|
Alice And Gwendoline Cave
The Alice and Gwendoline Cave is a limestone cave in County Clare, Ireland. It is known as the site of brown bear bones bearing the mark of butchery, which have pushed back the first known human habitation of Ireland by over two thousand years. Location The Alice and Gwendoline Cave is located about southwest of Ennis, near to Edenvale House and Edenvale Lough. History Previously called the Bull Paddock Cave, the Alice and Gwendoline Cave was named for two of Alice Julia Stacpoole's daughters, Alice Jane and Gwendoline Clare Surprise, nieces of Thomas Johnson Westropp. It was investigated in 1902. In 2016, a bear patella was discovered among the samples recovered in 1902 and deposited in the National Museum of Ireland, bearing clear butchery marks; cut marks that showed that someone was trying to remove the tendons; these could be used for sewing, fletching and hafting. It was dated to the 11th millennium BC: between 10860 and 10641 BC. This is over two thousand years earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ennis
Ennis () is the county town of County Clare, in the mid-west of Ireland. The town lies on the River Fergus, north of where the river widens and enters the Shannon Estuary. Ennis is the largest town in County Clare, with a population of 25,276, making it the 6th largest town, and 12th largest urban settlement, as of 2016. Dating from the 12th century the town's Irish name is short for ' ("island of the long rowing meadow") deriving from its location between two courses of the River Fergus. Ennis has had considerable success in the Irish Tidy Towns competition. In 2005 and 2021, the town was named Ireland's tidiest town, and was named Ireland's tidiest large urban centre on multiple occasions. History The name Ennis derives from the Irish word "Inis", meaning "island". This name relates to an island called ' ("Calf Island") or ' ("island of the long rowing meadow") formed between two courses of the River Fergus. The history of Ennis is closely linked with the O'Brien dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sewing
Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with a sewing needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic era. Before the invention of spinning yarn or weaving fabric, archaeologists believe Stone Age people across Europe and Asia sewed fur and leather clothing using bone, antler or ivory sewing-needles and "thread" made of various animal body parts including sinew, catgut, and veins. For thousands of years, all sewing was done by hand. The invention of the sewing machine in the 19th century and the rise of computerization in the 20th century led to mass production and export of sewn objects, but hand sewing is still practiced around the world. Fine hand sewing is a characteristic of high-quality tailoring, haute couture fashion, and custom dressmaking, and is pursued by both textile artists and hobbyists as a means of creative expression. The first known use of the word "sewing" was in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caves Of The Republic Of Ireland
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorgani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone Caves
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limestone c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In County Clare
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IT Sligo
The Institute of Technology, Sligo (ITS; ga, Institiúid Teicneolaíochta, Sligeach) was an institute of technology, located in Sligo, Ireland. In April 2022, it was formally dissolved, and its functions became part of Atlantic Technological University (ATU). As of 2021, the institute had three faculties and nine departments. History The institute opened in 1970 as a Regional Technical College, and adopted its present name on 7 May 1997. The first students graduated with degrees from Sligo RTC in 1986. Con Power served as principal of the college from its foundation in 1972 until 1979. Prof. Terri Scott was the institute's first female president, serving from 2008 until 2014. She was succeeded by Prof. Vincent Cunnane in October 2014. Dr. Brendan McCormack was appointed president of the institute in September 2016. Development IT Sligo developed a number of distance learning options, and as of 2016 reportedly had 1,800 online learners registered on various online programme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Sandel Mesolithic Site
The Mount Sandel Mesolithic site is in Coleraine, County Londonderry, Northern Ireland, just to the east of the Iron Age Mount Sandel Fort. It is one of the oldest archaeological sites in Ireland with carbon dating indicating an age of 9,000 years old (7,000BC). Gwendoline Cave, County Clare is the only site in Ireland with evidence of human occupation which pre-dates this location. Mount Sandel Mesolithic site is a Scheduled Historic Monument in the townland of Mount Sandel, in Causeway Coast and Glens Council area, at Grid Ref: C8533 3076. It was excavated by Peter Woodman in the 1970s. It has been said that "The Mt. Sandel excavations dominate the picture of the Early Mesolithic (in Ireland) as so few other sites have been excavated and fully published, let alone found. Not only that, but here was evidence for dwellings – until recently it was not until the Neolithic that there was again evidence for houses in Ireland." (M. Litt thesis) These excavations revealed the remai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th Millennium BC
This timeline of prehistory covers the time from the first appearance of ''Homo sapiens'' in Africa 315,000 years ago to the invention of writing, over 4,000 years ago, with the earliest records going back to 3,200 BC. Prehistory covers the time from the Middle Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) to the very beginnings of ancient history. All dates are approximate and subject to revision based on new discoveries or analyses. Middle Paleolithic :''See Timeline of human evolution, Timeline of natural history for earlier evolutionary history.'' * ∼320,000 to 305,000 years ago: Populations at Olorgesailie in Southern Kenya undergo technological improvements in tool making and engage in long-distance trade. * 315,000 years ago: approximate date of appearance of ''Homo sapiens'' (Jebel Irhoud, Morocco). * 270,000 years ago: age of Y-DNA haplogroup A00 ("Y-chromosomal Adam"). * 250,000 years ago: first appearance of ''Homo neanderthalensis'' ( Saccopastore skulls). * 230,000–150,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hafting
Hafting is a process by which an artifact, often bone, stone, or metal is attached to a ''haft'' (handle or strap). This makes the artifact more useful by allowing it to be shot (arrow), thrown by hand (spear), or used with more effective leverage (axe). When constructed properly, hafting can tremendously improve a weapon's damage and range. It is estimated that hafted weapons were most common during the Upper Paleolithic and Middle Paleolithic. It was one of the first tools where hominins took separate elements and united them into a single tool. The development of hafting is considered by archaeologists to have been a significant milestone. It was not only an improvement in the technology at the time; it also showed the progression of the human mind toward a world of complex tool-making. Hafting weapons is perhaps best known for its use by humans in prehistory, but it is still practiced by enthusiasts today and the handle of a tool such as an axe is still known as a haft. Many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fletching
Fletching is the fin-shaped aerodynamic stabilization device attached on arrows, bolts, darts, or javelins, and are typically made from light semi-flexible materials such as feathers or bark. Each piece of such fin is a fletch, also known as a flight or feather. A fletcher is a person who attaches fletchings to the shaft of arrows. The word is related to the French word , meaning 'arrow', via the ultimate root of Old Frankish . Description As a noun, ''fletching'' refers collectively to the fins or vanes, each of which individually is known as a fletch. Traditionally, the fletching consists of three matched half-feathers attached near the back of the arrow or shaft of the dart that are equally spaced around its circumference. Four fletchings have also been used. In English archery, the male feather, from a cock, is used on the outside of the arrow, while the other two stabilizing feathers are from a female, or hen. Traditional archery lore about feather curvature is that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability to withstand significant amounts of tension. Tendons are similar to ligaments; both are made of collagen. Ligaments connect one bone to another, while tendons connect muscle to bone. Structure Histologically, tendons consist of dense regular connective tissue. The main cellular component of tendons are specialized fibroblasts called tendon cells (tenocytes). Tenocytes synthesize the extracellular matrix of tendons, abundant in densely packed collagen fibers. The collagen fibers are parallel to each other and organized into tendon fascicles. Individual fascicles are bound by the endotendineum, which is a delicate loose connective tissue containing thin collagen fibrils and elastic fibres. Groups of fascicles are bounded by the epi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
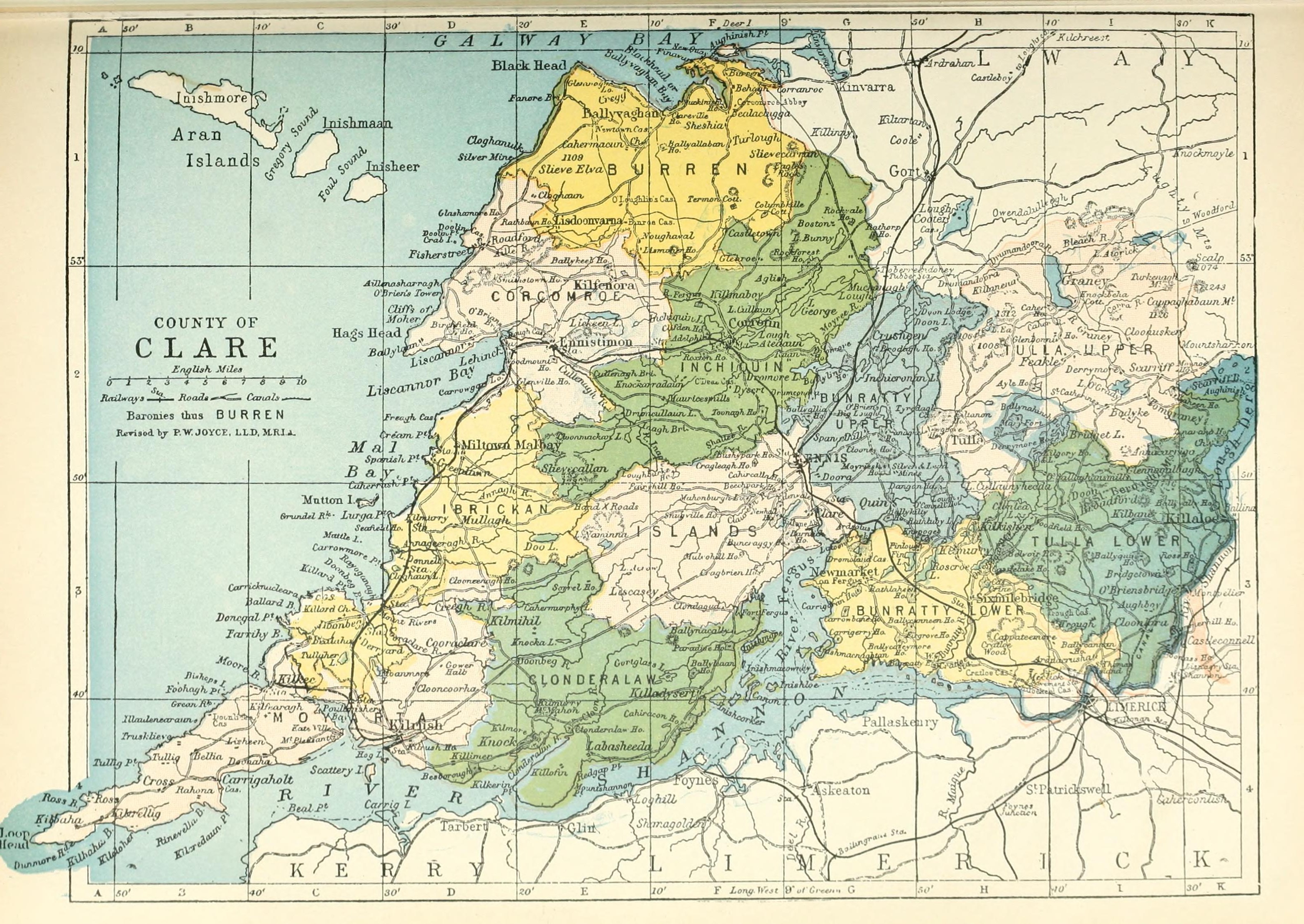
County Clare
County Clare ( ga, Contae an Chláir) is a county in Ireland, in the Southern Region and the province of Munster, bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean. Clare County Council is the local authority. The county had a population of 118,817 at the 2016 census. The county town and largest settlement is Ennis. Geography and subdivisions Clare is north-west of the River Shannon covering a total area of . Clare is the seventh largest of Ireland's 32 traditional counties in area and the 19th largest in terms of population. It is bordered by two counties in Munster and one county in Connacht: County Limerick to the south, County Tipperary to the east and County Galway to the north. Clare's nickname is ''the Banner County''. Baronies, parishes and townlands The county is divided into the baronies of Bunratty Lower, Bunratty Upper, Burren, Clonderalaw, Corcomroe, Ibrickan, Inchiquin, Islands, Moyarta, Tulla Lower and Tulla Upper. These in turn are divided into civil pari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)


.jpg)