|
Alfred M. Pride
Alfred Melville Pride (September 10, 1897 – December 24, 1988) was a United States Navy admiral and pioneer naval aviator, who distinguished himself during World War II as an aircraft carrier commander. He served during the late 1940s as Chief of the Bureau of Aeronautics and during the Korean War as Commander of the U.S. Seventh Fleet. Pride's career was remarkable for its time, in that he achieved flag rank without having attended the United States Naval Academy or even completing college. (He did, however, later complete advanced studies in aeronautical engineering.) A native of Somerville, Massachusetts, he studied engineering at Tufts University in Medford, Massachusetts, for several years before dropping out to enlist in the Navy during World War I. He served first as a machinist's mate in the Naval Reserve, but was soon given the chance to receive flight training and gain a commission as an ensign. Pride was sent to France, where he served briefly during the latter par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somerville, Massachusetts
Somerville ( ) is a city located directly to the northwest of Boston, and north of Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. As of the 2020 United States Census, the city had a total population of 81,045 people. With an area of , the city has a density of , making it the most densely populated municipality in New England and the List of United States cities by population density, 16th most densely populated incorporated municipality in the country. Somerville was established as a town in 1842, when it was separated from Charlestown, Massachusetts, Charlestown. In 2006, the city was named the best-run city in Massachusetts by ''The Boston Globe''. In 1972, 2009, and 2015, the city received the All-America City Award. It is home to Tufts University, which has its campus along the Somerville and Medford, Massachusetts, Medford border. History Early settlement The territory now comprising the city of Somerville was first settled by Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (US Naval Academy, USNA, or Navy) is a federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as Secretary of the Navy. The Naval Academy is the second oldest of the five U.S. service academies and it educates midshipmen for service in the officer corps of the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps. The campus is located on the former grounds of Fort Severn at the confluence of the Severn River and Chesapeake Bay in Anne Arundel County, east of Washington, D.C., and southeast of Baltimore. The entire campus, known colloquially as the Yard, is a National Historic Landmark and home to many historic sites, buildings, and monuments. It replaced Philadelphia Naval Asylum, in Philadelphia, that had served as the first United States Naval Academy from 1838 to 1845, when the Naval Academy formed in Annapolis. Candidates for admission generally must apply directly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
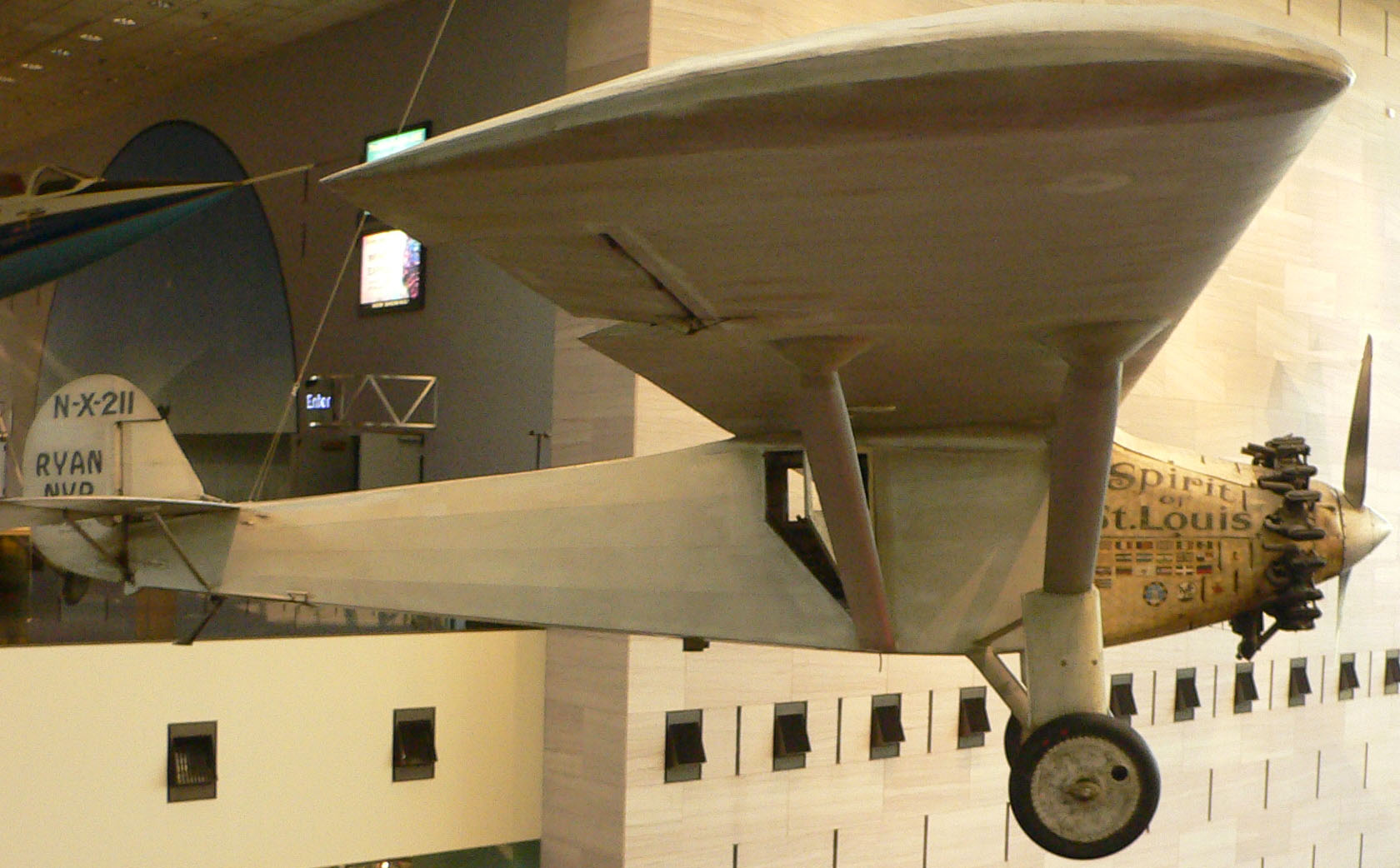
National Air And Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum of the Smithsonian Institution, also called the Air and Space Museum, is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States. Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, it opened its main building on the National Mall near L'Enfant Plaza in 1976. In 2018, the museum saw about 6.2 million visitors, making it the fifth-most-visited museum in the world, and the second-most-visited museum in the United States. In 2020, due to long closures and a drop in foreign tourism caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, museum attendance dropped to 267,000. The National Air and Space Museum is a center for research into the history and science of aviation and spaceflight, as well as planetary science and terrestrial geology and geophysics. Almost all spacecraft and aircraft on display are originals or the original backup craft. The museum contains the Apollo 11 Command Module ''Columbia'', the ''Friendship 7'' capsule which was flown by John Glenn, Charles Lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arlington, Virginia
Arlington County is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. The county is situated in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from the District of Columbia, of which it was once a part. The county is coextensive with the U.S. Census Bureau's census-designated place of Arlington. Arlington County is considered to be the second-largest "principal city" of the Washington metropolitan area, although Arlington County does not have the legal designation of independent city or incorporated town under Virginia state law. In 2020, the county's population was estimated at 238,643, making Arlington the sixth-largest county in Virginia by population; if it were incorporated as a city, Arlington would be the third most populous city in the state. With a land area of , Arlington is the geographically smallest self-governing county in the U.S., and by reason of state law regarding population density, it has no incorporated towns within its borders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patuxent River, Maryland
The Patuxent River is a tributary of the Chesapeake Bay in the state of Maryland. There are three main river drainages for central Maryland: the Potomac River to the west passing through Washington, D.C., the Patapsco River to the northeast passing through Baltimore, and the Patuxent River between the two. The Patuxent watershed had a rapidly growing population of 590,769 in 2000. It is the largest and longest river entirely within Maryland, and its watershed is the largest completely within the state. Geography The river source, from the Chesapeake, is in the hills of the Maryland Piedmont near the intersection of four counties – Howard, Frederick, Montgomery and Carroll, and only from Parr's Spring, the source of the south fork of the Patapsco River. Flowing in a generally southeastward direction, the Patuxent crosses the urbanized corridor between Baltimore and Washington, D.C., and opens up into a navigable tidal estuary near the colonial seaport of Queen Ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearl Harbor, Hawaii
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu, Hawaii, Honolulu. It was often visited by the Naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reciprocity Treaty of 1875. Much of the harbor and surrounding lands are now a United States Navy deep-water naval base. It is also the headquarters of the United States Pacific Fleet. The U.S. government first obtained exclusive use of the inlet and the right to maintain a repair and coaling station for ships here in 1887. The surprise attack by the Imperial Japanese Navy on December 7, 1941, led the United States to declare war on the Empire of Japan, making the attack on Pearl Harbor the immediate cause of the United States' entry into World War II. History Pearl Harbor was originally an extensive shallow embayment called ''Wai Momi'' (meaning, “Waters of Pearl”) or ''Puuloa'' (meaning, “long hill”) by the Hawai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Belleau Wood (CVL-24)
USS ''Belleau Wood'' was a United States Navy light aircraft carrier active during World War II in the Pacific Theater from 1943 to 1945. The ship also served in the First Indochina War under French Navy temporary service as ''Bois Belleau''. Originally laid down as the ''New Haven'' (CL-76), she was finished as an aircraft carrier. Reclassified CV-24 on 16 February 1942 and renamed ''Belleau Wood'' on 31 March 1942 in honor of the Battle of Belleau Wood in World War I. She was launched on 6 December 1942 by New York Shipbuilding Corporation, Camden, New Jersey, and sponsored by Mrs. Thomas Holcomb, wife of the Commandant of the Marine Corps. She was commissioned on 31 March 1943, with Captain A. M. Pride in command. During the war, she was reclassified CVL-24 on 15 July 1943. Service history United States Navy After a brief shakedown cruise, ''Belleau Wood'' reported to the Pacific Fleet, arriving at Pearl Harbor on 26 July 1943. After supporting the occupation of Bak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Air Station Anacostia
Anacostia is a historic neighborhood in Southeast Washington, D.C. Its downtown is located at the intersection of Good Hope Road and Martin Luther King Jr. Avenue. It is located east of the Anacostia River, after which the neighborhood is named. Anacostia includes all of the Anacostia Historic District, which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978. Often the name "Anacostia" is used to refer to the entire portion of the city that is southeast of the Anacostia River. The Anacostia Business Improvement District is responsible for the development of the area. History The name "Anacostia" comes from the anglicized name of a Nacochtank settlement along the Anacostia River. Captain John Smith explored the area in 1608, traveling up the "Eastern Branch"—later the Anacostia River—mistaking it for the main body of the Potomac River, and met Anacostans. Before the arrival of whites, the Nacostine villages in this area were a lively center of trade visite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the most prestigious and highly ranked academic institutions in the world. Founded in response to the increasing industrialization of the United States, MIT adopted a European polytechnic university model and stressed laboratory instruction in applied science and engineering. MIT is one of three private land grant universities in the United States, the others being Cornell University and Tuskegee University. The institute has an urban campus that extends more than a mile (1.6 km) alongside the Charles River, and encompasses a number of major off-campus facilities such as the MIT Lincoln Laboratory, the Bates Center, and the Haystack Observatory, as well as affiliated laboratories such as the Broad and Whitehead Institutes. , 98 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Lexington (CV-2)
USS ''Lexington'' (CV-2), nicknamed "Lady Lex", was the name ship of her class of two aircraft carriers built for the United States Navy during the 1920s. Originally designed as a battlecruiser, she was converted into one of the Navy's first aircraft carriers during construction to comply with the terms of the Washington Naval Treaty of 1922, which essentially terminated all new battleship and battlecruiser construction. The ship entered service in 1928 and was assigned to the Pacific Fleet for her entire career. ''Lexington'' and her sister ship, , were used to develop and refine carrier tactics in a series of annual exercises before World War II. On more than one occasion these included successfully staged surprise attacks on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The ship's turbo-electric propulsion system allowed her to supplement the electrical supply of Tacoma, Washington, during a drought in late 1929 to early 1930. She also delivered medical personnel and relief supplies to Managua, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Saratoga (CV-3)
USS ''Saratoga'' (CV-3) was a built for the United States Navy during the 1920s. Originally designed as a battlecruiser, she was converted into one of the Navy's first aircraft carriers during construction to comply with the Washington Naval Treaty of 1922. The ship entered service in 1928 and was assigned to the Pacific Fleet for her entire career. ''Saratoga'' and her sister ship, , were used to develop and refine carrier tactics in a series of annual exercises before World War II. On more than one occasion these exercises included successful surprise attacks on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. She was one of three prewar US fleet aircraft carriers, along with and , to serve throughout World War II. Shortly after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, ''Saratoga'' was the centerpiece of the unsuccessful American effort to relieve Wake Island and was torpedoed by a Japanese submarine a few weeks later. After lengthy repairs, the ship supported forces participating in the Guadalcanal Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Langley (CV-1)
USS ''Langley'' (CV-1/AV-3) was the United States Navy's first aircraft carrier, converted in 1920 from the collier USS ''Jupiter'' (Navy Fleet Collier No. 3), and also the US Navy's first turbo-electric-powered ship. Conversion of another collier was planned but canceled when the Washington Naval Treaty required the cancellation of the partially built s '' Lexington'' and '' Saratoga'', freeing up their hulls for conversion to the aircraft carriers and . ''Langley'' was named after Samuel Langley, an American aviation pioneer. Following another conversion to a seaplane tender, ''Langley'' fought in World War II. On 27 February 1942, while ferrying a cargo of USAAF P-40s to Java, she was attacked by nine twin-engine Japanese bombers of the Japanese 21st and 23rd naval air flotillas and so badly damaged that she had to be scuttled by her escorts. Construction President William H. Taft attended the ceremony when ''Jupiter''s keel was laid down on 18 October 1911, at the Mare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

_underway_on_22_December_1943_(NH_97269).jpg)

.jpg)
_on_building_ways%2C_1925.jpg)
_-_19-N-11981.jpg)
_insignia_(NH_82611-KN).png)