|
Alsactide
Alsactide (INN) (brand name Synchrodyn 1-17 or simply Synchrodyn, former development code name Hoechst 433), also known as alisactide, is a synthetic peptide and analogue of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) which is used in Italy as a diagnostic agent in kidney function for adrenal insufficiency. Like ACTH, alsactide is thought to act as a non-selective agonist of the melanocortin receptors, including the ACTH receptor (MC2RHowever, it appears to show a different profile of receptor (biochemistry), receptor selectivity relative to ACTH, as it apparently demonstrated no evidence of inhibition of endogenous ACTH in Addison's disease patients. See also * Tetracosactide Adrenocorticotropic hormone is used as a medication and as diagnostic agent in the ACTH stimulation test. The form that is purified from pig pituitary glands is known as corticotropin is a medication and naturally occurring polypeptide trop ... References {{Melanocortin receptor modulators Pepti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocortin Receptor
Melanocortin receptors are members of the rhodopsin family of 7-transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors. There are five known members of the melanocortin receptor system each with differing specificities for melanocortins: * . MC1R is associated with pigmentation genetics. * . MC2R is also known as the ACTH receptor or corticotropin receptor because it is specific for ACTH alone. * . MC3R is associated with childhood growth, accrual of lean mass and onset of puberty. * . Defects in MC4R are a cause of autosomal dominant obesity, accounting for 6% of all cases of early-onset obesity. * . MC5R These receptors are inhibited by endogenous inverse agonists agouti signalling peptide and agouti-related peptide, and activated by synthetic (i.e. afamelanotide) and endogenous agonist melanocyte-stimulating hormones. Selective ligands Several selective ligands for the melanocortin receptors are known, and some synthetic compounds have been investigated as potential tanning, anti-obesity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as |
Tetracosactide
Adrenocorticotropic hormone is used as a medication and as diagnostic agent in the ACTH stimulation test. The form that is purified from pig pituitary glands is known as corticotropin is a medication and naturally occurring polypeptide tropic hormone produced and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. The form that is made synthetically is tetracosactide, also known as synacthen, tetracosactrin and cosyntropin. It consists of the first 24 (of a total of 39) amino acids of ACTH and retains full function of the parent peptide. Tetracosactide stimulates the release of corticosteroids such as cortisol from the adrenal glands, and is used for the ACTH stimulation test to assess adrenal gland function. Medical uses Both corticotropin and tetracosactide have been used for diagnostic purposes to determine adrenocortical insufficiency, particularly in Addison's disease, via the ACTH stimulation test. However, as of 2015 the US label for corticotropin does not include diagnostic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addison's Disease
Addison's disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, is a rare long-term endocrine disorder characterized by inadequate production of the steroid hormones cortisol and aldosterone by the two outer layers of the cells of the adrenal glands (adrenal cortex), causing adrenal insufficiency. Symptoms generally come on slowly and insidiously and may include abdominal pain and gastrointestinal abnormalities, weakness, and weight loss. Darkening of the skin in certain areas may also occur. Under certain circumstances, an adrenal crisis may occur with low blood pressure, vomiting, lower back pain, and loss of consciousness. Mood changes may also occur. Rapid onset of symptoms indicates acute adrenal failure which is a serious and emergent condition. An adrenal crisis can be triggered by stress, such as from an injury, surgery, or infection. Addison's disease arises from problems with the adrenal gland such that not enough of the steroid hormone cortisol and possibly aldo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell. In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism. For example, estradiol is an endogenous estrogen hormone produced within the body, whereas ethinylestradiol Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disord ... is an exogenous synthetic estrogen, commonly used in birth control pills. References External links *{{Wiktionary-inline, endogeny Biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binding Selectivity
Binding selectivity is defined with respect to the binding of ligands to a substrate forming a complex. Binding selectivity describes how a ligand may bind more preferentially to one receptor than another. A selectivity coefficient is the equilibrium constant for the reaction of displacement by one ligand of another ligand in a complex with the substrate. Binding selectivity is of major importance in biochemistry and in chemical separation processes. Selectivity coefficient The concept of selectivity is used to quantify the extent to which one chemical substance, A, binds each of two other chemical substances, B and C. The simplest case is where the complexes formed have 1:1 stoichiometry. Then, the two interactions may be characterized by equilibrium constants ''K''AB and ''K''AC.The constant used here are ''association'' constants. ''Dissociation'' constants are used in some contexts. A dissociation constant is the reciprocal of an association constant. : + B AB; \mathit K_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and cause some form of cellular/tissue response, e.g. a change in the electrical activity of a cell. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Transmembrane receptors include ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and enzyme-linked hormone receptors. Intracellular receptors are those found inside the cell, and include cytoplasmic receptors and nuclear receptors. A molecule that binds to a receptor is called a ligand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACTH Receptor
The adrenocorticotropic hormone receptor or ACTH receptor also known as the melanocortin receptor 2 or MC2 receptor is a type of melanocortin receptor (type 2) which is specific for ACTH. A G protein–coupled receptor located on the external cell plasma membrane, it is coupled to Gαs and upregulates levels of cAMP by activating adenylyl cyclase. The ACTH receptor plays a role in immune function and glucose metabolism. Structure ACTH receptors are the shortest of the melanocortin receptor family and are the smallest known G-coupled receptors. Both human and bovine ACTH receptors are synthesized as 297 residue long proteins with 81% sequence homology. There are currently no available protein X-ray crystallography structures for the ACTH receptor available in the Protein Data Bank; while the ACTH receptor and the β2 adrenergic receptor are relatively distantly-related with a sequence identity of approximately 26%, MC2R investigators such as David Fridmanis have assumed that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
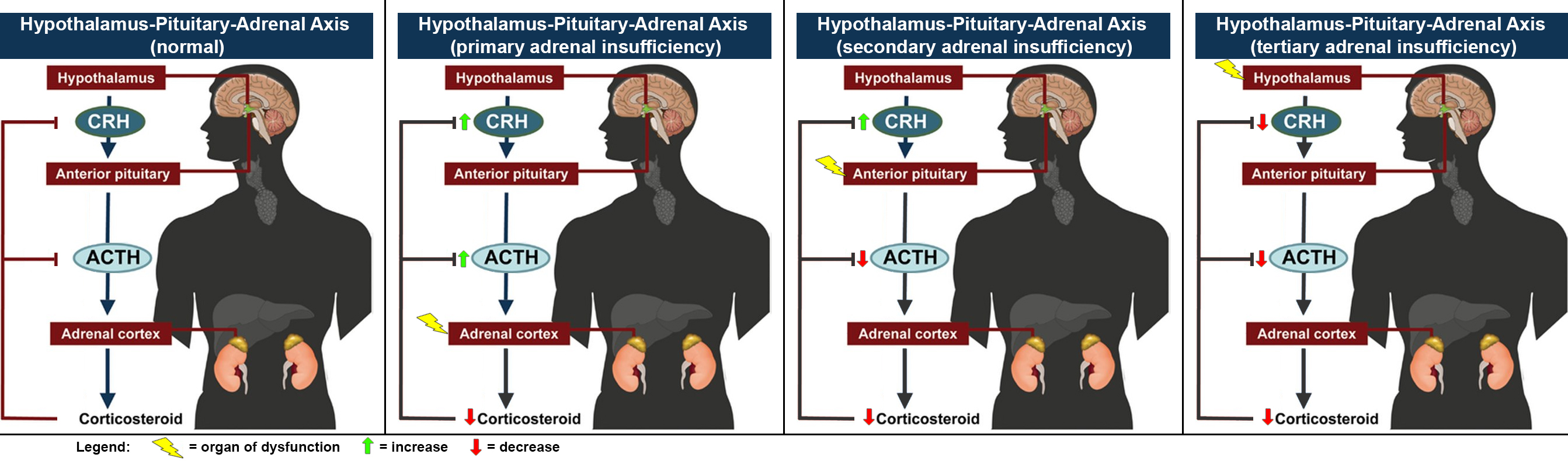
Adrenal Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androgens. These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole. Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle weakness and fatigue, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes (in mild cases) to organ failure and shock (in severe cases). An adrenal crisis may occur if the body is subjected to stress, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body. Death may quickly follow. Adrenal insufficiency can be caused by dysfunction of the adrenal gland itself, whether by destruction (e.g. Addison's disease), failure of development ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |