|
Alternative Therapies For Developmental And Learning Disabilities
Alternative therapies for developmental and learning disabilities include a range of practices used in the treatment of dyslexia, ADHD, autism spectrum disorders, Down syndrome and other developmental and learning disabilities. Treatments include changes in diet, dietary supplements, biofeedback, chelation therapy, homeopathy, massage and yoga. These therapies generally rely on theories that have little scientific basis, lacking well-controlled, large, randomized trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy; small trials that have reported beneficial effects can be generally explained by the ordinary waxing and waning of the underlying conditions. Treatment needs There are a number of non-standard treatments for developmental and learning disabilities. There is a call for alternative therapies particularly when a condition lacks a reliable remediation. For example, there is no cure for autism; the main goals of mainstream behavioral and medical management are to lessen associated def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyslexia
Dyslexia, also known until the 1960s as word blindness, is a disorder characterized by reading below the expected level for one's age. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, writing words, "sounding out" words in the head, pronouncing words when reading aloud and understanding what one reads. Often these difficulties are first noticed at school. The difficulties are involuntary, and people with this disorder have a normal desire to learn. People with dyslexia have higher rates of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), developmental language disorders, and difficulties with numbers. Dyslexia is believed to be caused by the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Some cases run in families. Dyslexia that develops due to a traumatic brain injury, stroke, or dementia is sometimes called "acquired dyslexia" or alexia. The underlying mechanisms of dyslexia result from diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychotherapeutic
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of psychological methods, particularly when based on regular personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase happiness, and overcome problems. Psychotherapy aims to improve an individual's well-being and mental health, to resolve or mitigate troublesome behaviors, beliefs, compulsions, thoughts, or emotions, and to improve relationships and social skills. Numerous types of psychotherapy have been designed either for individual adults, families, or children and adolescents. Certain types of psychotherapy are considered evidence-based for treating some diagnosed mental disorders; other types have been criticized as pseudoscience. There are hundreds of psychotherapy techniques, some being minor variations; others are based on very different conceptions of psychology. Most involve one-to-one sessions, between the client and therapist, but some are conducted with groups, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melatonin
Melatonin is a natural product found in plants and animals. It is primarily known in animals as a hormone released by the pineal gland in the brain at night, and has long been associated with control of the sleep–wake cycle. In vertebrates, melatonin is involved in synchronizing circadian rhythms, including sleep–wake timing and blood pressure regulation, and in control of seasonal rhythmicity including reproduction, fattening, moulting and hibernation. Many of its effects are through activation of the melatonin receptors, while others are due to its role as an antioxidant. In plants, it functions to defend against oxidative stress. It is also present in various foods. Melatonin was discovered in 1958. In addition to its role as a natural hormone, melatonin is used as a dietary supplement and medication in the treatment of sleep disorders such as insomnia and circadian rhythm sleep disorders; for information on melatonin as a supplement and medication, see the mel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essential Fatty Acid
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them. Only two fatty acids are known to be essential for humans: alpha-linolenic acid (an omega-3 fatty acid) and linoleic acid (an omega-6 fatty acid). These are supplied to the body both as the free fatty acid or more commonly as some glyceride derivative. Deficiency in these fatty acids is rare. These fatty acids are essential because they are precursors to vitamins, cofactors. These derivatives include prostaglandins, leukotrienes, thromboxanes, lipoxins, and others. When the two EFAs were discovered in 1923, they were designated "vitamin F", but in 1929, research on rats showed that the two EFAs are better classified as fats rather than vitamins. Functions :''The biological effects of the ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids are mediated by their mutual interactions, see Essential fatty acid interactions for detail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
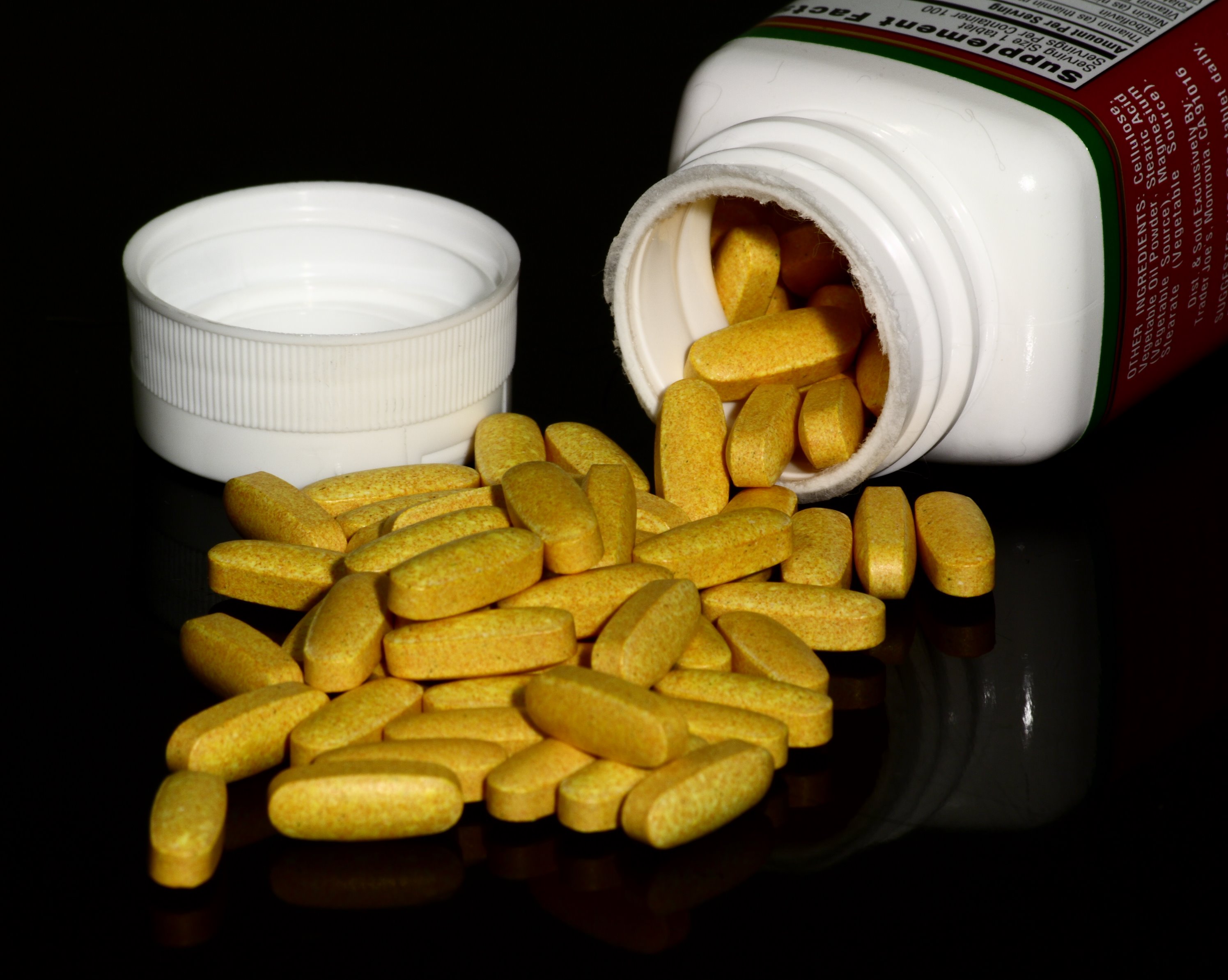
Multivitamin
A multivitamin is a preparation intended to serve as a dietary supplement with vitamins, dietary minerals, and other nutritional elements. Such preparations are available in the form of tablets, capsules, pastilles, powders, liquids, or injectable formulations. Other than injectable formulations, which are only available and administered under medical supervision, multivitamins are recognized by the Codex Alimentarius Commission (the United Nations' authority on food standards) as a category of food. In healthy people, most scientific evidence indicates that multivitamin supplements do not prevent cancer, heart disease, or other ailments, and regular supplementation is not necessary. However, specific groups of people may benefit from multivitamin supplements, for example, people with poor nutrition or those at high risk of macular degeneration. There is no standardized scientific definition for multivitamin. In the United States, a multivitamin/mineral supplement is defined a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Care Physician
A primary care physician (PCP) is a physician who provides both the first contact for a person with an undiagnosed health concern as well as continuing care of varied medical conditions, not limited by cause, organ system, or diagnosis. The term is primarily used in the United States. In the past, the equivalent term was 'general practitioner' in the US; however in the United Kingdom and other countries the term general practitioner is still used. A core element in general practice is continuity that bridges episodes of various illnesses. Greater continuity with a general practitioner has been shown to reduce the need for out-of-hours services and acute hospital admittance. Furthermore, continuity by a general practitioner reduces mortality. All physicians first complete medical school ( MD, MBBS, or DO). To become primary care physicians, medical school graduates then undertake postgraduate training in primary care programs, such as family medicine (also called family pract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Herbology
Chinese herbology () is the theory of traditional Chinese herbal therapy, which accounts for the majority of treatments in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). A ''Nature (journal), Nature'' editorial described TCM as "fraught with pseudoscience", and said that the most obvious reason why it has not delivered many cures is that the majority of its treatments have no logical mechanism of action. The term herbology is misleading in the sense that, while plant elements are by far the most commonly used substances, animal, human, and mineral products are also utilized, among which some are poisonous. In the ''Huangdi Neijing'' they are referred to as () which means toxin, poison, or medicine. Paul U. Unschuld points out that this is similar etymology to the Greek ''Pharmakon (philosophy), pharmakon'' and so he uses the term "pharmaceutic". Thus, the term "medicinal" (instead of herb) is usually preferred as a translation for (). Research into the effectiveness of traditional Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Integration Therapy
Sensory integration therapy (SIT) was originally developed by occupational therapist A. Jean Ayres in the 1970s to help children with sensory-processing difficulties. It was specifically designed to treat Sensory Processing Disorder (sometimes called Sensory Integrative Dysfunction). Sensory Integration Therapy is based on A. Jean Ayres's Sensory Integration Theory, which proposes that sensory-processing is linked to emotional regulation, learning, behavior, and participation in daily life. Sensory integration is the process of organizing sensations from the body and from environmental stimuli. Theoretical concept A. Jean Ayres' sensory integration theory describes the following: * How the neurological process of processing and integrating sensory information from the body and the environment contribute to emotional regulation, learning, behavior, and participation in daily life. * Empirically derived disorders of sensory integration. * Intervention approaches and strategie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery. There is a range of acupuncture variants which originated in different philosophies, and techniques vary depending on the country in which it is performed, but can be divided into two main foundational philosophical applications and approaches, the first being the modern standardized form called eight principles TCM and the second an older system that is based on the ancient Daoist '' wuxing'', better known as the five elements or phases in the West. Acupuncture is most often used to attempt pain relief, though acupuncturists say that it can also be used for a wide range of other conditions. Acupuncture is generally used only in combination with other forms of treatment. The glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Medicine
Alternative medicine is any practice that aims to achieve the healing effects of medicine despite lacking biological plausibility, testability, repeatability, or evidence from clinical trials. Complementary medicine (CM), complementary and alternative medicine (CAM), integrated medicine or integrative medicine (IM), and holistic medicine attempt to combine alternative practices with those of mainstream medicine. Alternative therapies share in common that they reside outside of medical science and instead rely on pseudoscience. Traditional practices become "alternative" when used outside their original settings and without proper scientific explanation and evidence. Frequently used derogatory terms for relevant practices are ''new age'' or ''pseudo-'' medicine, with little distinction from quackery. Some alternative practices are based on theories that contradict the established science of how the human body works; others resort to the supernatural or superstitious to expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self Hypnosis
Self-hypnosis or auto-hypnosis (as distinct from hetero-hypnosis) is a form, a process, or the result of a self-induced hypnotic state. Frequently, self-hypnosis is used as a vehicle to enhance the efficacy of self-suggestion; and, in such cases, the subject "plays the dual role of suggester and suggestee". The nature of the auto-suggestive practice may be, at one extreme, "''concentrative''", wherein "all attention is so totally focused on (the words of the auto-suggestive formula, e.g. "Every day, in every way, I'm getting better and better") that everything else is kept out of awareness" and, at the other, "''inclusive''", wherein subjects "allow all kinds of thoughts, emotions, memories, and the like to drift into their consciousness". Typological distinctions From their extensive investigations, Erika Fromm and Stephen Kahn (1990) identified significant and distinctive differences between the application of the wide variety of practices that lie within the domain commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbs
In general use, herbs are a widely distributed and widespread group of plants, excluding vegetables and other plants consumed for macronutrients, with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicinal purposes, or for fragrances. Culinary use typically distinguishes herbs from spices. ''Herbs'' generally refers to the leafy green or flowering parts of a plant (either fresh or dried), while ''spices'' are usually dried and produced from other parts of the plant, including seeds, bark, roots and fruits. Herbs have a variety of uses including culinary, medicinal, aromatic and in some cases, spiritual. General usage of the term "herb" differs between culinary herbs and medicinal herbs; in medicinal or spiritual use, any parts of the plant might be considered as "herbs", including leaves, roots, flowers, seeds, root bark, inner bark (and cambium), resin and pericarp. The word "herb" is pronounced in Commonwealth English, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |