|
Alternaria Japonica
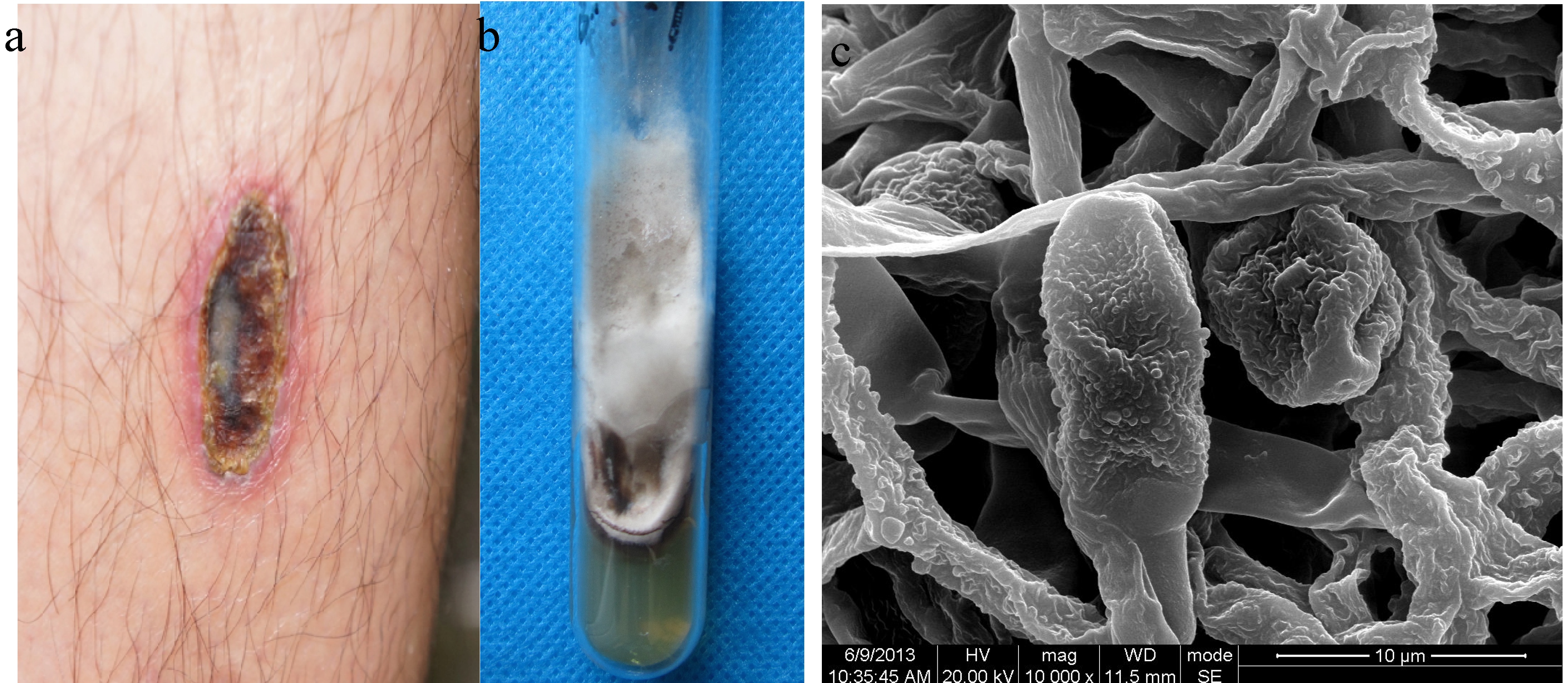
''Alternaria japonica'' is a fungal plant pathogen. It is a cause of black spot disease in cruciferous plants. It is not a major source of crop loss, but is considered dangerous for plants during the seedling stage. Symptoms ''Alternaria japonica'' affects its hosts in all stages of life. Infection causes a black or grey sunken lesion with a characteristic yellow border. On the leaves of some plants, infection can cause dark, water-soaked spots. The lesions can be observed anywhere on the plant. In seedlings, fungal lesions on the stem are a cause of damping-off. Infected seeds appear black or grey. Identification The fungus can first be detected by visually observing symptoms on infected plants. When cultured on potato carrot agar, it will form a grey or brownish, cobweb-like mycelium. Upon microscopic inspection, ''A. japonica'' has septate, branched hyphae and appears colorless to greenish grey. Chlamydospores are multicellular with thick, rough walls. Conidia are solitary a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables are vegetables of the family Brassicaceae (also called Cruciferae) with many genera, species, and cultivars being raised for food production such as cauliflower, cabbage, kale, garden cress, bok choy, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, mustard plant and similar green leaf vegetables. The family takes its alternative name (Cruciferae, New Latin for "cross-bearing") from the shape of their flowers, whose four petals resemble a cross. Ten of the most common cruciferous vegetables eaten by people, known colloquially in North America as cole crops and in the UK, Ireland and Australia as brassicas, are in a single species (''Brassica oleracea''); they are not distinguished from one another taxonomically, only by horticultural category of cultivar groups. Numerous other genera and species in the family are also edible. Cruciferous vegetables are one of the dominant food crops worldwide. They are high in vitamin C and soluble fiber and contain multiple nutrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbiological Culture
A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagnostic methods used as a research tool in molecular biology. The term ''culture'' can also refer to the microorganisms being grown. Microbial cultures are used to determine the type of organism, its abundance in the sample being tested, or both. It is one of the primary diagnostic methods of microbiology and used as a tool to determine the cause of infectious disease by letting the agent multiply in a predetermined medium. For example, a throat culture is taken by scraping the lining of tissue in the back of the throat and blotting the sample into a medium to be able to screen for harmful microorganisms, such as '' Streptococcus pyogenes'', the causative agent of strep throat. Furthermore, the term culture is more generally used inform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomal DNA
Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) is a DNA sequence that codes for ribosomal RNA. These sequences regulate transcription initiation and amplification, and contain both transcribed and non-transcribed spacer segments. In the human genome there are 5 chromosomes with nucleolus organizer regions: the acrocentric chromosomes 13 (RNR1), 14 ( RNR2), 15 ( RNR3), 21 (RNR4) and 22 ( RNR5). The genes that are responsible for encoding the various sub-units of rRNA are located across multiple chromosomes in humans. But the genes that encode for rRNA are highly conserved across the domains, with only the copy numbers involved for the genes having varying numbers per species. In Bacteria, Archaea, and chloroplasts the rRNA is composed of different (smaller) units, the large (23S) ribosomal RNA, 16S ribosomal RNA and 5S rRNA. The 16S rRNA is widely used for phylogenetic studies. Eukaryotes The rRNA transcribed from the approximately 600 rDNA repeats forms the most abundant section of RNA found in ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternaria
''Alternaria'' is a genus of Deuteromycetes fungi. All species are known as major plant pathogens. They are also common allergens in humans, growing indoors and causing hay fever or hypersensitivity reactions that sometimes lead to asthma. They are present in the human mycobiome and readily cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised people such as AIDS patients. There are 299 species in the genus; they are ubiquitous in the environment and are a natural part of fungal flora almost everywhere. They are normal agents of decay and decomposition. The spores are airborne and found in the soil and water, as well as indoors and on objects. The club-shaped spores are single or form long chains. They can grow thick colonies which are usually green, black, or gray. At least 20% of agricultural spoilage is caused by ''Alternaria'' species, with the most severe losses reaching 80% of yield. Many human health disorders can be caused by these fungi, which grow on skin and mucous m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungicide
Fungicides are biocidal chemical compounds or biological organisms used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. A fungistatic inhibits their growth. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in critical losses of yield, quality, and profit. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals. Chemicals used to control oomycetes, which are not fungi, are also referred to as fungicides, as oomycetes use the same mechanisms as fungi to infect plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upwardly. Most fungicides that ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated pest management (IPM), also known as integrated pest control (IPC) is a broad-based approach that integrates both chemical and non-chemical practices for economic control of pests. IPM aims to suppress pest populations below the economic injury level (EIL). The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization defines IPM as "the careful consideration of all available pest control techniques and subsequent integration of appropriate measures that discourage the development of pest populations and keep pesticides and other interventions to levels that are economically justified and reduce or minimize risks to human health and the environment. IPM emphasizes the growth of a healthy crop with the least possible disruption to agro-ecosystems and encourages natural pest control mechanisms." Entomologists and ecologists have urged the adoption of IPM pest control since the 1970s. IPM allows for safer pest control. The introduction and spread of invasive species can also be managed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungal Plant Pathogens And Diseases
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)