|
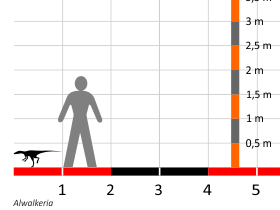
Alwalkeria
''Alwalkeria'' (; "for Alick Walker") is a genus partly based on basal saurischian dinosaur remains from the Late Triassic, living in India. A thighbone found indicates a small bipedal form. It has been seen as a chimera. Etymology This taxon was originally named ''Walkeria maleriensis'' by Sankar Chatterjee in 1987, in honor of British paleontologist Alick Walker. However, since the original generic name was found to be preoccupied by a bryozoan, the name ''Alwalkeria'' was created in 1994 by Chatterjee and Ben Creisler. The specific name ''maleriensis'' is a reference to the Maleri Formation, in southern India, where its fossils were found. Description The only known specimen, holotype ISI R306 is incomplete and consists of parts of the front ends of the upper and lower jaws, 28 incomplete vertebrae from all parts of the spinal column, most of a femur, and an astragalus (ankle bone). The partial skull is about 4 centimeters long (1.5 in). Although material of ''Alw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alwalkeria G
''Alwalkeria'' (; "for Alick Walker") is a genus partly based on basal saurischian dinosaur remains from the Late Triassic, living in India. A thighbone found indicates a small bipedal form. It has been seen as a chimera. Etymology This taxon was originally named ''Walkeria maleriensis'' by Sankar Chatterjee in 1987, in honor of British paleontologist Alick Walker. However, since the original generic name was found to be preoccupied by a bryozoan, the name ''Alwalkeria'' was created in 1994 by Chatterjee and Ben Creisler. The specific name ''maleriensis'' is a reference to the Maleri Formation, in southern India, where its fossils were found. Description The only known specimen, holotype ISI R306 is incomplete and consists of parts of the front ends of the upper and lower jaws, 28 incomplete vertebrae from all parts of the spinal column, most of a femur, and an astragalus (ankle bone). The partial skull is about 4 centimeters long (1.5 in). Although material of ''Alw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alwalkeria Maleriensis
''Alwalkeria'' (; "for Alick Walker") is a genus partly based on basal saurischian dinosaur remains from the Late Triassic, living in India. A thighbone found indicates a small bipedal form. It has been seen as a chimera. Etymology This taxon was originally named ''Walkeria maleriensis'' by Sankar Chatterjee in 1987, in honor of British paleontologist Alick Walker. However, since the original generic name was found to be preoccupied by a bryozoan, the name ''Alwalkeria'' was created in 1994 by Chatterjee and Ben Creisler. The specific name ''maleriensis'' is a reference to the Maleri Formation, in southern India, where its fossils were found. Description The only known specimen, holotype ISI R306 is incomplete and consists of parts of the front ends of the upper and lower jaws, 28 incomplete vertebrae from all parts of the spinal column, most of a femur, and an astragalus (ankle bone). The partial skull is about 4 centimeters long (1.5 in). Although material of ''Alw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Maleri Formation
The Lower Maleri Formation is a sedimentary geological formation, rock formation found in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, India. It is the lowermost member of the Pranhita–Godavari Basin. It is of late Carnian to early Norian age (Upper Triassic), and is notable for its fossils of early dinosaurs, including the basal (phylogenetics), basal saurischian (possible theropod) ''Alwalkeria''.Weishampel et al., 2004, pp.525–527 Vertebrate fauna cf. ''Angistorhinus'' and cf. ''Typothorax'' have also been recovered from it.Novas et al, 2011Kutty et al., 2007 Correlations The formation has been correlated with the Molteno Formation (Karoo Basin) and Pebbly Arkose Formation of Africa, the Santa Maria Formation of the Paraná Basin in Brazil, the Ischigualasto Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin of Argentina and the lowermost Chinle Formation of North America.Novas et al., 2011, p.343 See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations References Bibliograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sankar Chatterjee
Sankar Chatterjee (born May 28, 1943) is a paleontologist, and is the Paul W. Horn Professor of Geosciences at Texas Tech University and Curator of Paleontology at the Museum of Texas Tech University. He earned his Ph. D. from the University of Calcutta in 1970 and was a Post-doctoral Fellow at the Smithsonian Institution from 1977-1978. Chatterjee has focused on the origin, evolution, functional anatomy, and systematics of Mesozoic vertebrates, including basal archosaurs, dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and birds. He has researched Late Triassic reptiles in India, such as phytosaurs, rhynchosaurs, and prolacertiformes. He is best known for his work on vertebrates recovered in the 1980s from the Post Quarry in the Late Triassic Cooper Canyon Formation (Dockum Group) of West Texas. The material includes the large rauisuchian ''Postosuchus'', which was named for the nearby town of Post. It also included controversial specimens Chatterjee identified as being avian (''Protoavis''). The ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walkeria
''Walkeria'' is a genus of colonial bryozoans in the order Ctenostomatida. Species The World Register of Marine Species includes the following species in the genus: *'' Walkeria atlantica'' (Busk, 1886) *'' Walkeria prorepens'' Kubanin, 1992 *'' Walkeria tuberosa'' Heller, 1867 *''Walkeria uva ''Walkeria uva'' is a species of colonial bryozoan in the order Ctenostomatida. It occurs on either side of the Atlantic Ocean, in the Baltic Sea, in the Mediterranean Sea and in the Indo-Pacific region. Description ''Walkeria uva'' is a coloni ...'' (Linnaeus, 1758) References Ctenostomatida Bryozoan genera Taxa named by John Fleming (naturalist) {{Bryozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saurischia
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithischia were originally called orders by Harry Seeley in 1888 though today most paleontologists classify Saurischia as an unranked clade rather than an order.Weishampel, D.B., Dodson, P., and Osmólska, H. (eds.). (2004). ''The Dinosauria. 2nd edition''. University of California Press, Berkeley. 833 pp. Description All carnivorous dinosaurs (certain types of theropods) are traditionally classified as saurischians, as are all of the birds and one of the two primary lineages of herbivorous dinosaurs, the sauropodomorphs. At the end of the Cretaceous Period, all saurischians except the birds became extinct in the course of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Birds, as direct descendants of one group of theropod dinosaurs, are a sub-clad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alick Walker
Alick Donald Walker (26 October 1925 – 4 December 1999) was a British palaeontologist, after whom the ''Alwalkeria'' genus of dinosaur is named. He was born in Skirpenbeck, near York and attended Pocklington School from 1936 to 1943. He began a degree course in engineering at Cambridge, but dropped out in 1944. In 1948 he returned to university after national service, reading Geology at the University of Bristol. On graduation, he join the research group of Professor Stanley Westoll at the University of Newcastle upon Tyne, working on the fossil reptiles of the Late Triassic found in Elgin. He was appointed Lecturer in Geology in 1954, while working on his PhD. The bony remains of the Elgin reptile fossils were poor, sometimes just indentations in rocks. Walker devised a new casting method to capture the anatomical information in these fossils, using PVC; many of the resulting casts are now in the National Museum of Scotland and the Natural History Museum. His early work was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with the tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap), forming the knee joint. By most measures the two (left and right) femurs are the strongest bones of the body, and in humans, the largest and thickest. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper leg. The two femurs converge medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle of convergence of the femora is a major factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. Human females have thicker pelvic bones, causing their femora to converge more than in males. In the condition ''genu valgum'' (knock knee) the femurs converge so much that the knees touch one another. The opposite extreme is ''genu varum'' (bow-leggedness). In the general populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of bone: vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. Individual vertebrae are named according to their region and position, and can be used as anatomical landmarks in order to guide procedures such as lumbar punctures. The vertebral column houses the spinal canal, a cavity that encloses and protects the spinal cord. There are about 50,000 species of animals that have a vertebral column. The human vertebral column is one of the most-studied examples. Many different diseases in humans can affect the spine, with spina bifida and scoliosis being recognisable examples. The general structure of human vertebrae is fairly typical of that found in mammals, reptiles, and birds. The shape of the vertebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |