|
Alveolate Taxonomy
The alveolates (meaning "pitted like a honeycomb") are a group of protists, considered a major clade and superphylum within Eukarya. They are currently grouped with the stramenopiles and Rhizaria among the protists with tubulocristate mitochondria, the group being referred to as SAR. Characteristics The most notable shared characteristic is the presence of cortical (near the surface) alveoli (sacs). These are flattened vesicles (sacs) arranged as a layer just under the membrane and supporting it, typically contributing to a flexible pellicle (thin skin). In armored dinoflagellates they may contain stiff plates. Alveolates have mitochondria with tubular cristae (invaginations), and cells often have pore-like intrusions through the cell surface. The group contains free-living and parasitic organisms, predatory flagellates, and photosynthetic organisms. Almost all sequenced mitochondrial genomes of ciliates and apicomplexa are linear. The mitochondria almost all carry m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and the beginning of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is named after the Ediacara Hills of South Australia. The Ediacaran Period's status as an official geological period was ratified in 2004 by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), making it the first new geological period declared in 120 years. Although the period takes its name from the Ediacara Hills where geologist Reg Sprigg first discovered fossils of the eponymous Ediacaran biota in 1946, the type section is located in the bed of the Enorama Creek within Brachina Gorge in the Flinders Ranges of South Australia, at . The Ediacaran marks the first appearance of widespread multicellular fauna following the end of Snowball Earth glaciation events, the so-called Ediacaran biota, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
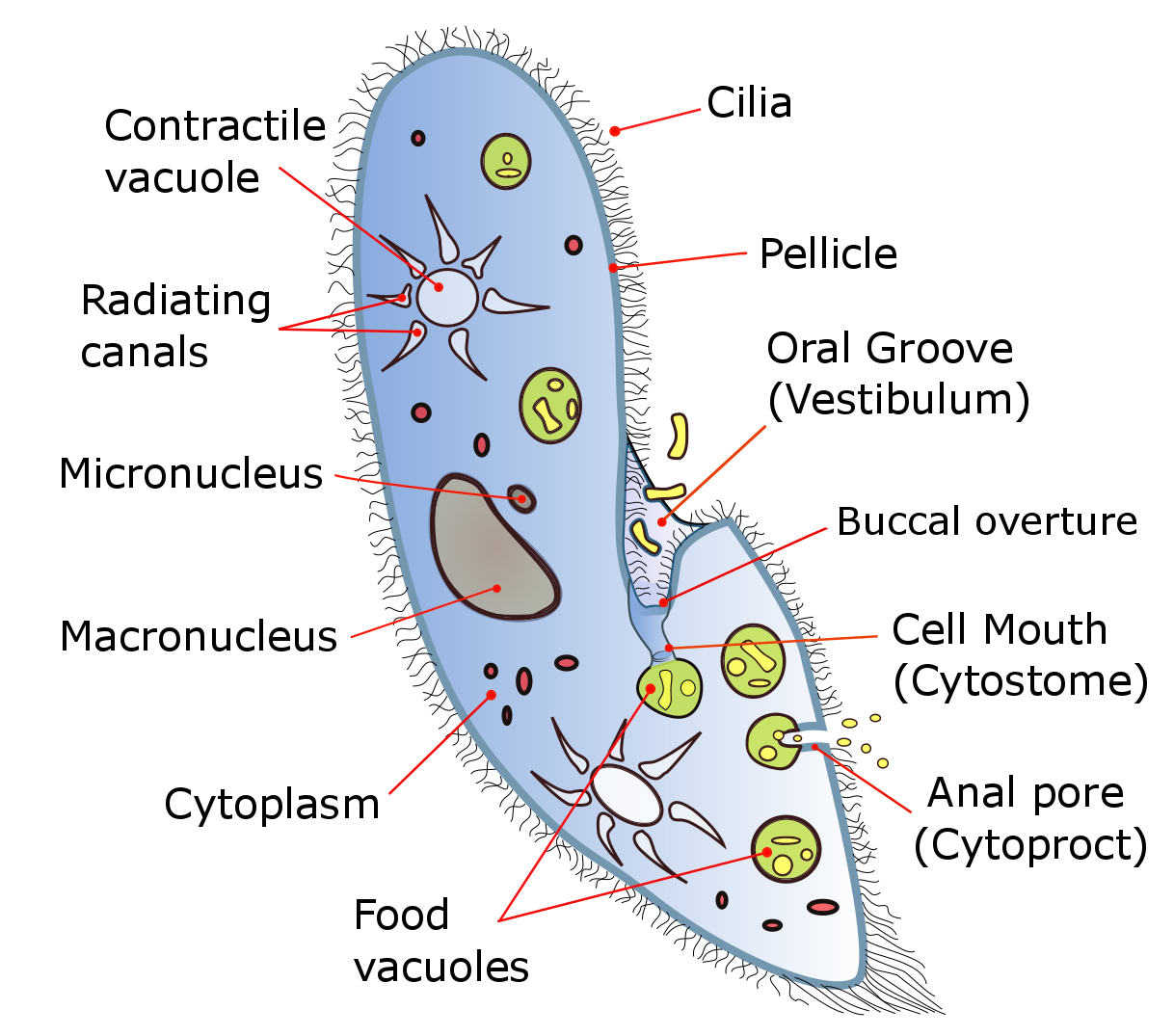
EM Alveoli Ciliate Paramecium Putrinum
EM, Em or em may refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * EM, the E major musical scale * Em, the E minor musical scale * Electronic music, music that employs electronic musical instruments and electronic music technology in its production * Encyclopedia Metallum, an online metal music database * Eminem, American rapper Other uses in arts and entertainment * ''Em'' (comic strip), a comic strip by Maria Smedstad Companies and organizations * European Movement, an international lobbying association * Aero Benin (IATA code), a defunct airline * Empire Airlines (IATA code), a charter and cargo airline based in Idaho, US * Erasmus Mundus, an international student-exchange program * ExxonMobil, a large oil company formed from the merger of Exxon and Mobil in 1999 * La République En Marche! (sometimes shortened to "En Marche!"), a major French political party Economics * Emerging markets, nations undergoing rapid industrialization Language and typography Language * M, a letter of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilium
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pair o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different wikt:undulating, undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their biological life cycle, life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many Ectosymbiosis, ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some Obligate parasite, obligate and Facultative parasite, opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic group (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of Synapomorphy and apomorphy, synapomorphies and symplesiomorphy, symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term was coined by Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia (reptiles) which, as commonly named and traditionally defined, is paraphyletic with respect to mammals and birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theileria
''Theileria'' is a genus of parasites that belongs to the phylum Apicomplexa, and is closely related to '' Plasmodium''. Two ''Theileria'' species, ''T. annulata'' and ''T. parva'', are important cattle parasites. ''T. annulata'' causes tropical theileriosis and ''T. parva'' causes East Coast fever. ''Theileria'' species are transmitted by ticks. The genomes of ''T. orientalis'' Shintoku'', Theileria equi'' WA, ''Theileria annulata'' Ankara and ''Theileria parva'' Muguga have been sequenced and published. ''Theileria equi'' is a known cause of equine piroplasmosis. Vaccines against ''Theileria'' are in development. In May 2010, a vaccine that was reported to protect cattle against East Coast fever had been approved and registered by the governments of Kenya, Malawi, and Tanzania. Description Species in this genus undergo exoerythrocytic merogony in the lymphocytes, histiocytes, erythroblasts, and other cells of the internal organs. This is followed by invasion of the ery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
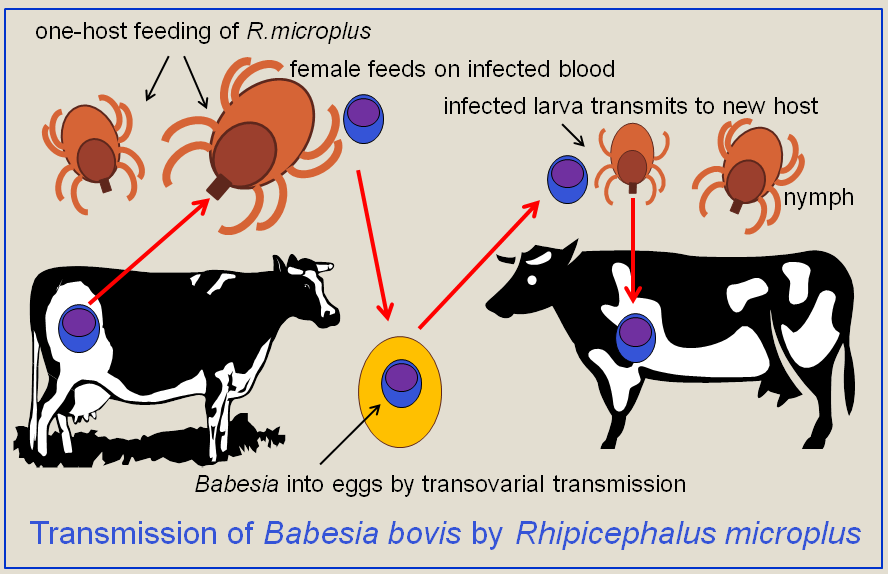
Babesia
''Babesia'', also called ''Nuttallia'', is an apicomplexan parasite that infects red blood cells and is transmitted by ticks. Originally discovered by the Romanian bacteriologist Victor Babeș in 1888, over 100 species of ''Babesia'' have since been identified. ''Babesia'' comprises more than 100 species of tick-borne parasites that infect erythrocytes (red blood cells) in many vertebrate hosts. ''Babesia'' species infect livestock worldwide, wild and domestic vertebrate animals, and occasionally humans, where they cause the disease babesiosis. In the United States, ''B. microti'' is the most common strain of the few which have been documented to cause disease in humans. Classification ''Babesia'' is a protozoan parasite found to infect vertebrate animals, mostly livestock mammals and birds, but also occasionally humans. Common names of the disease that ''Babesia microti'' causes are Texas cattle fever, redwater fever, tick fever, and Nantucket fever. The disease it caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babesia Microti
Babesia microti is a parasitic blood-borne piroplasm transmitted by deer ticks. ''B. microti'' is responsible for the disease babesiosis, a malaria-like disease which also causes fever and hemolysis. Life cycle The life cycle of ''B. microti'' includes human red blood cells and is an important transfusion-transmitted infectious organism. Between 2010 and 2014 it caused four out of fifteen (27%) fatalities associated with transfusion-transmitted microbial infections reported to the US FDA (the highest of any single organism). In 2018, the FDA approved an antibody-based screening test for blood and organ donors. An important difference from malaria is that ''B. microti'' does not infect liver cells. Additionally, the piroplasm is spread by tick bites (''Ixodes scapularis'', the same tick that spreads Lyme disease), while the malaria protozoans are spread via mosquito. Finally, under the microscope, the merozoite form of the ''B. microti'' lifecycle in red blood cells forms a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Reviews (publisher)
Annual Reviews is an independent, non-profit academic publishing company based in San Mateo, California. As of 2021, it publishes 51 journals of review articles and ''Knowable Magazine'', covering the fields of life, biomedical, physical, and social sciences. Review articles are usually “peer-invited” solicited submissions, often planned one to two years in advance, which go through a peer-review process. The organizational structure has three levels: a volunteer board of directors, editorial committees of experts for each journal, and paid employees. Annual Reviews' stated mission is to synthesize and integrate knowledge "for the progress of science and the benefit of society". The first Annual Reviews journal, the ''Annual Review of Biochemistry'', was published in 1932 under the editorship of Stanford University chemist J. Murray Luck, who wanted to create a resource that provided critical reviews on contemporary research. The second journal was added in 1939. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Microbiology
The ''Annual Review of Microbiology'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes review articles about microbiology. It was first published in 1947 as the third journal title released by Annual Reviews. It covers significant developments in the field of microbiology, including the study of bacteria, archaea, viruses, and unicellular eukaryotes. As of 2020, it has had four editors, with Charles E. Clifton and L. Nicholas Ornston serving more than twenty years each. The current editor is Susan Gottesman. History The ''Annual Review of Microbiology'' was first published in 1947, the third journal title released by the publishing company Annual Reviews, following titles in biochemistry and physiology. Its first editor was Charles E. Clifton. From 1956 to 1958, Pierre Grabar provided a summary of the microbiologic literature appearing in the Russian language through a partnership with the National Science Foundation. This was no longer necessary as abstracts became incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |