|
Allegany Central Railroad
The Allegany Central Railroad was a tourist railroad that took place in three different locations from the 1970s to the 1990s. It originally operated in Covington, Virginia, before ownership disputes moved it to Cumberland, Maryland. From there, ownership disputes moved it again to Staunton, Virginia. Rising insurance costs shut down the railroad altogether by the end of the 1990s. History Original location in Covington, Virginia The Allegany Central Railroad was founded by Jack Showalter in Alleghany County, Virginia, and he acquired Canadian Pacific 4-6-2 steam locomotives Nos 1238 and 1286 to be used for their operations. The Allegany Central originally ran over the Chesapeake and Ohio's former Hot Springs branch between Intervale and Covington from 1975 to 1984. Although, it originally reached Hot Springs, the Hot Springs resort no longer wanted the railroad near them when the C&O abandoned the line, so the line at Hot Springs was ripped up, and the branch was shortened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heritage Railway
A heritage railway or heritage railroad (US usage) is a railway operated as living history to re-create or preserve railway scenes of the past. Heritage railways are often old railway lines preserved in a state depicting a period (or periods) in the history of rail transport. Definition The British Office of Rail and Road defines heritage railways as follows:...'lines of local interest', museum railways or tourist railways that have retained or assumed the character and appearance and operating practices of railways of former times. Several lines that operate in isolation provide genuine transport facilities, providing community links. Most lines constitute tourist or educational attractions in their own right. Much of the rolling stock and other equipment used on these systems is original and is of historic value in its own right. Many systems aim to replicate both the look and operating practices of historic former railways companies. Infrastructure Heritage railway lines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
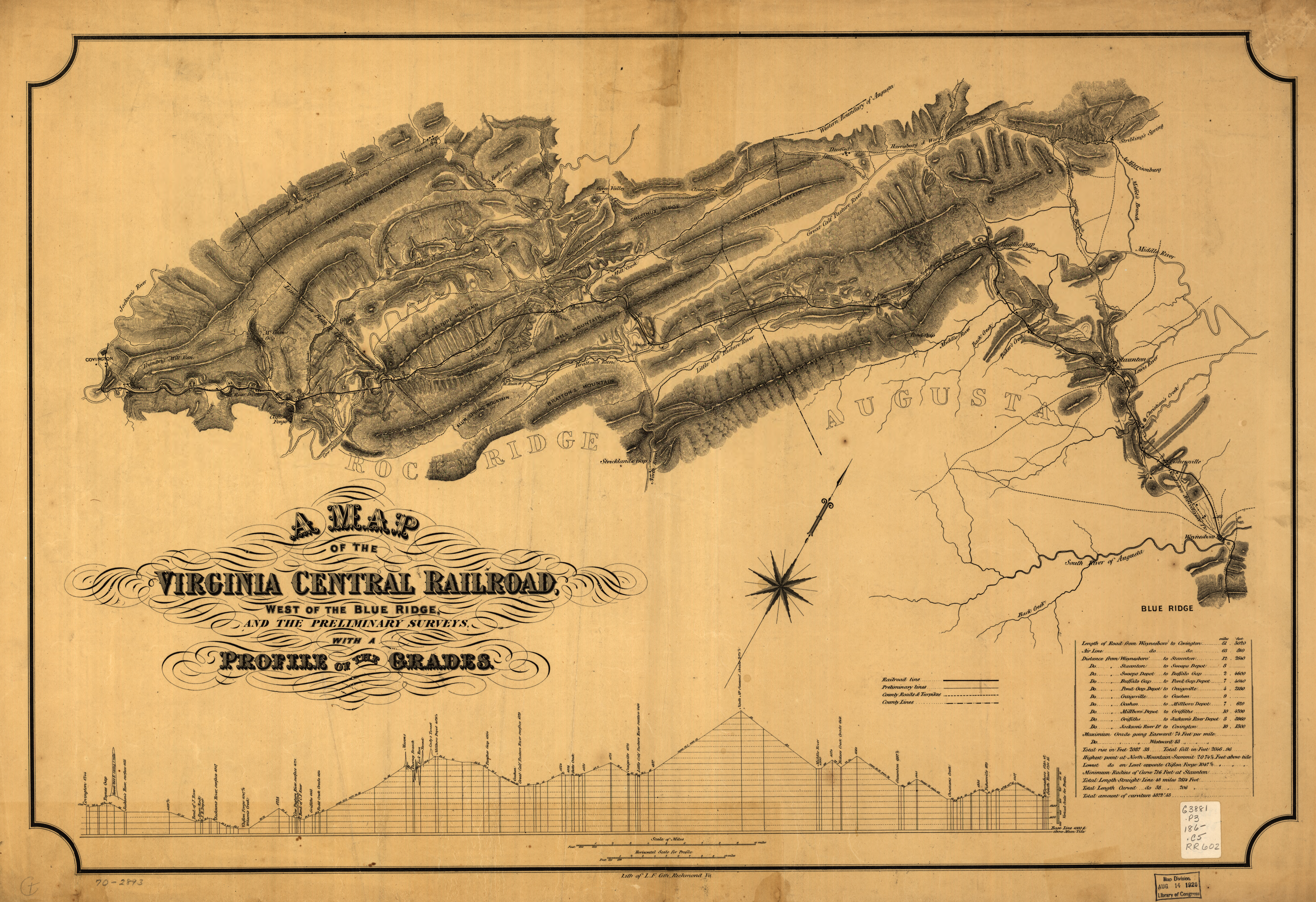
Virginia Central Railroad
The Virginia Central Railroad was an early railroad in the U.S. state of Virginia that operated between 1850 and 1868 from Richmond westward for to Covington. Chartered in 1836 as the Louisa Railroad by the Virginia General Assembly, the railroad began near the Richmond, Fredericksburg and Potomac Railroad's line and expanded westward to Orange County, reaching Gordonsville by 1840. In 1849, the Blue Ridge Railroad was chartered to construct a line over the Blue Ridge Mountains for the Louisa Railroad which reached the base of the Blue Ridge in 1852. After a decision from the U.S. Supreme Court, the Louisa Railroad was allowed to expand eastward from a point near Doswell to Richmond. Renamed as the Virginia Central Railroad in 1850, the railroad bypassed the under construction Blue Ridge Railroad via a temporary track built over Rockfish Gap. This connected the railroad's eastern division with its expanding line across the Blue Ridge in the Shenandoah Valley. Having reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. In the United States and elsewhere, this wheel arrangement is commonly known as a Consolidation, after the Lehigh and Mahanoy Railroad’s ''Consolidation'', the name of the first 2-8-0.White, John H. Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, p. 65. The notation 2-8-0T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in side-tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender. The Consolidation represented a notable advance in locomotive power. After 1875, it became "the most popular type of freight locomotive in the United States and was built in greater quantities than any other si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Superior And Ishpeming Railroad
The Lake Superior and Ishpeming Railroad , is a U.S. railroad offering service from Marquette, Michigan, to nearby locations in Michigan's Upper Peninsula. It began operations in 1896. The LS&I continues to operate as an independent railroad from its headquarters in Marquette. At the end of 1970, LS&I operated 117 miles of road on 241 miles of track (188 on 388 km); that year it reported of freight. In 2011, LS&I had been reduced to of track. History The Lake Superior and Ishpeming Railway was organized in 1893 as a subsidiary of Cleveland-Cliffs Iron Company (now Cleveland-Cliffs Inc.), the iron ore mining company. From the start the railroad's primary business was the transport of iron ore from the Marquette Iron Range, west of Marquette, to docks on Lake Superior from which the ore could be shipped to steel mills on the lower Great Lakes. The primary towns on the iron range are Ishpeming and Negaunee, Michigan.In 1904 the railroad carried over of freight, and ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population of 1,342,153 as of 2021, of widely varied landscape, from arctic tundra and the Hudson Bay coastline in the Northern Region, Manitoba, north to dense Boreal forest of Canada, boreal forest, large freshwater List of lakes of Manitoba, lakes, and prairie grassland in the central and Southern Manitoba, southern regions. Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous peoples have inhabited what is now Manitoba for thousands of years. In the early 17th century, British and French North American fur trade, fur traders began arriving in the area and establishing settlements. The Kingdom of England secured control of the region in 1673 and created a territory named Rupert's Land, which was placed under the administration of the Hudson's Bay Company. Rupe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749,607 and a metropolitan population of 834,678, making it the sixth-largest city, and eighth-largest metropolitan area in Canada. The city is named after the nearby Lake Winnipeg; the name comes from the Western Cree words for "muddy water" - “winipīhk”. The region was a trading centre for Indigenous peoples long before the arrival of Europeans; it is the traditional territory of the Anishinabe (Ojibway), Ininew (Cree), Oji-Cree, Dene, and Dakota, and is the birthplace of the Métis Nation. French traders built the first fort on the site in 1738. A settlement was later founded by the Selkirk settlers of the Red River Colony in 1812, the nucleus of which was incorporated as the City of Winnipeg in 1873. Being far inland, the local cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prairie Dog Central Railway
The Prairie Dog Central Railway is a heritage railway just outside Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. Regular trips are every Saturday, Sunday and Holiday Monday from May through September, and last almost four hours with one stop in the rural community of Grosse Isle. Special dinner excursions occur during the season, as well as the Howlin' Halloween Express Trains in October. Details of the operations can be found by reviewing the schedules. Private Charters, School Programs and Engineer for a Day are also available. History Initiated in 1970 by The Vintage Locomotive Society Inc., the first operations were in July, 1970. From 1970–1974, the train operated out of Charleswood on the now-abandoned Canadian National Cabot Subdivision. From 1975 to 1996 the train operated out of St. James, immediately west of Polo Park on a now abandoned Canadian National Railways line. In 1999 the station, now a Federal Heritage Site, was moved to its present location at Inkster Junction in R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories (NWT) to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada (Saskatchewan being the other). The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds. Alberta is the fourth largest province by area at , and the fourth most populous, being home to 4,262,635 people. Alberta's capital is Edmonton, while Calgary is its largest city. The two are Alberta's largest census metropolitan areas. More tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durbin And Greenbrier Valley Railroad
The Durbin and Greenbrier Valley Railroad is a heritage and freight railroad in the U.S. states of Virginia and West Virginia. It operates the West Virginia State Rail Authority-owned Durbin Railroad and West Virginia Central Railroad , as well as the Shenandoah Valley Railroad in Virginia. Beginning in 2015, DGVR began operating the historic geared steam-powered Cass Scenic Railroad, which was previously operated by the West Virginia Division of Natural Resources as part of Cass Scenic Railroad State Park. Trains The DGVR operates five different excursion trains in West Virginia: * The ''New Tygart Flyer'', which operates out of Elkins. * The ''Durbin Rocket'', powered by a Climax or Heisler geared logging locomotive, operates from Durbin. * The ''Cheat Mountain Salamander'' which operates out of Elkins. * The ''Mountain Explorer Dinner Train'' which also leaves from Elkins. * The ''Cass Scenic Railroad'' which operates from Cass Cass may refer to: People and fictio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shenandoah Valley Railroad (short-line)
The Shenandoah Valley Railroad is a shortline railroad operating of track between Staunton and Pleasant Valley, Virginia. The railroad interchanges with CSX and Buckingham Branch in Staunton and Norfolk Southern in Pleasant Valley. The railroad was purchased from Norfolk Southern in 1993 and is currently operated by the Durbin and Greenbrier Valley Railroad. Shenandoah Valley Railroad (retrieved 30 June 2014) Gallery [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Maryland Scenic Railroad
The Western Maryland Scenic Railroad (WMSR) is a heritage railroad based in Cumberland, Maryland, that operates passenger excursion trains and occasional freight trains using both steam and diesel locomotives over ex-Western Maryland Railway (WM) tracks between Cumberland and Frostburg. The railroad offers coach and first class service, murder mystery excursions, and special seasonal trips. Rail line history and description The Western Maryland (WM) was a railroad that served Cumberland, Maryland, along with a branch line that ran between there and Frostburg, as well as stretching to other small towns, like Hancock and Connellsville.. In 1973, the WM joined the Baltimore and Ohio and Chesapeake and Ohio railroads to group into the Chessie System, which would eventually be completely merged into the new CSX transportation system. The Cumberland-Frostburg branch was subsequently abandoned. In the late 1980s, the city of Cumberland started seeing the old branch line as a possible t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSXT
CSX Transportation , known colloquially as simply CSX, is a Class I freight railroad operating in the Eastern United States and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The railroad operates approximately 21,000 route miles () of track. The company operates as the leading subsidiary of CSX Corporation, a Fortune 500 company headquartered in Jacksonville, Florida. CSX Corporation (the parent of CSX Transportation) was formed in 1980 from the merger of Chessie System and Seaboard Coast Line Industries, two holding companies which controlled a number of railroads operating in the Eastern United States. Initially only a holding company itself, the subsidiaries that made up CSX Corporation were gradually merged, with this process completed in 1987. CSX Transportation formally came into existence in 1986, as the successor of Seaboard System Railroad. In 1999, CSX Transportation acquired approximately half of Conrail, in a joint purchase with competitor Norfolk Southern Railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)


.jpg)