|
Allison Glacier
Allison Glacier () is an ice stream on the west side of Heard Island in the southern Indian Ocean. Allison Glacier flows from Big Ben massif down to the sea to the south of Cape Gazert. To the north of Allison Glacier is Vahsel Glacier, whose terminus is at South West Bay, between Erratic Point and Cape Gazert. Immediately to the north of Vahsel Glacier is Schmidt Glacier, whose terminus is located between Mount Drygalski and North West Cornice. To the south of Allison Glacier is Abbotsmith Glacier, while Cape Gazert is immediately west. Discovery and naming Allison Glacier was named after Ian Allison, an Australian glaciologist who carried out glaciological research in this area in 1971 for the Australian Antarctic Division during the French-Australian Antarctic Expedition. See also *List of glaciers in the Antarctic *Retreat of glaciers since 1850 The retreat of glaciers since 1850 affects the availability of fresh water for irrigation and domestic use, mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Stream
An ice stream is a region of fast-moving ice within an ice sheet. It is a type of glacier, a body of ice that moves under its own weight. They can move upwards of a year, and can be up to in width, and hundreds of kilometers in length. They tend to be about deep at the thickest, and constitute the majority of the ice that leaves the sheet. In Antarctica, the ice streams account for approximately 90% of the sheet's mass loss per year, and approximately 50% of the mass loss in Greenland. The shear forces cause deformation and recrystallization that drive the movement, this movement then causes topographic lows and valleys to form after all of the material in the ice sheet has been discharged. Sediment also plays an important role in flow velocity, the softer and more easily deformed the sediment present, the easier it is for flow velocity to be higher. Most ice streams contain a layer of water at the bottom, which lubricates flow and acts to increase speed. Mechanics Ice st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmidt Glacier (Heard Island And McDonald Islands)
Schmidt Glacier () is a glacier, 0.7 nautical miles (1.3 km) long, flowing west from Baudissin Glacier between Mount Drygalski and North West Cornice, on the west side of Heard Island in the southern Indian Ocean. To the north of Schmidt Glacier is Baudissin Glacier, whose terminus is located at the western side of Corinthian Bay, near Sealers Cove. Kildalkey Head is west of Schmidt Glacier. To the south of Schmidt Glacier is Vahsel Glacier, whose terminus is at South West Bay, between Erratic Point and Cape Gazert. Immediately south of Vahsel Glacier is Allison Glacier. Clichereto see a map of Schmidt Glacier and the northwestern coast of Heard Island. Discovery and naming Schmidt Glacier was roughly charted in 1902 by the 1st German Antarctic Expedition under Erich von Drygalski Erich Dagobert von Drygalski (; February 9, 1865 – January 10, 1949) was a German geographer, geophysicist and polar scientist, born in Königsberg, East Prussia. Between 1882 and 1887, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Glaciers In The Antarctic
There are many glaciers in the Antarctic. This set of lists does not include ice sheets, ice caps or ice fields, such as the Antarctic ice sheet, but includes glacial features that are defined by their flow, rather than general bodies of ice. The lists include outlet glaciers, valley glaciers, cirque glaciers, tidewater glaciers and ice streams. Ice streams are a type of glacier and many of them have "glacier" in their name, e.g. Pine Island Glacier. Ice shelves are listed separately in the List of Antarctic ice shelves. For the purposes of these lists, the Antarctic is defined as any latitude further south than 60° (the continental limit according to the Antarctic Treaty System). List by letters * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: A–H * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: I–Z See also * List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands * List of Antarctic ice rises * List of Antarctic ice shelves This is a list of Antarctic ice shelves. Ice shelves ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Antarctic Division
The Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) is a division of the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water. The Division undertakes science programs and research projects to contribute to an understanding of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. It conducts and supports collaborative research programs with other Australian and international organisations, such as the Bureau of Meteorology and Geoscience Australia, as well as administering and maintaining a presence in Australian Antarctic and sub-Antarctic territories. Their website includes articles on the Antarctic wildlife, threats, guidelines and they have blogs written by Australians at the three Australian bases in Antarctica: Mawson, Davis and Casey. Charter Under its charter the Australian Antarctic Division: * Administers the Australian Antarctic Territory and the Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands * Conducts research in high priority areas of Antarctic science * Coordinates and manag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciology
Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, climatology, meteorology, hydrology, biology, and ecology. The impact of glaciers on people includes the fields of human geography and anthropology. The discoveries of water ice on the Moon, Mars, Europa and Pluto add an extraterrestrial component to the field, which is referred to as "astroglaciology". Overview A glacier is an extended mass of ice formed from snow falling and accumulating over a long period of time; glaciers move very slowly, either descending from high mountains, as in valley glaciers, or moving outward from centers of accumulation, as in continental glaciers. Areas of study within glaciology include glacial history and the reconstruction of past glaciation. A glaciologist is a person who studies glaciers. A glaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Allison (scientist)
Ian Frederick Allison AO AAM FAA is an internationally recognised Australian glaciologist and climate scientist. He was elected a Fellow of the Australian Academy of Science in 2016 in recognition of his work in understanding the role of "sea ice and Antarctica in the global climate system". Career and impact Allison received his MSc and PhD both in Meteorology from the University of Melbourne in 1970 and 1987 respectively. He worked at the Australian Antarctic Division for 42 years. His research focuses on the global climate system and in particular the role of Antarctica in the world's climate. His research spans disciplines including ice shelf-ocean interaction, meteorology, glaciology and oceanography. Allison led or participated in 25 expeditions to Antarctica, and during this time he conducted foundational research on Antarctic sea ice. His research documented the seasonal change in sea ice driven by its interaction with the water column and the atmosphere. Allis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbotsmith Glacier
Following is a list of glaciers of Heard Island and McDonald Islands in Antarctica. This list may not reflect recently named glaciers in Heard Island and McDonald Islands. Context Heard Island is a volcanic island in the Southern Ocean that is 80% covered in ice. The island is cold and steep, and experiences high levels of snowfall. There are many glaciers, which descend for up to from up to down to sea level. The larger glaciers lose as much as 80% of their volume through calving into the ocean, and they are not particularly sensitive to temperature changes. Melting is a more significant factor in loss of volume for the smaller glaciers. Spring temperatures in the 1980s were about higher than the average in 1946–54. Comparison of air photographs from 1947 and early 1970 show that glaciers have generally retreated, particularly on the eastern flanks, and that they have narrowed on northern and windward western flanks. The area covered by glaciers had shrunk from in 1947 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North West Cornice
North West Cornice () is a narrow rock ridge descending in a northwest direction from Big Ben on Heard Island, and terminating at Schmidt Glacier in the northwest part of the island. Surveyed and given this descriptive name by ANARE (Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions The Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE ) is the historical name for the Australian Antarctic Program (AAp) administered for Australia by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). History Australia has had a long involv ...) in 1948. Clichereto see a map of North West Cornice and the northwestern coast of Heard Island. Ridges of Antarctica {{Subantarctic-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Drygalski
Mount Drygalski is an ice-free hill, high, standing southeast of Atlas Cove, near the northwest end of Heard Island in the southern Indian Ocean. The feature appears to have been roughly charted on an 1882 sketch map compiled by Ensign Washington Irving Chambers aboard the USS ''Marion'' during the rescue of the shipwrecked crew of the American sealing bark ''Trinity''. It was more accurately charted and named by the First German Antarctica Expedition in 1902. Professor Erich von Drygalski, the leader of the German Expedition, was a member of the landing party which investigated the area between Rogers Head Rogers Head () is a conspicuous headland marking the north extremity of the peninsula between Atlas Cove and Corinthian Bay on the north coast of Heard Island. Named for the Rogers family of New London, Connecticut, including Captain Erasmus Dar ... and the summit of this feature. References External linksMap of Mount Drygalski and the northwestern coast of Hear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erratic Point
Erratic Point is a small, moss-covered point at the head of South West Bay, northeast of Cape Gazert, on the west side of Heard Island in the southern Indian Ocean. The First German Antarctica Expedition in 1902 charted a cape in this vicinity, from the summit of Mount Drygalski, and applied the name "Kap Lerche." In November 1929 the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Douglas Mawson charted a small point in this position and applied the name "Erratic Point" because of the large number of massive erratic boulders encountered there. The Australian National Antarctic Research Expedition The Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE ) is the historical name for the Australian Antarctic Program (AAp) administered for Australia by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). History Australia has had a long involv ... was unable to find any significant feature in this immediate area during their 1948 survey of the island, hence the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
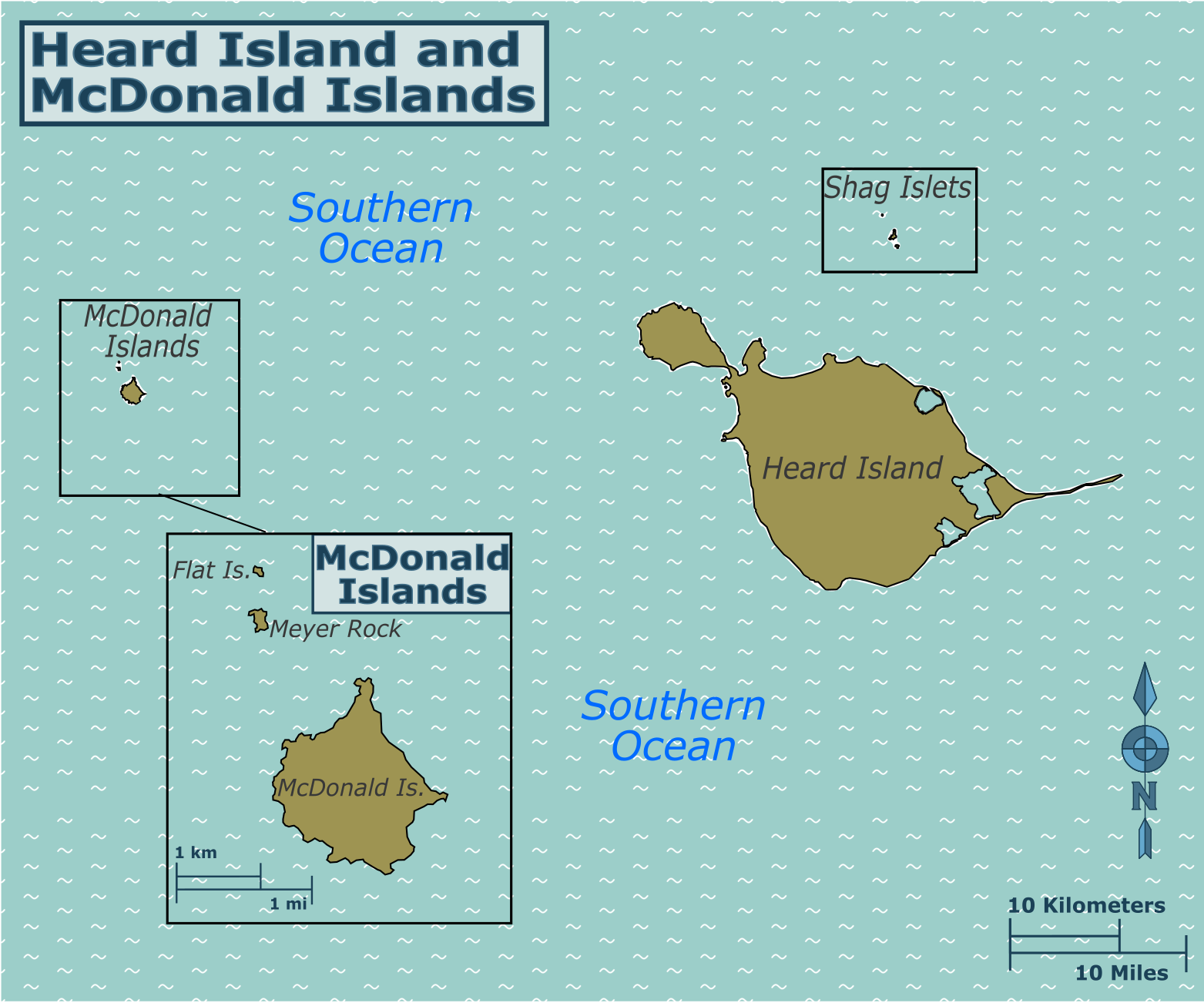
Heard Island And McDonald Islands
The Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands (HIMI) is an Australian external territory comprising a volcanic group of mostly barren Antarctic islands, about two-thirds of the way from Madagascar to Antarctica. The group's overall size is in area and it has of coastline. Discovered in the mid-19th century, the islands lie on the Kerguelen Plateau in the Indian Ocean and have been an Australian territory since 1947. They contain Australia's only two active volcanoes. The summit of one, Mawson Peak, is higher than any mountain in all other Australian states or territories, except Dome Argus, Mount McClintock and Mount Menzies in the Australian Antarctic Territory. The islands are among the most remote places on Earth: They are located about southwest of Perth, southwest of Cape Leeuwin, Australia, southeast of South Africa, southeast of Madagascar, north of Antarctica, and southeast of the Kerguelen Islands (part of French Southern and Antarctic Lands). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South West Bay
South West Bay () is an open bay indenting the west side of Heard Island immediately north of Cape Gazert in the southern Indian Ocean. The bay was roughly charted on an 1860 sketch map compiled by Captain H.C. Chester, an American American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, pe ... sealer. The name "S.W. Bay" appears on an 1882 chart compiled by Ens. Washington Irving Chambers aboard the USS ''Marion'' at Heard Island in January 1882. The bay name appears to have developed from an American sealer name, "Southwest Beach," in use about 1860 for the pebble beach at the north end of this bay. External links map of South West Bay and the northwestern coast of Heard Islandmap of Heard Island and McDonald Islands, including all major topographical features Bays of Heard Island and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |