|
All Saints Church, Claverley
All Saints Church is in the village of Claverley, Shropshire, England. It is an active Anglican parish church in the deanery of Bridgnorth, the archdeaconry of Ludlow, and the diocese of Hereford. Its benefice is united with that of Holy Innocents, Tuck Hill. The church is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade I listed building. History The church can trace its origins back to the 7th century. The present church was founded by Roger de Montgomerie, 1st Earl of Shrewsbury, who died in 1094. The tower was doubled in height and angle buttresses were added to it towards the end of the 15th century. At about the same time the north chapel was added. In 1902 the top two stages of the tower were rebuilt, faithfully copying the original design, by W. Wood Bethell. Architecture Exterior All Saints is constructed in local red sandstone. Its plan consists of a nave with a clerestory, north and south aisles, and a three- bay chancel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claverley
Claverley is a village and civil parish in east Shropshire, England. The parish also includes the hamlets of Beobridge, Hopstone, Upper Aston, Ludstone, Heathton and a number of other small settlements. Claverley village is east of the market town of Bridgnorth, near the Staffordshire county boundary. The village has three public houses, although one is currently unoccupied and its future unclear. On the edge of the village is the Arts and Crafts style mansion, Brook House; it was built in 1937 for the Gibbons family, who made their money as lock and window merchants in Wolverhampton. Church The Church of England parish church of All Saints dates from the 11th century and has a rare 13th-century wall painting. On the north side of the nave, and dated to around 1200, a frieze of painted scenes some long shows a series of 15 knights in armour, mostly engaged in single combat. It has been suggested that this portrays scenes from the 5th-century poem ''Psychomachia'', a battle be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yale University Press
Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day, and became an official department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and operationally autonomous. , Yale University Press publishes approximately 300 new hardcover and 150 new paperback books annually and has a backlist of about 5,000 books in print. Its books have won five National Book Awards, two National Book Critics Circle Awards and eight Pulitzer Prizes. The press maintains offices in New Haven, Connecticut and London, England. Yale is the only American university press with a full-scale publishing operation in Europe. It was a co-founder of the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Harvard University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Series and publishing programs Yale Series of Younger Poets Since its inception in 1919, the Yale Series of Younger Poets Competition has published the first collection of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
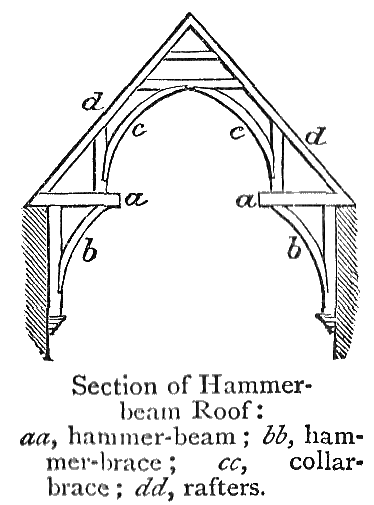
Hammerbeam Roof
A hammerbeam roof is a decorative, open timber roof truss typical of English Gothic architecture and has been called "...the most spectacular endeavour of the English Medieval carpenter". They are traditionally timber framed, using short beams projecting from the wall on which the rafters land, essentially a tie beam which has the middle cut out. These short beams are called hammer-beams and give this truss its name. A hammerbeam roof can have a single, double or false hammerbeam truss. Design A hammer-beam is a form of timber roof truss, allowing a hammerbeam roof to span greater than the length of any individual piece of timber. In place of a normal tie beam spanning the entire width of the roof, short beams – the hammer beams – are supported by curved braces from the wall, and hammer posts or arch-braces are built on top to support the rafters and typically a collar beam. The hammerbeam truss exerts considerable thrust on the walls or posts that support it. Hamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niche (architecture)
A niche (CanE, or ) in Classical architecture is an exedra or an apse that has been reduced in size, retaining the half-dome heading usual for an apse. Nero's Domus Aurea (AD 64–69) was the first semi-private dwelling that possessed rooms that were given richly varied floor plans, shaped with niches and exedrae; sheathed in dazzling polished white marble, such curved surfaces concentrated or dispersed the daylight. A is a very shallow niche, usually too shallow to contain statues, and may resemble a blind window (a window without openings) or sealed door. (Compare: blind arcade) The word derives from the Latin (), via the French . The Italian '' nicchio'' () may also be involved,OED, "Niche" as the traditional decoration for the top of a niche is a scallop shell, as in the illustration, hence also the alternative term of "conch" for a semi-dome, usually reserved for larger exedra. In Gothic architecture, a niche may be set within a tabernacle framing, like a richly de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital (architecture)
In architecture the capital (from the Latin ''caput'', or "head") or chapiter forms the topmost member of a column (or a pilaster). It mediates between the column and the load thrusting down upon it, broadening the area of the column's supporting surface. The capital, projecting on each side as it rises to support the abacus, joins the usually square abacus and the usually circular shaft of the column. The capital may be convex, as in the Doric order; concave, as in the inverted bell of the Corinthian order; or scrolling out, as in the Ionic order. These form the three principal types on which all capitals in the classical tradition are based. The Composite order established in the 16th century on a hint from the Arch of Titus, adds Ionic volutes to Corinthian acanthus leaves. From the highly visible position it occupies in all colonnaded monumental buildings, the capital is often selected for ornamentation; and is often the clearest indicator of the architectural orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pier (architecture)
A pier, in architecture, is an upright support for a structure or superstructure such as an arch or bridge. Sections of structural walls between openings (bays) can function as piers. External or free-standing walls may have piers at the ends or on corners. Description The simplest cross section of the pier is square, or rectangular, but other shapes are also common. In medieval architecture, massive circular supports called drum piers, cruciform (cross-shaped) piers, and compound piers are common architectural elements. Columns are a similar upright support, but stand on a round base. In buildings with a sequence of bays between piers, each opening (window or door) between two piers is considered a single bay. Bridge piers Single-span bridges have abutments at each end that support the weight of the bridge and serve as retaining walls to resist lateral movement of the earthen fill of the bridge approach. Multi-span bridges require piers to support the ends of spans betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcade (architecture)
An arcade is a succession of contiguous arches, with each arch supported by a colonnade of columns or piers. Exterior arcades are designed to provide a sheltered walkway for pedestrians. The walkway may be lined with retail stores. An arcade may feature arches on both sides of the walkway. Alternatively, a blind arcade superimposes arcading against a solid wall. Blind arcades are a feature of Romanesque architecture that influenced Gothic architecture. In the Gothic architectural tradition, the arcade can be located in the interior, in the lowest part of the wall of the nave, supporting the triforium and the clerestory in a cathedral, or on the exterior, in which they are usually part of the walkways that surround the courtyard and cloisters. Many medieval arcades housed shops or stalls, either in the arcaded space itself, or set into the main wall behind. From this, "arcade" has become a general word for a group of shops in a single building, regardless of the architectural f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular Gothic
Perpendicular Gothic (also Perpendicular, Rectilinear, or Third Pointed) architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-centred arches, straight vertical and horizontal lines in the tracery, and regular arch-topped rectangular panelling. Perpendicular was the prevailing style of Late Gothic architecture in England from the 14th century to the 17th century. Perpendicular was unique to the country: no equivalent arose in Continental Europe or elsewhere in the British Isles. Of all the Gothic architectural styles, Perpendicular was the first to experience a second wave of popularity from the 18th century on in Gothic Revival architecture. The pointed arches used in Perpendicular were often four-centred arches, allowing them to be rather wider and flatter than in other Gothic styles. Perpendicular tracery is characterized by mullions that rise vertically as fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decorated Gothic
English Gothic is an architectural style that flourished from the late 12th until the mid-17th century. The style was most prominently used in the construction of cathedrals and churches. Gothic architecture's defining features are pointed arches, rib vaults, buttresses, and extensive use of stained glass. Combined, these features allowed the creation of buildings of unprecedented height and grandeur, filled with light from large stained glass windows. Important examples include Westminster Abbey, Canterbury Cathedral and Salisbury Cathedral. The Gothic style endured in England much longer than in Continental Europe. The Gothic style was introduced from France, where the various elements had first been used together within a single building at the choir of the Abbey of Saint-Denis north of Paris, completed in 1144. The earliest large-scale applications of Gothic architecture in England were Canterbury Cathedral and Westminster Abbey. Many features of Gothic architecture had e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse. Overview The chancel is generally the area used by the clergy and choir during worship, while the congregation is in the nave. Direct access may be provided by a priest's door, usually on the south side of the church. This is one definition, sometimes called the "strict" one; in practice in churches where the eastern end contains other elements such as an ambulatory and side chapels, these are also often counted as part of the chancel, especially when discussing architecture. In smaller churches, where the altar is backed by the outside east wall and there is no distinct choir, the chancel and sanctuary may be the same area. In churches with a retroquire area behind the altar, this may only be included in the broader definition of chancel. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay (architecture)
In architecture, a bay is the space between architectural elements, or a recess or compartment. The term ''bay'' comes from Old French ''baie'', meaning an opening or hole."Bay" ''Online Etymology Dictionary''. http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?allowed_in_frame=0&search=bay&searchmode=none accessed 3/10/2014 __NOTOC__ Examples # The spaces between posts, columns, or buttresses in the length of a building, the division in the widths being called aisles. This meaning also applies to overhead vaults (between ribs), in a building using a vaulted structural system. For example, the Gothic architecture period's Chartres Cathedral has a nave (main interior space) that is '' "seven bays long." '' Similarly in timber framing a bay is the space between posts in the transverse direction of the building and aisles run longitudinally."Bay", n.3. def. 1-6 and "Bay", n.5 def 2. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) © Oxford University Press 2009 # Where there a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aisle
An aisle is, in general, a space for walking with rows of non-walking spaces on both sides. Aisles with seating on both sides can be seen in airplanes, certain types of buildings, such as churches, cathedrals, synagogues, meeting halls, parliaments and legislatures, courtrooms, theatres, and in certain types of passenger vehicles. Their floors may be flat or, as in theatres, stepped upwards from a stage. Aisles can also be seen in shops, warehouses, and factories, where rather than seats, they have shelving to either side. In warehouses and factories, aisles may be defined by storage pallets, and in factories, aisles may separate work areas. In health club A health club (also known as a fitness club, fitness center, health spa, and commonly referred to as a gym) is a place that houses exercise equipment for the purpose of physical exercise. In recent years, the number of fitness and health se ...s, exercise equipment is normally arranged in aisles. Aisles are disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |