|
Alitrunk
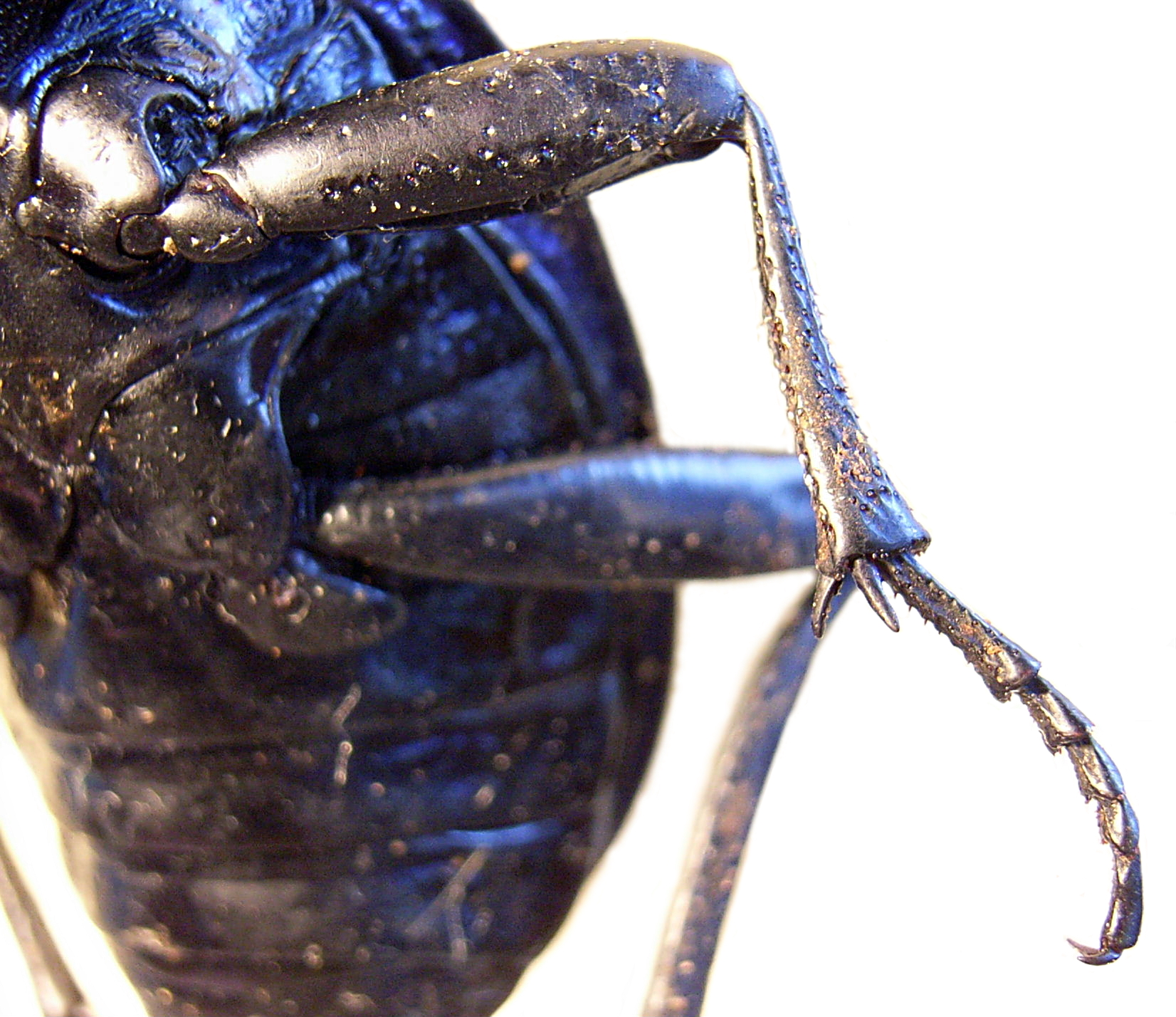
The mesosoma is the middle part of the body, or tagma, of arthropods whose body is composed of three parts, the other two being the prosoma and the metasoma. It bears the legs, and, in the case of winged insects, the wings. In hymenopterans of the suborder Apocrita (wasps, bees and ants), it consists of the three thoracic segments and the first abdominal segment (the propodeum). For historical reasons, in ants it is commonly referred to by the alternative name alitrunk. In scorpions, it is composed of six segments and forms the first part of the abdomen, containing all of the major organs. The first segment contains the sexual organs as well as a pair of vestigial and modified appendages forming a structure called the genital operculum. The second segment bears a pair of featherlike sensory organs known as the pectines; the final four segments each contain a pair of book lungs. The mesosoma is armoured with chitinous plates, on the upper surface by the tergites and on the low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpion Anatomy
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the order Scorpiones. They have eight legs, and are easily recognized by a pair of grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always ending with a stinger. The evolutionary history of scorpions goes back 435 million years. They mainly live in deserts but have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, and can be found on all continents except Antarctica. There are over 2,500 described species, with 22 extant (living) families recognized to date. Their taxonomy is being revised to account for 21st-century genomic studies. Scorpions primarily prey on insects and other invertebrates, but some species hunt vertebrates. They use their pincers to restrain and kill prey, or to prevent their own predation. The venomous sting is used for offense and defense. During courtship, the male and female grasp each other's pincers and dance while he tries to move her onto his sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the order Scorpiones. They have eight legs, and are easily recognized by a pair of grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always ending with a stinger. The evolutionary history of scorpions goes back 435 million years. They mainly live in deserts but have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, and can be found on all continents except Antarctica. There are over 2,500 described species, with 22 extant (living) families recognized to date. Their taxonomy is being revised to account for 21st-century genomic studies. Scorpions primarily prey on insects and other invertebrates, but some species hunt vertebrates. They use their pincers to restrain and kill prey, or to prevent their own predation. The venomous sting is used for offense and defense. During courtship, the male and female grasp each other's pincers and dance while he tries to move her onto his s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthosoma
The opisthosoma is the posterior part of the body in some arthropods, behind the prosoma (cephalothorax). It is a distinctive feature of the subphylum Chelicerata (arachnids, horseshoe crabs and others). Although it is similar in most respects to an abdomen (and is often referred to as such), the opisthosoma is differentiated by its inclusion of the respiratory organs (book lungs or book gills) and the heart. Segments The number of segments and appendages on the opisthosoma vary. Scorpions have 13, but the first is only seen during its embryological development. Other arachnids have fewer; harvestmen, for instance, have only ten. In general, appendages are absent or reduced, although in horseshoe crabs they persist as large plate-like limbs, called opercula or branchiophores, bearing the book gills, and that function in locomotion and gas exchange. In most chelicerates the opisthosomal limbs are greatly reduced and persist only as specialized structures, such as the silk-producing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spider
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternites
The sternum (pl. "sterna") is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen. In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case the subunits are called sternites, and may also be modified on the terminal abdominal segments so as to form part of the functional genitalia, in which case they are frequently reduced in size and development, and may become internalized and/or membranous. For a detailed explanation of the terminology, see Kinorhynchs have tergal and sternal plates too, though seemingly not homologous with those of arthropods.Sørensen, M. V. et al. Phylogeny of Kinorhyncha based on morphology and two molecular loci. PLoS One 10, 1–33 (2015). Ventrites are externally visible sternites. Usually the first sternite is covered up, so that vertrite numbers do not correspond to sternid numbers. The term is also used in other arthropod groups such as crustaceans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tergite
A ''tergum'' (Latin for "the back"; plural ''terga'', associated adjective tergal) is the dorsal ('upper') portion of an arthropod segment other than the head. The anterior edge is called the 'base' and posterior edge is called the 'apex' or 'margin'. A given tergum may be divided into hardened plates or sclerites commonly referred to as tergites. In a thoracic segment, for example, the tergum may be divided into an anterior notum and a posterior scutellum. Lateral extensions of a tergite are known as paranota (Greek for "alongside the back") or ''carinae'' (Latin for "keel"), exemplified by the flat-backed millipedes of the order Polydesmida. Kinorhynchs have tergal and sternal plates too, though seemingly not homologous with those of arthropods. Tergo-tergal is a stridulatory mechanism in which fine spines of the abdominal tergites are rubbed together to produce sound. This process is known as abdominal telescoping. Examples File:Andrena spiraeana abdomen.jpg , Abdominal t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chitin are produced each year in the biosphere. It is a primary component of cell walls in fungi (especially basidiomycetes and filamentous fungi), the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans and insects, the radulae, cephalopod beaks and gladii of molluscs and in some nematodes and diatoms. It is also synthesised by at least some fish and lissamphibians. Commercially, chitin is extracted from the shells of crabs, shrimps, shellfishes and lobsters, which are major by-products of the seafood industry. The structure of chitin is comparable to cellulose, forming crystalline nanofibrils or whiskers. It is functionally comparable to the protein keratin. Chitin has proved useful for several medicinal, industrial and biotechnological purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armour
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or from a potentially dangerous environment or activity (e.g. cycling, construction sites, etc.). Personal armour is used to protect soldiers and war animals. Vehicle armour is used on warships, armoured fighting vehicles, and some mostly ground attack combat aircraft. A second use of the term ''armour'' describes armoured forces, armoured weapons, and their role in combat. After the development of armoured warfare, tanks and mechanised infantry and their combat formations came to be referred to collectively as "armour". Etymology The word "armour" began to appear in the Middle Ages as a derivative of Old French. It is dated from 1297 as a "mail, defensive covering worn in combat". The word originates from the Old French , itself derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas exchange that is present in many arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is located inside an open ventral abdominal, air-filled cavity (atrium) and connects with the surroundings through a small opening for the purpose of respiration. Structure and function Book lungs are not related to the lungs of modern land-dwelling vertebrates. Their name describes their structure and purpose. Stacks of alternating air pockets and tissue filled with hemolymph give them an appearance similar to a "folded" book. Their number varies from just one pair in most spiders to four pairs in scorpions. The unfolded "pages" (plates) of the book lung are filled with hemolymph. The folds maximize the surface exposed to air, and thereby maximize the amount of gas exchanged with the environment. In most species, no motion of the plates is needed to facilitate this kind of respiration. Occasionally absent Sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensor
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon. In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends the information to other electronics, frequently a computer processor. Sensors are always used with other electronics. Sensors are used in everyday objects such as touch-sensitive elevator buttons (tactile sensor) and lamps which dim or brighten by touching the base, and in innumerable applications of which most people are never aware. With advances in micromachinery and easy-to-use microcontroller platforms, the uses of sensors have expanded beyond the traditional fields of temperature, pressure and flow measurement, for example into Attitude and heading reference system, MARG sensors. Analog sensors such as potentiometers and force-sensing resistors are still widely used. Their applications include manufacturing and machinery, airplane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body. In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including antennae, mouthparts (including mandibles, maxillae and maxillipeds), gills, locomotor legs ( pereiopods for walking, and pleopods for swimming), sexual organs (gonopods), and parts of the tail (uropods). Typically, each body segment carries one pair of appendages. An appendage which is modified to assist in feeding is known as a maxilliped or gnathopod. In vertebrates, an appendage can refer to a locomotor part such as a tail, fins on a fish, limbs (legs, flippers or wings) on a tetrapod; exposed sex organ; defensive parts such as horns and antlers; or sensory organs such as auricles, proboscis ( trunk and snout) and barbels. Appendages may become ''uniramous'', as in insects and centipedes, where each appendage comprises a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on comparison with homologous features in related species. The emergence of vestigiality occurs by normal evolutionary processes, typically by loss of function of a feature that is no longer subject to positive selection pressures when it loses its value in a changing environment. The feature may be selected against more urgently when its function becomes definitively harmful, but if the lack of the feature provides no advantage, and its presence provides no disadvantage, the feature may not be phased out by natural selection and persist across species. Examples of vestigial structures (also called degenerate, atrophied, or rudimentary organs) are the loss of functional wings in island-dwelling birds; the human vomeronasal organ; and the hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)



.jpg)



