyonic League, principally represented by Thebes, and latterly by Philip II of Macedon, and the Phocians. The war was caused by a large fine imposed in 357 BC on the Phocians by the Amphictyonic League (dominated at that moment by Thebes), for the offense of cultivating sacred land; refusing to pay, the Phocians instead seized the Temple of Apollo in Delphi, and used the accumulated treasures to fund large mercenary armies. Thus, although the Phocians suffered several major defeats, they were able to continue the war for many years, until eventually all parties were nearing exhaustion. Philip II used the distraction of the other states to increase his power in northern Greece, in the process becoming ruler of Thessaly. In the end, Philip's growing power, and the exhaustion of the other states, allowed him to impose a peaceful settlement of the war, marking a major step in the rise of Maced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Greece
Thebes (; ell, Θήβα, ''Thíva'' ; grc, Θῆβαι, ''Thêbai'' .) is a city in Boeotia, Central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myths, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus, Heracles and others. Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed a Mycenaean settlement and clay tablets written in the Linear B script, indicating the importance of the site in the Bronze Age. Thebes was the largest city of the ancient region of Boeotia and was the leader of the Boeotian confederacy. It was a major rival of ancient Athens, and sided with the Persians during the 480 BC invasion under Xerxes I. Theban forces under the command of Epaminondas ended Spartan hegemony at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC, with the Sacred Band of Thebes, an elite military unit of male lovers celebrated as instrumental there. Macedonia would rise in power at the Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, bringing decisive victory to Philip II over an alliance of Thebes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stadion (unit)
The stadion (plural stadia, grc-gre, ; Romanization, latinized as stadium), also anglicized as stade, list of obsolete units of measurement, was an ancient Greek units of measurement, ancient Greek unit of length, consisting of 600 Ancient Greek feet (''podes''). Calculations According to Herodotus, one stadium was equal to 600 pous, Greek feet (''podes''). However, the length of the foot varied in different parts of the Greek world, and the length of the stadion has been the subject of argument and hypothesis for hundreds of years. An empirical determination of the length of the stadion was made by Lev Vasilevich Firsov, who compared 81 distances given by Eratosthenes and Strabo with the straight-line distances measured by modern methods, and averaged the results. He obtained a result of about . Various equivalent lengths have been proposed, and some have been named. Among them are: Which measure of the stadion is used can affect the interpretation of ancient texts. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_1887.jpg)