|
Algolagnia
Algolagnia (; from el, ἄλγος, ''álgos'', "pain", and el, λαγνεία, ''lagneía'', "lust") is a sexual tendency which is defined by deriving sexual pleasure and stimulation from physical pain, often involving an erogenous zone. Studies conducted indicate differences in how the brains of those with algolagnia interpret nerve input. History of research In 1892, Albert von Schrenck-Notzing introduced the term algolagnia to describe "sexual" masochism, to differentiate it from Charles Féré's earlier term called "algophilia"; Schrenck-Notzing's interpretation was that algolagnia involved ''lust'', not ''love'' as Fere interpreted the phenomenon. (It should be cautioned, though, that the definitions regarding sadomasochism, sadism and masochism as medical terms have changed over the years (as also noted in the main article for that topic) and are still evolving, and there are also non-medical definitions of sadomasochism.) However, Krafft-Ebing's theories in Psychopathia Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
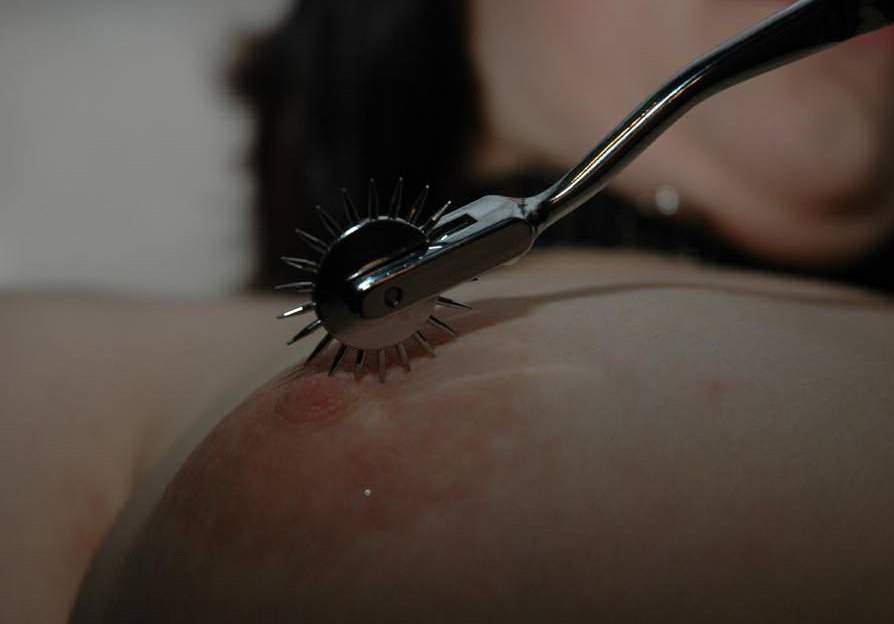
BDSM Wartenberg Wheel
BDSM is a variety of often erotic practices or roleplaying involving bondage, discipline, dominance and submission, sadomasochism, and other related interpersonal dynamics. Given the wide range of practices, some of which may be engaged in by people who do not consider themselves to be practising BDSM, inclusion in the BDSM community or subculture often is said to depend on self-identification and shared experience. The initialism ''BDSM'' is first recorded in a Usenet post from 1991, and is interpreted as a combination of the abbreviations B/D (Bondage and Discipline), D/s (Dominance and submission), and S/M (Sadism and Masochism). ''BDSM'' is now used as a catch-all phrase covering a wide range of activities, forms of interpersonal relationships, and distinct subcultures. BDSM communities generally welcome anyone with a non-normative streak who identifies with the community; this may include cross-dressers, body modification enthusiasts, animal roleplayers, rubber fetishi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BDSM
BDSM is a variety of often erotic practices or roleplaying involving bondage, discipline, dominance and submission, sadomasochism, and other related interpersonal dynamics. Given the wide range of practices, some of which may be engaged in by people who do not consider themselves to be practising BDSM, inclusion in the BDSM community or subculture often is said to depend on self-identification and shared experience. The initialism ''BDSM'' is first recorded in a Usenet post from 1991, and is interpreted as a combination of the abbreviations B/D (Bondage and Discipline), D/s (Dominance and submission), and S/M (Sadism and Masochism). ''BDSM'' is now used as a catch-all phrase covering a wide range of activities, forms of interpersonal relationships, and distinct subcultures. BDSM communities generally welcome anyone with a non-normative streak who identifies with the community; this may include cross-dressers, body modification enthusiasts, animal roleplayers, rubber fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Masochism Disorder
Sexual masochism disorder (SMD) is the condition of experiencing recurring and intense sexual arousal in response to enduring moderate or extreme pain, suffering, or humiliation.American Psychiatric Association. (2013). ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.).'' Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-5) of the American Psychiatric Association indicates that a person may have a masochistic sexual interest but that the diagnosis of sexual masochism disorder would only apply to individuals who also report psychosocial difficulties because of it. Related terms and conditions Current terminology ''Sexual masochism disorder'' is the term employed by the current version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-5) of the American Psychiatric Association. It refers to the "recurrent and intense sexual arousal from the act of being humiliated, beaten, bound, or otherwise made to suffer, as manifested by fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosadism
Autosadism, or automasochism, is behaviour inflicting pain or humiliation on oneself. It may be related to self-harm or a paraphilia involving sexual arousal. It can be viewed as a form of masochism, a sublimated form of sadism, or a means to experiencing algolagnia, a sexual tendency which is defined by deriving sexual pleasure and stimulation from physical pain. See also *Self-defeating personality disorder *Self-destructive behaviour Self-destructive behavior is any behavior that is harmful or potentially harmful towards the person who engages in the behavior. Self-destructive behaviors have been shown by many people throughout the years. It is on a continuum, with one extr ... Notes References * * Paraphilias {{BDSM-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Von Schrenck-Notzing
Albert Freiherr von Schrenck-Notzing (18 May 1862 – 12 February 1929) was a German physician, psychiatrist and notable psychical researcher, who devoted his time to the study of paranormal events connected with mediumship, hypnotism and telepathy. He investigated Spiritualist mediums such as Willi Schneider, Rudi Schneider, and Valentine Dencausse. He is credited as the first forensic psychologist by Guinness World Records. Mediumship Eva C Schrenck-Notzing investigated the medium Eva Carrière and believed the ectoplasm she produced was genuine. However, Schrenck-Notzing did not believe her ectoplasm " materializations" were anything to do with spirits, he claimed they were the result of "ideoplasty" in which the medium could form images onto ectoplasm from her mind.M. Brady Brower. (2010). ''Unruly Spirits: The Science of Psychic Phenomena in Modern France''. University of Illinois Press. p. 120. Schrenck-Notzing published the book ''Phenomena of Materialisation'' in Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Freiherr Von Schrenck-Notzing
Albert Freiherr von Schrenck-Notzing (18 May 1862 – 12 February 1929) was a German physician, psychiatrist and notable psychical researcher, who devoted his time to the study of paranormal events connected with mediumship, hypnotism and telepathy. He investigated Spiritualist mediums such as Willi Schneider, Rudi Schneider, and Valentine Dencausse. He is credited as the first forensic psychologist by Guinness World Records. Mediumship Eva C Schrenck-Notzing investigated the medium Eva Carrière and believed the ectoplasm she produced was genuine. However, Schrenck-Notzing did not believe her ectoplasm " materializations" were anything to do with spirits, he claimed they were the result of "ideoplasty" in which the medium could form images onto ectoplasm from her mind.M. Brady Brower. (2010). ''Unruly Spirits: The Science of Psychic Phenomena in Modern France''. University of Illinois Press. p. 120. Schrenck-Notzing published the book ''Phenomena of Materialisation'' in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage." In medical diagnosis, pain is regarded as a symptom of an underlying condition. Pain motivates the individual to withdraw from damaging situations, to protect a damaged body part while it heals, and to avoid similar experiences in the future. Most pain resolves once the noxious stimulus is removed and the body has healed, but it may persist despite removal of the stimulus and apparent healing of the body. Sometimes pain arises in the absence of any detectable stimulus, damage or disease. Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. It is a major symptom in many medical conditions, and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general functioning. Simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erogenous Zone
An erogenous zone (from Greek , ''érōs'' "love"; and English ''-genous'' "producing", from Greek , ''-genḗs'' "born") is an area of the human body that has heightened sensitivity, the stimulation of which may generate a sexual response, such as relaxation, sexual fantasies, sexual arousal and orgasm. Erogenous zones are located all over the human body, but the sensitivity of each varies, and depends on concentrations of nerve endings that can provide pleasurable sensations when stimulated. The touching of another person's erogenous zone is regarded as an act of physical intimacy. Whether a person finds stimulation in these areas to be pleasurable or objectionable depends on a range of factors, including their level of arousal, the circumstances in which it takes place, the cultural context, the nature of the relationship between the partners, and the partners' personal histories. Erogenous zones may be classified by the type of sexual response that they generate. Many peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphilia
Paraphilia (previously known as sexual perversion and sexual deviation) is the experience of intense sexual arousal to atypical objects, situations, fantasies, behaviors, or individuals. It has also been defined as sexual interest in anything other than a consenting human partner. There is no scientific consensus for any precise border between unusual sexual interests and paraphilic ones. There is debate over which, if any, of the paraphilias should be listed in diagnostic manuals, such as the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM) or the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). The number and taxonomy of paraphilia is under debate; one source lists as many as 549 types of paraphilia. The DSM-5 has specific listings for eight paraphilic disorders. Several sub-classifications of the paraphilias have been proposed, and some argue that a fully dimensional, spectrum or complaint-oriented approach would better reflect the evidence. Terminology Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadomasochism
Sadomasochism ( ) is the giving and receiving of pleasure from acts involving the receipt or infliction of pain or humiliation. Practitioners of sadomasochism may seek sexual pleasure from their acts. While the terms sadist and masochist refer respectively to one who enjoys giving and receiving pain, some practitioners of sadomasochism may switch between activity and passivity. The abbreviation S&M is commonly used for Sadomasochism (or Sadism & Masochism), although the initialisms S-M, SM, or S/M are also used, particularly by practitioners. Sadomasochism is not considered a clinical paraphilia unless such practices lead to clinically significant distress or impairment for a diagnosis. Similarly, sexual sadism within the context of mutual consent, generally known under the heading BDSM, is distinguished from non-consensual acts of sexual violence or aggression.:"Sexual arousal from consensual interactions that include domination should be distinguished from nonconsensual sex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DSM IV
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM; latest edition: DSM-5-TR, published in March 2022) is a publication by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) for the classification of mental disorders using a common language and standard criteria and is the main book for the diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders in the United States and is considered one of the "Bibles" of psychiatry along with the ICD, CCMD and the Psychodynamic Diagnostic Manual. It is usedmainly in the United Statesby researchers, psychiatric drug regulation agencies, health insurance companies, pharmaceutical companies, the legal system, and policymakers. Mental health professionals use the manual to determine and help communicate a patient's diagnosis after an evaluation. Hospitals, clinics, and insurance companies in the United States may require a DSM diagnosis for all patients with mental disorders. Health-care researchers use the DSM to categorize patients for research pur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Psychiatric Association
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) is the main professional organization of psychiatrists and trainee psychiatrists in the United States, and the largest psychiatric organization in the world. It has more than 37,000 members are involved in psychiatric practice, research, and academia representing a diverse population of patients in more than 100 countries. The association publishes various journals and pamphlets, as well as the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM). The DSM codifies psychiatric conditions and is used mostly in the United States as a guide for diagnosing mental disorders. The organization has its headquarters in Washington, DC. History At a meeting in 1844 in Philadelphia, thirteen superintendents and organizers of insane asylums and hospitals formed the Association of Medical Superintendents of American Institutions for the Insane (AMSAII). The group included Thomas Kirkbride, creator of the asylum model which was used thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)