|
Ali Al-Hadi Ibn Nizar
Abū ʿAlī Ḥasan, or ʿAlī, surnamed Al-Hādī (Arabic: علي الهادي بن نزار) (470 AH/1076 CE - 530 AH/1136 CE) was the 20th Ismaili Nizari Imam. Born in Cairo, he was about 17 years old when his predecessor, Imam al-Mustansir, died and 20 years old during the assumption of his Imamate in 490 AH/1097 CE. Henceforward, the seat of Ismaili Imamate was transferred from Egypt to Persia owing to the division among the Ismailis, where Hasan bin Sabbah had founded the Nizari Ismaili state. Name ''Abu Ali Al-Hasan'' son of Nizar son of Al-Mustansir Billah. Syrian resources mention his name as Ali Al-Hadi Ibn Nizar, علي الهادي بن نزار commonly referred to by the title al-Hadi الهادي meaning ''The Guide.'' According to a copy of a letter from the 21st Imam Al-Muhtadi to the Syrian Ismaili, the proper name was Al-Hadi Ali. A careful reading of this important letter composed by his son the 21st Ismaili Nizari Imam Al-Muhtadi may imply that he had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Hadi
Abū Muḥammad Mūsā ibn al-Mahdī al-Hādī ( ar, أبو محمد موسى بن المهدي الهادي; 26 April 764 CE 14 September 786 CE) better known by his laqab Al-Hādī (الهادي) was the fourth Arab Abbasid caliph who succeeded his father Al-Mahdi and ruled from 169 AH (785 CE) until his death in 170 AH (786 CE). His short reign ended with internal chaos and power struggles with his mother. Biography Al-Hadi was the eldest son of Al-Mahdi and Al-Khayzuran and the older brother of Harun al-Rashid. He was very dear to his father and was appointed as the first crown prince by his father at the age of 16 and was chosen as the leader of the army. Prior to his death, Al-Mahdi supposedly favored his second son, Harun al-Rashid, as his successor, taking him on multiple military expeditions in 779 and 781 to train him to be the next caliph, as his own father prepared him, but died before the formal transfer of the crown prince title could occur. Alternatively, Al-R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Afdal Shahanshah
Al-Afdal Shahanshah ( ar, الأفضل شاهنشاه, al-Afḍal Shāhanshāh; la, Lavendalius/Elafdalio; 1066 – 11 December 1121), born Abu al-Qasim Shahanshah bin Badr al-Jamali was a vizier of the Fatimid caliphs of Egypt. According to a later biographical encyclopedia, he was surnamed al-Malik al-Afdal ("the excellent king"), but this is not supported by contemporary sources. Ascent to power He was born in Acre, the son of Badr al-Jamali, an Armenian mamluk who became Muslim. Badr was vizier for the Fatimids in Cairo from 1074 until his death in 1094, when al-Afdal succeeded him. Caliph Al-Mustansir Billah died soon afterwards, and al-Afdal appointed as caliph al-Musta'li, a child, instead of al-Mustali's much older brother Nizar ibn al-Mustansir. Nizar revolted and was defeated in 1095; his supporters, led by Hassan-i Sabbah, fled east, where Sabbah established the Nizari Isma'ili sect, known also as the order of Assassins. At this time Fatimid power in Palestine had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian (), also known by its endonym Farsi (, ', ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964) and Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, a der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambsar Castle
Lambsar ( fa, لمبسر, also pronounced Lamsar), Lamasar, Lambasar, Lambesar () or Lomasar () was probably the largest and the most fortified of the Ismaili castles. The fortress is located in the central Alburz mountains, south of the Caspian Sea, about 120 km from present-day Tehran, Iran. Lambsar is to the northeast of Razmian village (the central district of Roodbar e Shahrestan). Kiya Buzurg Ummid (died 1138) captured the castle from Rasamuj and rebuilt it into a major stronghold using local labour. He was appointed by Hassan-i Sabbah (died 1124) as its governor. Only ruins remain of this magnificent fortress today. Very deep valleys surrounding the fortress make it impossible to access from the East and West sides. The North and South fronts are the only possible ways to get into the fortress. Although the slope of the mountain with a difference of 150m on both levels is stretched from north to south with a length of 480m, the castle is more than 190m in width. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambsar Fortress 1
Lambsar ( fa, لمبسر, also pronounced Lamsar), Lamasar, Lambasar, Lambesar () or Lomasar () was probably the largest and the most fortified of the Ismaili castles. The fortress is located in the central Alburz mountains, south of the Caspian Sea, about 120 km from present-day Tehran, Iran. Lambsar is to the northeast of Razmian village (the central district of Roodbar e Shahrestan). Kiya Buzurg Ummid (died 1138) captured the castle from Rasamuj and rebuilt it into a major stronghold using local labour. He was appointed by Hassan-i Sabbah (died 1124) as its governor. Only ruins remain of this magnificent fortress today. Very deep valleys surrounding the fortress make it impossible to access from the East and West sides. The North and South fronts are the only possible ways to get into the fortress. Although the slope of the mountain with a difference of 150m on both levels is stretched from north to south with a length of 480m, the castle is more than 190m in width. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zakariya Al-Qazwini
Zakariyya' al-Qazwini ( , ar, أبو يحيى زكرياء بن محمد بن محمود القزويني), also known as Qazvini ( fa, قزوینی), born in Qazvin (Iran) and died 1283, was a Persian cosmographer and geographer of Arab ancestry. He belonged to a family of jurists originally descended from Anas bin Malik (a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad) which had been well established in Qazvin long before al-Qazwini was born. His most famous work is the (), a seminal work in cosmography. He is also the author of the geographical dictionary (lit. 'Monuments of the Lands and Historical Traditions about Their Peoples'). Career Born in Qazvin, Iran, al-Qazwini served as a legal expert and judge in several localities in Iran. He traveled around in Mesopotamia and the Levant, and finally entered the circle patronized by the Ilkhanid governor of Baghdad, Ata-Malik Juvayni (d. 1283 CE). It was to the latter that al-Qazwini dedicated his famous cosmography titled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
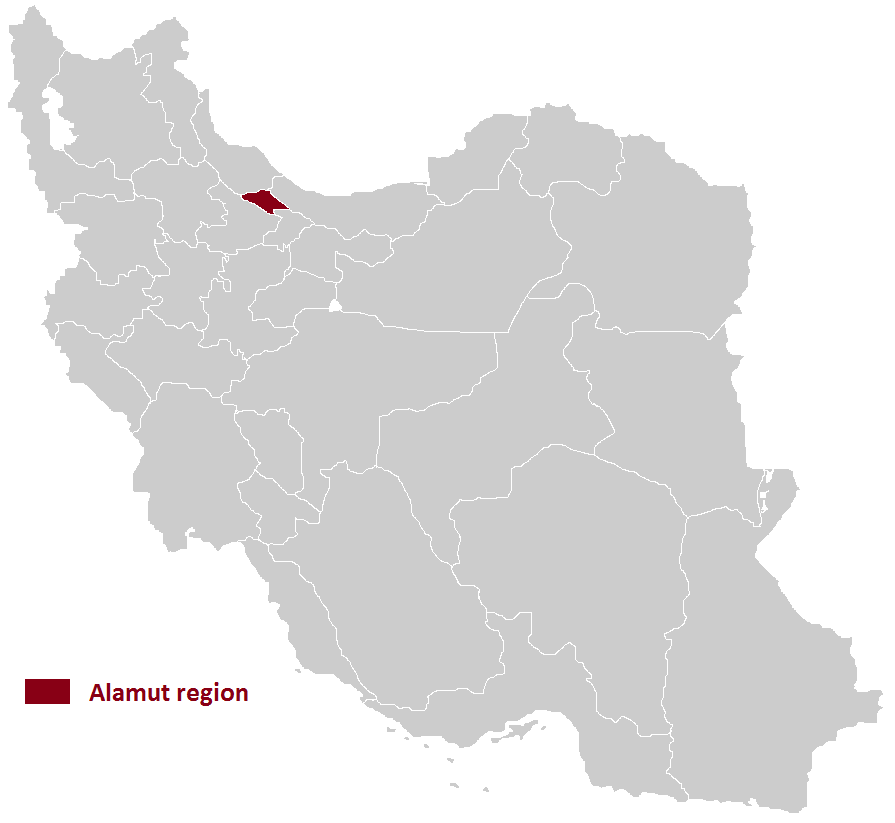
Alamut
Alamut ( fa, الموت) is a region in Iran including western and eastern parts in the western edge of the Alborz (Elburz) range, between the dry and barren plain of Qazvin in the south and the densely forested slopes of the Mazandaran province in the north. Starting from Qazvin toward Alamut, passing through the first range of hills, curvatures, forms, are significant themes in nature's composition of this area. The famous Ismaili castle of Alamut and numerous others are in this area, which served as the heartland of the state founded by Hassan-i Sabbah. According to some sources, the majority of people in northern Qazvin (Alamut) are Tats who speak a dialect of the Tati language.گونههای زبانی تاتی، دونالد استیلو، ۱۹۸۱ However, other sources claim that the majority of people in Alamut are Mazanderani or Gilaks who speak a dialect of the Mazanderani language or Gilaki language. According to some linguists, the term ‘Tati’ was us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alamut Period
The Nizari state (the Alamut state) was a Shia Nizari Ismaili state founded by Hassan-i Sabbah after he took control of the Alamut Castle in 1090 AD, which marked the beginning of an era of Ismailism known as the "Alamut period". Their people were also known as the ''Assassins'' or ''Hashashins''. The state consisted of a nexus of strongholds throughout Persia and Syria, with their territories being surrounded by huge swathes of hostile territory. It was formed as a result of a religious and political movement of the minority Nizari sect supported by the anti-Seljuk population. Being heavily outnumbered, the Nizaris resisted adversaries by employing strategic, self-sufficient fortresses and the use of unconventional tactics, notably assassination of important adversaries and psychological warfare. Despite being occupied with survival in their hostile environment, the Ismailis in this period developed a sophisticated outlook and literary tradition. Almost two centuries after i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Depicting The Transition Of Ismaili Nizari Seat From Egypt To Persia Between 980 And 1153, With Important Dates Around The 20th Nizari Ismaili Imam Al-Hadi
A timeline is a display of a list of events in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events. Timelines can use any suitable scale representing time, suiting the subject and data; many use a linear scale, in which a unit of distance is equal to a set amount of time. This timescale is dependent on the events in the timeline. A timeline of evolution can be over millions of years, whereas a timeline for the day of the September 11 attacks can take place over minutes, and that of an explosion over milliseconds. While many timelines use a linear timescale—especially where very large or small timespans are relevant -- logarithmic timelines entail a logarithmic scale of time; some "hurry up and wait" chronologies are depicted with zoom lens metaphors. History Time and space, particularly the line, are intertwined concepts in human thought. The line is ubiquitous in clocks in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Ibn Buzurg-Ummid
Muḥammad ibn Buzurg-Ummīd ( fa, محمد بن بزرگ امید) (died February 20, 1162) was the son of Kiyā Buzurg-Ummīd, and the third ruler of the Nizari Ismailis from 1138 until 1162 based in Alamut. Career Upon the demise of Kiyā Buzurg-Ummīd on February 9, 1138, he was appointed as the commander of Alamut Castle by the third concealed Imam Hasan Al-Qāhir ibn Al-Muḥammad (القاهر) of the Nizārī Ismā'īlī state The Nizari state (the Alamut state) was a Shia Nizari Ismaili state founded by Hassan-i Sabbah after he took control of the Alamut Castle in 1090 AD, which marked the beginning of an era of Ismailism known as the "Alamut period". Their people wer .... He died in 1162 and was succeeded by his son Hasan ‘Alā Dhīkr‘īhī's-Salām. Succession References External links Muhammad bin Kiya Buzrug Ummid 1162 deaths Medieval legends Iranian missionaries Iranian Ismailis People from Alamut Daylamites 12th-century Iranian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiya Buzurg-Ummid
Kiyā Buzurg-Ummīd ( fa, کیا بزرگ امید; died 1138) was a ''dawah, dāʿī'' and the second ruler (''da'i'') of the Nizari Ismaili state#Rulers and Imams, Nizari Isma'ili State, ruling Alamut Castle from 1124 to 1138 CE (or 518—532 AH). He was of Dailamite, Daylami origin from the region of Alamut, Rudbar. Career Prior to ruling the Nizari Isma'ilis, Buzurg Ummid captured Lambsar Castle for the Order of Assassins, Assassins and ruled it as commander for over twenty years. As the ruler of Alamut On 25 Rabīʿ II 518 (11 June 1124), a day before death of Hassan-i Sabbah, Ḥassan-i Ṣabbaḥ, Ḥassan appointed him his successor. He generally followed the policies of Hassan-i Sabbah, Ḥassan-i Ṣabbaḥ and enforced the Sharia strictly. In his early reign the Isma'ili hold was expanded in particular in Eshkevar and Taleghan. As opposed to Hassan Sabbah, who is depicted as a revolutionary leader, the Ismaili sources depict Buzurg-Ummid as an administrator and a ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hujja
A term used in Shi'i terminology, "hujja" means "proof mplied: proof of God" It is usually used to refer to a single individual in any given human era who represents God's "proof" to humanity.http://iranica.com/articles/hojjat. The hujja is a prophet or an Imam who possess a relationship with God that is greater than anyone else. The Imam who is the hujja of his time functions as the ultimate mediator between God and humanity, giving the Imam the greatest precedence for interpretation of the Qur'an. As the mediator between God and humanity, the Imam is the only one who can properly resolve conflicting interpretations of the Qur'an's words, giving the Imam ultimate authority over divine knowledge. In Twelver shi'ism the title "hujja" is specifically applied to the Twelfth Imam who is currently in a period of hiding and is attributed with the tradition of using Shi'i hadith to guide the religious community. The word Imam and hujja do not necessarily refer to the same perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpeg)
